Retirement planning involves the careful consideration of financial aspects, particularly the search for safe sources of income to sustain one's lifestyle. A 6% return holds significance in retirement for several reasons. It ensures income adequacy by providing a steady stream of earnings to cover essential expenses and discretionary spending. It can also outpace inflation, preserving the retirees' purchasing power. Additionally, a 6% return contributes to the growth of retirement savings, offering a buffer for emergencies and legacy planning. Achieving a consistent and safe 6% return requires portfolio diversification, investment selection, and assessing individual risk tolerance. Safe income in retirement refers to dependable earnings that cover living expenses, ensuring financial stability and peace of mind. This includes low-risk sources such as Social Security benefits, pensions, and conservative investments like bonds and certificates of deposit, known for their stability and reliable income generation. Social Security is a federal program in the United States that provides benefits to retirees, their survivors, and workers who become disabled. The amount of your Social Security benefits is based on your earnings history, with a higher lifetime income resulting in higher benefits. You can start receiving benefits as early as age 62, although waiting until a later age can increase the amount you receive each month. Defined Benefit Pension Plans, or traditional pension plans, promise a specified monthly benefit at retirement. The plan may state this promised benefit as an exact dollar amount, such as $100 per month at retirement. Alternatively, it might calculate a benefit through a plan formula that considers factors such as salary and service - for example, 1 percent of average salary for the last five years of employment for every year of service with an employer. The benefits in most traditional defined benefit plans are protected, within certain limitations, by federal insurance provided through the Pension Benefit Guaranty Corporation (PBGC). Defined Contribution Plans, such as a 401(k) or 403(b), are retirement plans in which the employee, and often the employer, contribute money to an account. The amount available at retirement depends on the contributions made and the investment returns on those contributions. Because the investment risk is borne entirely by the employee, the retirement benefits from these plans can fluctuate based on investment performance. IRAs are tax-advantaged retirement savings accounts that can be funded with a variety of investments, including stocks, bonds, and mutual funds. Traditional IRAs offer tax-deductible contributions and tax-deferred growth, but withdrawals in retirement are taxed. Roth IRAs are funded with after-tax dollars, so withdrawals in retirement, including earnings, are typically tax-free, provided certain conditions are met. Annuities are insurance products that can provide a steady income stream in retirement. You make an initial investment (either a lump sum or a series of contributions) and in return, the insurance company makes regular payments to you for a specified period. These payments can be deferred (starting at a future date) or immediate (starting right away). Investment income is derived from assets you've invested in such as stocks, bonds, mutual funds, or real estate. This can be an important source of retirement income, but it also comes with risks. Market fluctuations can affect the value of your investments and the income they generate. Therefore, it's crucial to have a well-diversified portfolio and a risk tolerance that aligns with your investment strategy. Savings accounts and CDs are considered safe because they're insured by the FDIC. However, the trade-off for this safety is that they generally provide lower returns compared to other investment options. A savings account provides a safe place to store cash and earn a small amount of interest. CDs, on the other hand, are time-bound deposits with a bank. They have a fixed term length (from a few months to several years) and a fixed interest rate. They're best for money you're sure you won't need before the term of the CD ends. If you do withdraw early, you'll likely have to pay a penalty. Some retirees may have a lower risk tolerance and prefer more conservative investments, such as fixed-income securities, that prioritize capital preservation and steady income. Others may be comfortable with taking on higher levels of risk, such as investing in stocks, with the potential for higher returns. The stability of income sources is influenced by prevailing market conditions and the overall economic environment. Market volatility, economic downturns, and fluctuations in interest rates can impact the safety of income sources. Diversification and asset allocation are essential factors to consider when evaluating the safety of income sources. Spreading investments across different asset classes, such as stocks, bonds, real estate, and cash equivalents, can help mitigate risk and enhance the stability of income. Dividend-paying stocks are shares of companies that distribute a portion of their profits to shareholders in the form of dividends. Blue-Chip Dividend Stocks: These are shares of large, well-established companies with a history of stable earnings and dividend payments. Blue-chip stocks are often considered reliable and lower-risk investments. High-Yield Dividend Stocks: These stocks offer higher dividend yields compared to the broader market. They can be attractive to retirees seeking higher income, although they may carry additional risks and require careful evaluation. Dividend Growth Stocks: These are stocks of companies that consistently increase their dividend payments over time. They are favored by retirees looking for a combination of current income and the potential for future dividend growth. Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) are investment vehicles that pool funds from investors to purchase and manage income-generating properties. Equity REITs: These REITs invest in and own income-generating properties, such as office buildings, apartments, shopping centers, or industrial facilities. They derive income primarily from rents collected from tenants. Mortgage REITs: Mortgage REITs invest in real estate mortgages or mortgage-backed securities. They earn income from interest payments on the mortgages they hold or the mortgage-backed securities they purchase. Hybrid REITs: Hybrid REITs combine characteristics of both equity and mortgage REITs. They may own properties and also invest in mortgage-related assets. Public vs Private REITs: Publicly traded REITs are listed on stock exchanges, allowing investors to buy and sell shares easily. Private REITs, on the other hand, are not traded on exchanges and often have more limited investor participation requirements. Fixed Annuities: Fixed annuities provide a guaranteed fixed income stream for a specified period or for life. The income payments remain constant and do not fluctuate based on market conditions. Variable Annuities: Variable annuities allow the annuitant to invest in a selection of investment options, typically mutual funds. The income payments from variable annuities fluctuate based on the performance of the underlying investment portfolio. Indexed Annuities: Indexed annuities provide returns linked to the performance of a specific market index, such as the S&P 500. These annuities offer the potential for higher returns compared to fixed annuities while still providing some level of downside protection. Immediate Annuities: Immediate annuities begin providing income payments shortly after the initial investment. They are suitable for individuals looking for immediate retirement income. Deferred Annuities: Deferred annuities allow individuals to accumulate funds over a specific period before initiating income payments. They can be used as a retirement savings vehicle. The importance of achieving a 6% return in retirement planning cannot be overstated, given its potential to ensure income adequacy, buffer against inflation, stimulate growth in retirement savings, and foster financial stability. Traditional retirement income sources like Social Security benefits, pensions, and conservative investments such as bonds and CDs play crucial roles in providing steady income. However, each comes with inherent challenges - the future funding uncertainty of Social Security, the decline of pension availability, and the often modest returns from conservative fixed-income securities. In this light, alternative income sources with the potential for a safe 6% income, such as dividend-paying stocks, real estate investment trusts (REITs), and annuities, present promising options. Dividend-paying stocks can offer consistent income and growth potential. REITs, which are tied to the real estate sector, can provide income from property investments. Annuities, on the other hand, can ensure a guaranteed stream of income in retirement. Evaluating the safety of these income sources requires careful consideration of factors like risk tolerance, market conditions, economic stability, and the necessity of a diversified portfolio.Significance of a 6% Return in Retirement Planning
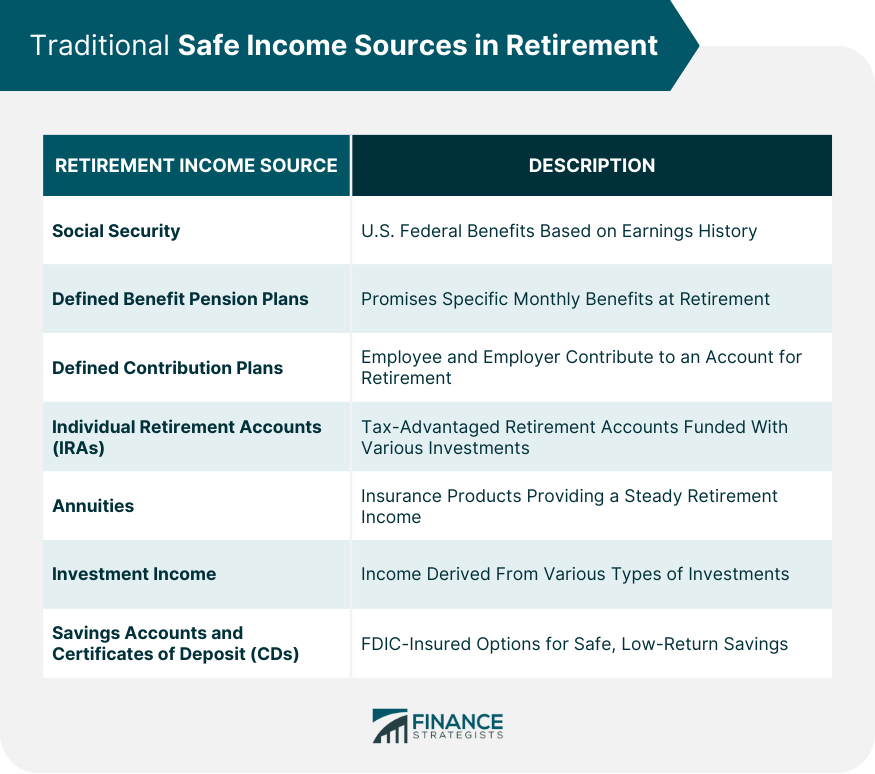
Traditional Safe Income Sources in Retirement
Social Security
Defined Benefit Pension Plans
Defined Contribution Plans
Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs)
Annuities
Investment Income
Savings Accounts and Certificates of Deposit (CDs)
Factors to Consider When Evaluating the Safety of Income Sources
Risk Tolerance and Investment Preferences
Market Conditions and Economic Stability
Diversification and Asset Allocation
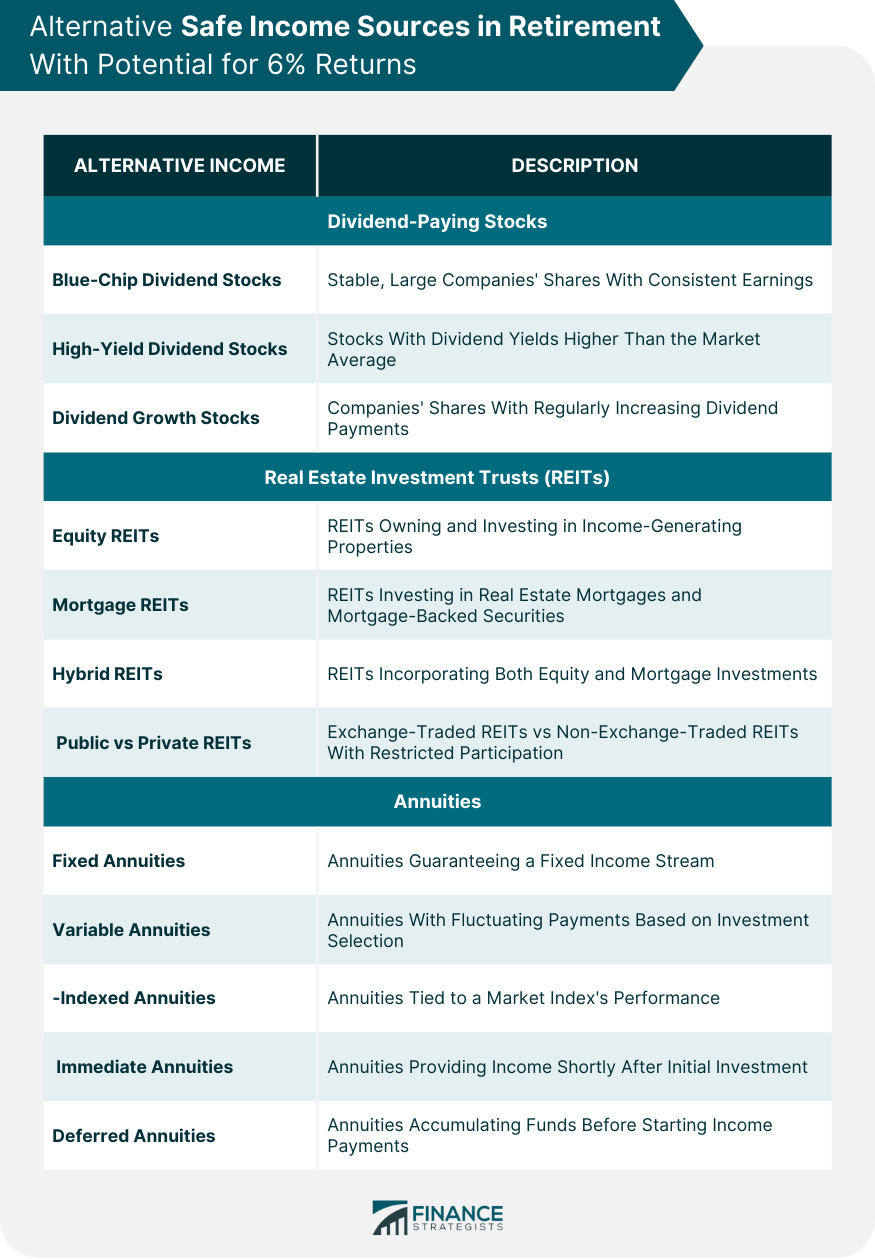
Alternative Income Sources With Potential for Safe 6% Income
Dividend-Paying Stocks
Types of Dividend-Paying Stocks
Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs)
Types of Real Estate Investments Trusts
Annuities
Types of Annuities
Conclusion
Retirement: Where Could You Get Safe 6% Income? FAQs
While guaranteed 6% income may be challenging to find, some options include dividend-paying stocks, real estate investment trusts (REITs), high-yield bonds, and certain annuities. It's important to evaluate the risks and consult with a financial advisor before making any investment decisions.
Social Security provides a steady income stream, but it typically does not offer a 6% return. The benefit amount is based on various factors, including your earnings history and the age you start claiming benefits. It's wise to supplement Social Security with other investment vehicles to achieve a higher income target.
Higher returns often come with increased risk. Investments offering a potential 6% income may involve market volatility, credit risk, or longer-term commitments. It's important to carefully assess your risk tolerance and diversify your portfolio to manage potential risks effectively.
Government-backed options like Treasury bonds or certificates of deposit (CDs) are considered safer investments but may not yield a consistent 6% income. These options typically provide lower returns due to their lower risk profile. It's essential to align your income expectations with the available investment options.
Yes, combining various income sources is a common strategy to achieve a target income. Diversifying your portfolio with a mix of investments, such as dividend stocks, bonds, and potentially higher-risk options, can help balance income generation and risk management. Working with a financial advisor can provide valuable guidance in creating a well-rounded retirement income plan.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.















