The 401(k) Summary Plan Description (SPD) is a document that offers employees a comprehensive overview of their employer's 401(k) plan, shedding light on the intricate details that govern the operation of the retirement scheme. The SPD goes beyond simply enumerating the basic aspects of the retirement plan. It lays out, in explicit detail, the modus operandi of the plan, the calculation of benefits, the terms and conditions that apply when it comes to making distributions, as well as the implications of special circumstances such as job termination or retirement. Indeed, the SPD serves as a roadmap to understanding and harnessing the full potential of the retirement benefits offered by employers. Armed with the knowledge that the SPD imparts, employees can make informed decisions that help maximize their retirement savings and secure their financial future. The vesting schedule in a 401(k) plan refers to the time period that an employee must work for a company before gaining full ownership of employer contributions to their 401(k) account. It is a type of incentive to encourage employees to stay with the company for a certain length of time, as leaving before full vesting means forfeiting some or all of the employer's contributions. Matching contributions are additional funds that an employer may add to an employee's 401(k) plan to match a portion of the employee's own contributions. The specific amount of the match can vary by employer, but it essentially serves as free money towards the employee's retirement savings, encouraging participation in the 401(k) plan. Eligible compensation refers to the types of earnings from an employer that can be used as the basis for contributions to a 401(k) plan. Typically, this includes wages, salaries, bonuses, commissions, and other forms of compensation. Not all types of income, such as certain benefits or reimbursements, are considered eligible compensation for 401(k) contributions. Rollover in a 401(k) plan is a process that allows an employee to move their retirement savings from one qualified retirement plan to another when changing jobs or retiring. There are two types of rollovers: direct and indirect. In a direct rollover, the money is transferred between plans without the individual handling the funds, while an indirect rollover requires the individual to receive the distribution and deposit it into a new plan within 60 days to avoid tax penalties. The plan name and type identify the specific retirement scheme or program an individual is enrolled in. Different types of plans include traditional 401(k), Roth 401(k), and SIMPLE 401(k), among others. The name usually reflects the company or organization offering the plan, while the type refers to the tax implications and rules governing the plan. Plan administration refers to the parties or entities that are responsible for managing and overseeing the retirement plan. These parties often include third-party administrators, plan sponsors, or financial advisors, and their responsibilities range from maintaining plan records, ensuring legal compliance, and providing communication to the participants about their investments and benefits. The plan sponsor is typically the employer or organization offering the 401(k) plan. The sponsor is responsible for establishing the retirement plan, selecting the investment options available to participants, and may also make contributions to the plan on behalf of the employees. Plan sponsors have a fiduciary duty to act in the best interest of the plan's participants. The plan trustee is the entity entrusted with the fiduciary responsibilities related to a 401(k) plan. This means they are responsible for managing the plan's assets, ensuring that the plan operates in accordance with federal law, and making decisions in the best interest of the plan participants. The trustee can be a person, a group of people, or a company specializing in retirement and investment services. Contribution limits refer to the maximum annual amount an employee can contribute to their 401(k) account. These limits are set by the IRS and can change annually to reflect inflation and cost of living adjustments. As of 2024, the limit is $23,000 for individuals under 50, and $30,500 for those 50 and older, with the higher limit including a catch-up contribution designed to assist those closer to retirement. Matching contributions are the funds that an employer may contribute to an employee's 401(k) plan, often matching a portion of the employee's own contributions. The specific terms of the match are outlined in the plan's documents and can vary by employer. This essentially provides free money to the employee's retirement savings, incentivizing them to contribute to their 401(k) plan. Investment options refer to the different types of funds or assets that an employee can choose to invest their 401(k) contributions in. These options may include a mix of stocks, bonds, mutual funds, and sometimes, company stock. The goal is to provide a diverse set of options that cater to different risk tolerances and investment goals of the plan participants. Plan loans and withdrawals refer to the guidelines and provisions for borrowing against one's 401(k) balance or making hardship withdrawals before reaching retirement age. These are generally subject to strict rules and penalties to discourage early withdrawal and to maintain the long-term savings purpose of a 401(k) plan. Nevertheless, they provide a possible source of funds in case of financial emergencies or significant immediate financial needs. The SPD is not just a document to be shelved and forgotten. Its active role in retirement planning is pivotal. The SPD, with its wealth of information, serves as a guiding light that aids employees in navigating the sometimes tumultuous seas of retirement planning. For example, understanding the rules governing the employer's matching contributions can guide employees in determining how much to contribute from their paychecks. By contributing at least as much as the employer is willing to match, employees can optimize their retirement savings. The SPD is instrumental in helping employees strategize their retirement savings. It enables them to make decisions such as how to distribute their contributions among the available investment options and how much to contribute based on their retirement goals and risk tolerance. Provisions on how a 401(k) is handled upon termination of employment are critical to prevent employees from losing out on their retirement savings. The Summary Plan Description (SPD) provides guidance on this, specifying whether employees can leave their funds in the plan or if they must roll them over into another retirement account. It also covers details about the timing and process of these decisions to ensure they comply with IRS regulations. When an employee retires, there are specific rules for plan distributions and rollovers that come into effect. The SPD outlines these, specifying the age at which an employee can start withdrawing funds, the process for doing so, and the frequency of these withdrawals. It also explains the penalties for early withdrawal and the requirements for mandatory distributions after reaching a certain age. Additionally, the SPD provides information on how to roll over a 401(k) into another retirement plan or an individual retirement account (IRA) if the retiree chooses to do so. Filing a claim for benefits refers to the procedure employees need to follow to claim benefits from their 401(k) plan. The SPD includes detailed information about this process, which can be of immense help to employees who are preparing to access their retirement savings. If a claim for benefits is denied, the SPD outlines the appeal procedures that employees can follow. This process is crucial to ensure that employees have the right to challenge any decisions about their benefits that they believe are unjust or incorrect. ERISA, or the Employee Retirement Income Security Act, provides legal protections by setting minimum standards for retirement plans offered by private industries. These protections aim to prevent the misuse or mishandling of the plan's assets. The details of these protections and what they mean for employees are outlined within the SPD. The 401(k) Summary Plan Description (SPD) is a vital guide to understanding and utilizing retirement benefits offered by employers to their full potential. It serves as a comprehensive tool that educates employees about their 401(k) plans, detailing the structure, key terms, contribution limits, investment options, and more. Moreover, the SPD highlights special circumstances such as job termination and retirement and details legal rights and protections that are in place for the welfare of employees. Understanding the contents of the SPD enables employees to make strategic decisions to maximize their retirement savings and secure their financial futures. Reach out to a professional retirement planning service to further customize your strategy to your unique circumstances. What Is a 401(k) Summary Plan Description?
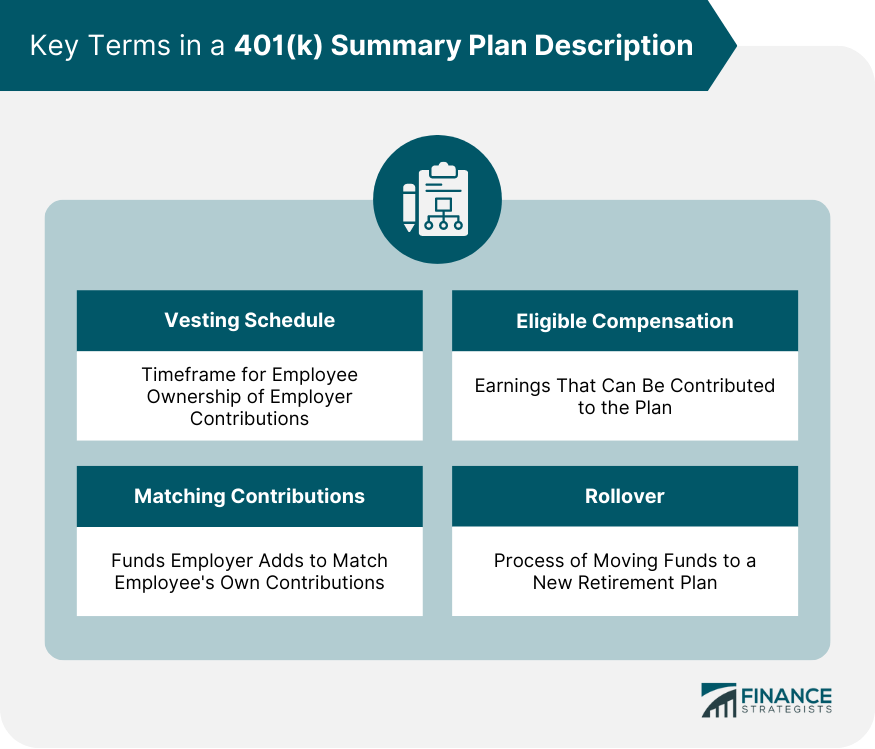
Key Terms in a 401(k) Summary Plan Description
Vesting Schedule
Matching Contributions
Eligible Compensation
Rollover
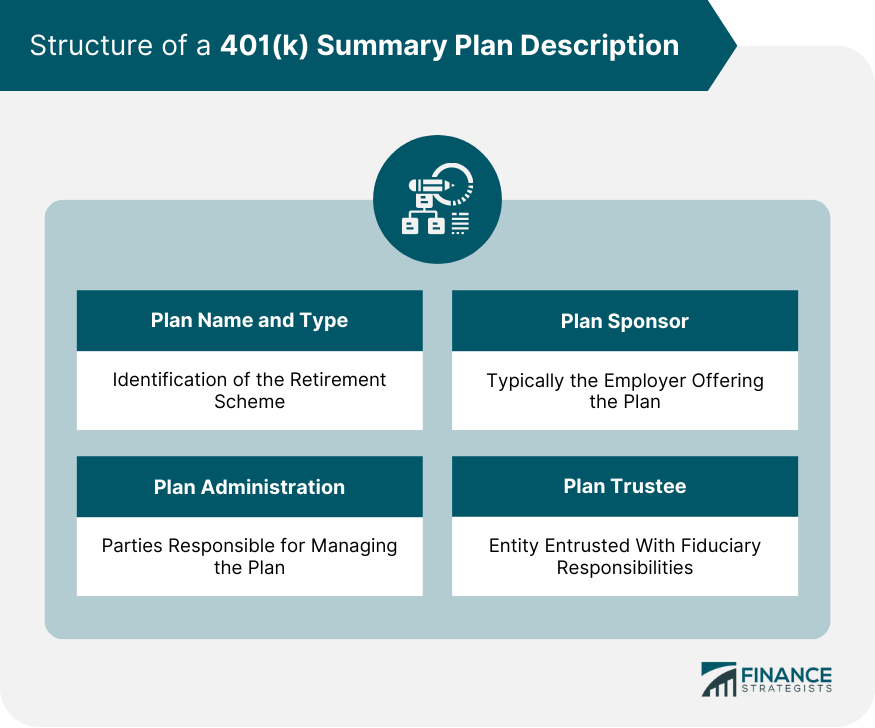
Understanding the 401(k) Summary Plan Description Structure
Plan Name and Type
Plan Administration
Plan Sponsor
Plan Trustee
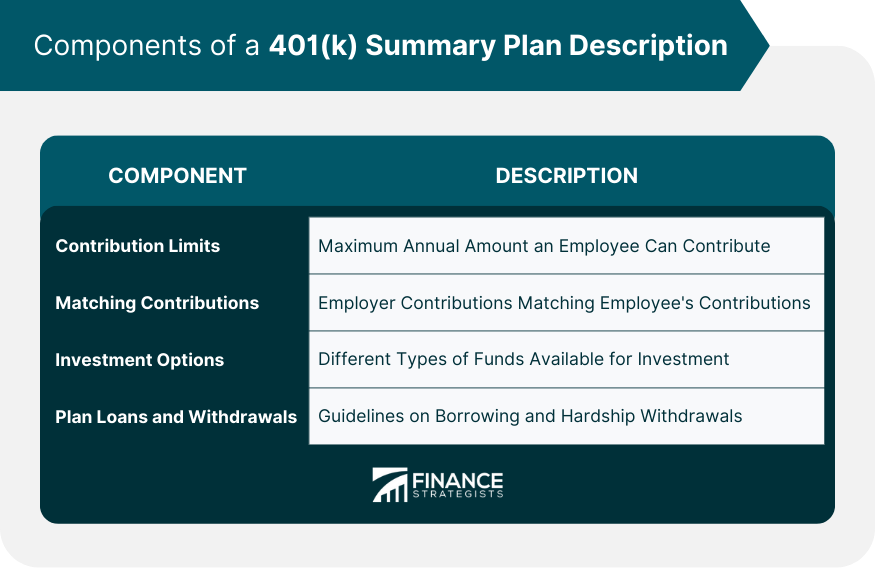
Components of a 401(k) Summary Plan Description
Contribution Limits
Matching Contributions
Investment Options
Plan Loans and Withdrawals
Role of a 401(k) Summary Plan Description in Retirement Planning
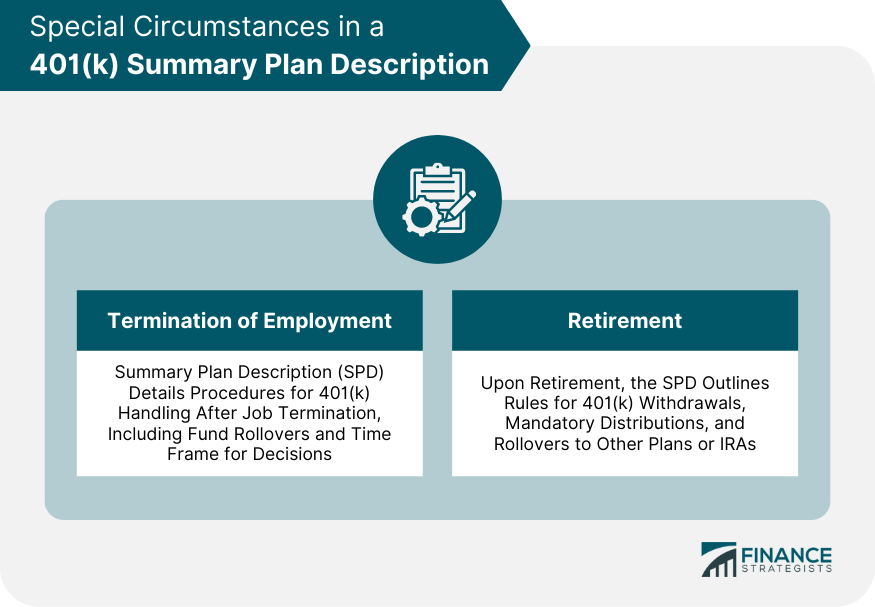
Special Circumstances in a 401(k) Summary Plan Description
Termination of Employment
Retirement
Legal Rights and Protections Under a 401(K) Summary Plan Description
Filing a Claim for Benefits
Appeal Procedures
ERISA Protections
Final Thoughts
401(k) Summary Plan Description FAQs
A 401(k) SPD is a document detailing the rules and guidelines of an employer's 401(k) plan, its structure, components, and procedures.
Understanding the SPD allows individuals to optimize retirement savings by making informed decisions on contributions, investment options, and more.
The SPD includes details on contribution limits, matching contributions, investment options, plan loans, withdrawals, and vesting schedules.
The SPD outlines the rules for plan distributions, rollovers, and what happens to the 401(k) plan under special circumstances like job termination or retirement.
The SPD outlines rights and protections under the Employee Retirement Income Security Act (ERISA), including procedures for filing claims and appeals.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.















