Social Security Income (SSI) is a federal income supplement program designed to help aged, blind, and disabled people who have little to no income. This program provides cash to meet basic needs for food, clothing, and shelter. Administered by the Social Security Administration (SSA), SSI represents an essential safety net for individuals who lack the resources to sustain themselves. Retirement income refers to the money that an individual receives after they stop working, typically after reaching a certain age known as 'retirement age.' This income can come from several sources, including Social Security benefits, personal savings, investments, and pension plans. The primary objective of retirement income is to provide financial stability and maintain a comfortable standard of living during the retirement years. No, SSI is not classified as retirement income. The basis for SSI benefits isn't one's employment history or the amount contributed in Social Security taxes. Instead, the funding for SSI benefits comes from general tax revenues, making it independent of a person's work record. Retirement income, conversely, is generally composed of various sources that have been earned or amassed over a lifetime of work. These might include Social Security benefits, pensions, annuities, and other income sources. Retirement income is meant to offer financial support during the retirement years, following the cessation of regular employment income. Individuals receiving SSI benefits might still qualify for other forms of retirement income, like Social Security benefits or pensions. This is contingent on the specific eligibility requirements for each type of retirement income. It's essential to remember, however, that while SSI benefits can supplement other forms of retirement income, they are not classified as retirement income in and of themselves. SSI was created to provide financial assistance to individuals who are aged, blind, or disabled and have little to no income. This program is intended to ensure a minimum level of income to people who are unable to work or who have not earned enough work credits for other types of Social Security benefits. Eligibility for SSI isn't based on work history, like Social Security retirement benefits are. Instead, to qualify for SSI, an individual must meet specific income and resource thresholds. They must also be: Aged (65 years or older) Blind Disabled (including children) SSI provides monthly payments to people in need. The amount varies depending on factors like income, living situation, and geographical location. It's designed to help cover basic necessities such as food, clothing, and shelter. Furthermore, in most states, if you receive SSI, you can automatically qualify for other assistance programs, including food stamps and Medicaid. SSI and Social Security retirement benefits share a common goal—providing income support—but they have fundamental differences. Social Security retirement benefits are funded through payroll taxes paid by workers and employers, meaning the beneficiaries have contributed to this program throughout their working years. SSI, on the other hand, is funded through general tax revenues, not Social Security taxes. Social Security retirement benefits are available to workers who have earned enough credits through their employment history, regardless of their personal wealth or other income sources. SSI, however, is strictly need-based. It's available to individuals who are aged, blind, or disabled, and who have limited income and resources, irrespective of their work history. Pension plans, also known as defined benefit plans, provide retirees with a predetermined monthly benefit upon retirement. These plans are funded by the employer and are typically based on factors such as salary, age, and years of service. 401(k) plans and Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs) are defined contribution plans. In these plans, individuals contribute a portion of their pre-tax salary into the account, often with matching contributions from the employer. The funds grow tax-deferred until withdrawal in retirement. Social Security retirement benefits are a federal program into which workers contribute throughout their working years via payroll taxes. The amount of benefits received depends on the individual's earnings history and the age at which they choose to start receiving benefits. Retirement income amounts depend on several factors, including the years of contributions into Social Security or a pension plan, the amount contributed to 401(k) or IRA accounts, investment returns, and the age at which an individual retires. Retirement income is usually distributed monthly, though some sources may allow for lump-sum or other forms of withdrawal. The distribution of retirement income can significantly impact its longevity and the retiree's tax situation. SSI, acting as a critical safety net, can significantly benefit low-income retirees who have been unable to accumulate sufficient retirement savings or who don't qualify for other types of benefits. Primarily, SSI helps in covering basic living expenses such as food, clothing, and shelter. By offering financial support for these fundamental needs, SSI ensures the maintenance of minimum living standards and protects retirees from falling into poverty. Another significant advantage of SSI is the potential automatic qualification for other benefits. Most states provide automatic Medicaid eligibility to SSI recipients, which can help meet the often high healthcare costs in the retirement years. In addition, SSI recipients might also qualify for food assistance programs, thus further enhancing their resource pool. While SSI can be a valuable support mechanism for some retirees, it's crucial to acknowledge its limitations, as it's not intended to serve as the primary source of retirement income. The benefits provided by SSI are relatively modest, designed primarily to ensure recipients can meet their most basic needs. Moreover, SSI is exclusively available to those with limited resources and income, meaning not all retirees will qualify. As a needs-based program, SSI takes into account all income and resources when determining eligibility. Consequently, retirees who have other income sources, such as personal savings, pensions, or Social Security retirement benefits, may experience a reduction in their SSI benefits or could even lose eligibility. Another notable limitation of SSI is that the program does not take into account past employment. Unlike a traditional retirement plan or Social Security retirement benefits, SSI does not provide increased benefits to individuals who have had long working histories or high-earning careers. While SSI can be a part of the income received in retirement, it is not classified as retirement income. The program serves as a lifeline for low-income individuals who are aged, blind, or disabled, with eligibility based on financial need rather than work history. SSI can be seen as a safety net program that supplements retirement income, especially for those with limited resources. As such, it plays a significant role in the overall retirement income landscape, ensuring that some of the most vulnerable members of society have access to basic necessities. Retirement planning is crucial for financial stability in later years. If you're unsure how SSI and other income sources factor into your retirement plan, consider reaching out to a financial advisor or retirement planning professional for guidance.Overview of Social Security Income (SSI) and Retirement Income
Is SSI Considered Retirement Income?
Understanding SSI in Depth
Purpose and Design of SSI
Eligibility Criteria for SSI
Benefits of SSI
Differences Between SSI and Social Security Retirement Benefits
Source of Funding
Beneficiary Groups

Understanding Retirement Income in Depth
Traditional Forms of Retirement Income
Pension Plans
401(k) and Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs)
Social Security Retirement Benefits
How Retirement Income Is Determined
Factors Influencing the Amount
Distribution of Retirement Income
Role of SSI in Retirement Planning
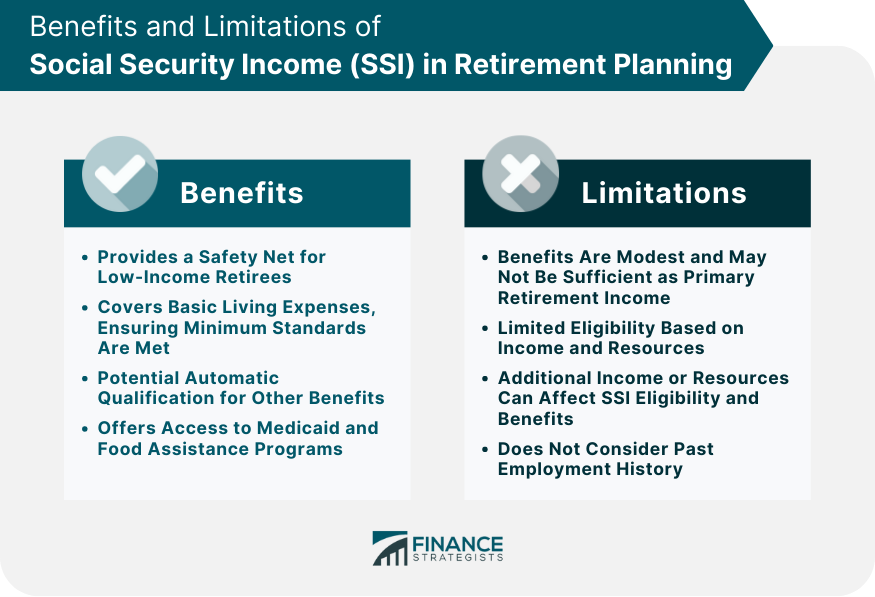
Benefits of SSI for Retirees
Covering Basic Living Expenses
Access to Additional Benefits
Limitations of SSI in Providing Retirement Security
Modest Benefits and Resource Limitations
Impact of Additional Income or Resources
Lack of Consideration for Past Employment
The Bottom Line
Is SSI Considered Retirement Income? FAQs
No, SSI is not considered retirement income for tax purposes. SSI payments are not taxable income.
Yes, it is possible to receive SSI and other types of retirement income simultaneously. However, other income sources can affect your eligibility for SSI or the amount you receive.
SSI is not specifically related to retirement or retirement age. It's available to eligible individuals based on need, not work history or retirement status.
The primary difference is that retirement income is typically earned through work and investment, while SSI is a needs-based program funded through general tax revenues.
SSI benefits can be reduced or eliminated if you have other sources of income, including retirement income. It's essential to report all income to the Social Security Administration when receiving SSI.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.















