Company stock represents ownership in a corporation and is issued in the form of shares. Shareholders who own company stock have a claim on the company's assets and earnings, and may have voting rights that allow them to participate in corporate decision-making. There are two main types of company stock: common stock and preferred stock. Common stock grants shareholders voting rights and potential dividends. The value of common stock may increase or decrease based on the company's performance and market conditions. Preferred stock typically does not grant voting rights but offers priority in dividend payments and asset distribution in the event of liquidation. Preferred stock often pays a fixed dividend and may have additional features, such as convertibility to common stock or callability. Companies issue stock through an initial public offering (IPO) or secondary offerings. The stock issuance process involves underwriters, regulatory filings, and eventually listing the shares on a stock exchange. Companies issue stock to raise capital for expansion, research and development, or other business needs. Stock issuance allows companies to access funding without incurring debt. Stock can be used as a form of compensation or incentive for employees through stock options, employee stock purchase plans (ESPPs), or restricted stock units (RSUs). A public listing of a company's stock can enhance its reputation and credibility in the market, potentially attracting more customers and business partners. Stock issuance can facilitate mergers and acquisitions by using company stock as a currency to acquire other companies. Investors should analyze a company's financial statements, including its income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement, to assess its financial health and growth prospects. Investors should consider the overall market conditions and the industry in which the company operates to evaluate potential risks and opportunities. A company's management team plays a crucial role in its success. Investors should assess management's track record, experience, and vision for the company's future. Company stock investments can generate returns through capital appreciation and dividend income. Investors should evaluate the company's dividend payment history and earnings growth potential. Growth investing focuses on companies with strong growth potential. These companies often reinvest earnings into the business for expansion, resulting in higher stock price appreciation. Value investing involves identifying undervalued companies with strong fundamentals. Value investors seek stocks trading below their intrinsic value, aiming to profit from potential price corrections. Dividend investing targets companies with consistent and growing dividend payments. Dividend investors seek income generation and capital preservation through stable, well-established companies. Market risk refers to the possibility that the entire stock market declines, affecting the value of individual company stocks. Industry risk pertains to factors affecting a specific industry, such as regulatory changes, technological advancements, or increased competition. Company-specific risk involves factors unique to a particular company, such as management decisions, financial performance, or legal issues. Liquidity risk occurs when an investor cannot buy or sell a company's stock easily due to low trading volume or limited market participants. Financial statement analysis involves examining a company's financial statements to assess its financial health and growth prospects. This analysis helps investors make informed decisions about the company's stock. Ratio analysis involves calculating financial ratios using data from a company's financial statements to evaluate its performance, liquidity, solvency, and profitability. DCF analysis estimates the intrinsic value of a company's stock by projecting its future cash flows and discounting them to their present value. This method helps investors determine if a stock is overvalued or undervalued. Chart patterns are visual representations of historical price movements that can help investors identify trends and potential trading opportunities in company stocks. Technical indicators are mathematical calculations based on a stock's price, volume, or other market data. These indicators can help investors assess market trends and make informed trading decisions. Trend analysis involves studying historical price movements to identify prevailing market trends, such as uptrends, downtrends, or sideways movement, to inform investment decisions. The NYSE is the largest stock exchange globally by market capitalization, and it lists many well-known companies across various industries. The NASDAQ is known for its technology-focused listings, featuring major technology companies such as Apple, Amazon, and Google parent company Alphabet. The LSE is one of the oldest stock exchanges globally and lists companies from various countries and industries. Investors can trade company stocks through online brokerage accounts, which provide access to stock exchanges and trading platforms. Trading platforms offer various tools and features, such as real-time quotes, charting, and research, to facilitate stock trading. Investors can place various order types, such as market orders, limit orders, and stop orders, to manage their trades and minimize risks. ESOs grant employees the right to purchase a specified number of company shares at a predetermined price, allowing them to benefit from the stock's appreciation. ESPPs enable employees to purchase company stock at a discounted price through payroll deductions, encouraging employee ownership and long-term investment. RSUs represent a promise by the company to grant employees a specified number of shares after a vesting period. RSUs offer employees potential capital appreciation and dividend income. Capital gains tax applies to the profit made when selling company stock at a higher price than its purchase price. Capital losses can offset capital gains and reduce tax liability. Dividend income from company stocks may be subject to taxation, depending on the investor's tax bracket and residency. Employee stock options and grants may have tax implications, including income tax, capital gains tax, and payroll taxes. Employees should consult a tax professional to understand their specific tax liabilities. Company stock represents ownership in a corporation and can offer investors potential capital appreciation and dividend income. Companies issue stock for various reasons, such as raising capital, compensating employees, or enhancing their reputation. Investors should consider factors such as company financials, market conditions, and management quality when investing in company stocks. Company stocks play a vital role in the financial market by providing companies with a means to raise capital and offering investors a diverse range of investment opportunities. The future of company stock investing will be influenced by factors such as technological advancements, regulatory changes, and global economic conditions. As the financial market continues to evolve, company stocks will remain an essential component of investment portfolios, offering investors opportunities for growth, income, and diversification. Investors must stay informed about market trends and company developments to make well-informed decisions and navigate the ever-changing landscape of company stock investing.What Is Company Stock?
Common Stock
Preferred Stock
Reasons for Companies to Issue Stock
Raising Capital
Employee Compensation and Incentives
Enhancing Corporate Reputation
Mergers and Acquisitions

Investing in Company Stocks
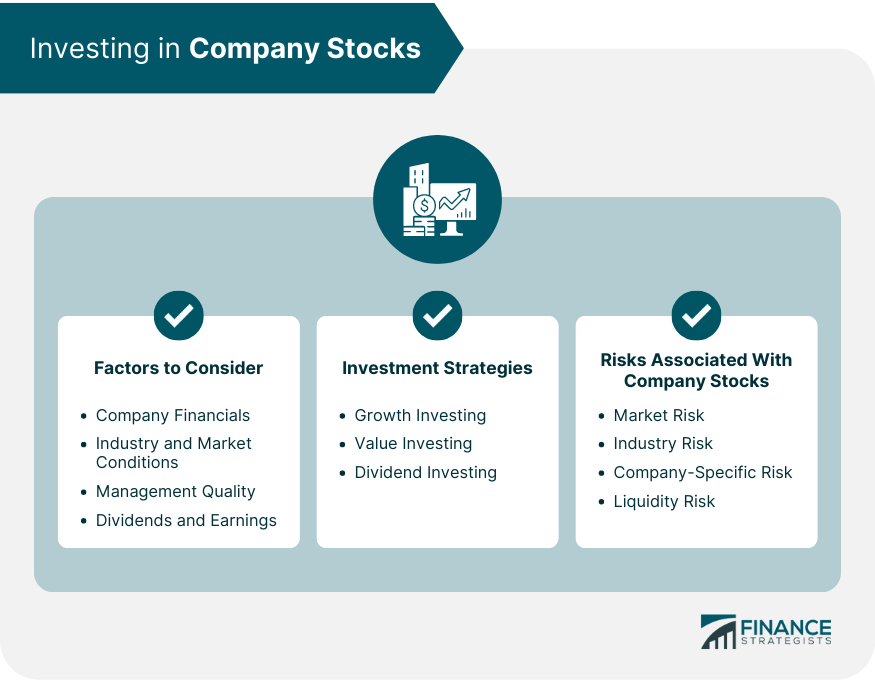
Factors to Consider
Company Financials
Industry and Market Conditions
Management Quality
Dividends and Earnings
Investment Strategies
Growth Investing
Value Investing
Dividend Investing
Risks Associated With Company Stocks
Market Risk
Industry Risk
Company-Specific Risk
Liquidity Risk
Company Stock Valuation
Fundamental Analysis
Financial Statement Analysis
Ratio Analysis
Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) Analysis
Technical Analysis
Chart Patterns
Technical Indicators
Trend Analysis
Stock Exchanges and Trading
Major Stock Exchanges
New York Stock Exchange (NYSE)
NASDAQ
London Stock Exchange (LSE)
Trading Company Stocks
Online Brokerage Accounts
Trading Platforms
Order Types
Company Stock in Employee Benefits
Employee Stock Options (ESOs)
Employee Stock Purchase Plans (ESPPs)
Restricted Stock Units (RSUs)
Tax Considerations for Company Stock
Capital Gains and Losses
Dividend Taxes
Employee Stock Options and Grants
Conclusion
Company Stock FAQs
Company stock refers to shares of a company that are owned by shareholders, including employees, executives, and investors. Company stock can be publicly traded on a stock exchange or held privately by a small group of shareholders.
Employees can acquire company stock through various programs such as employee stock options, employee stock purchase plans, and restricted stock units. These programs typically allow employees to purchase or receive shares of company stock at a discounted price or as part of their compensation package.
The benefits of owning company stock can include potential capital appreciation, dividend payments, and ownership in the company. Employees who own company stock may also feel more invested in the success of the company and may have the opportunity to participate in company decisions through voting rights.
The main risk of owning company stock is the potential for the stock price to decline, which can result in a loss of value for the shareholder. Additionally, owning a large amount of company stock can expose the shareholder to concentration risk, as their financial well-being may be tied to the performance of a single company. Finally, investors should be aware of the potential for conflicts of interest when owning company stock, particularly if they are also employed by the company.
Investors can evaluate company stock by analyzing factors such as the company's financial health, industry trends, competition, management team, and growth potential. Investors should also consider the company's earnings per share, price-to-earnings ratio, dividend history, and other key financial metrics. Finally, investors should consider their own investment goals and risk tolerance before investing in company stock.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.















