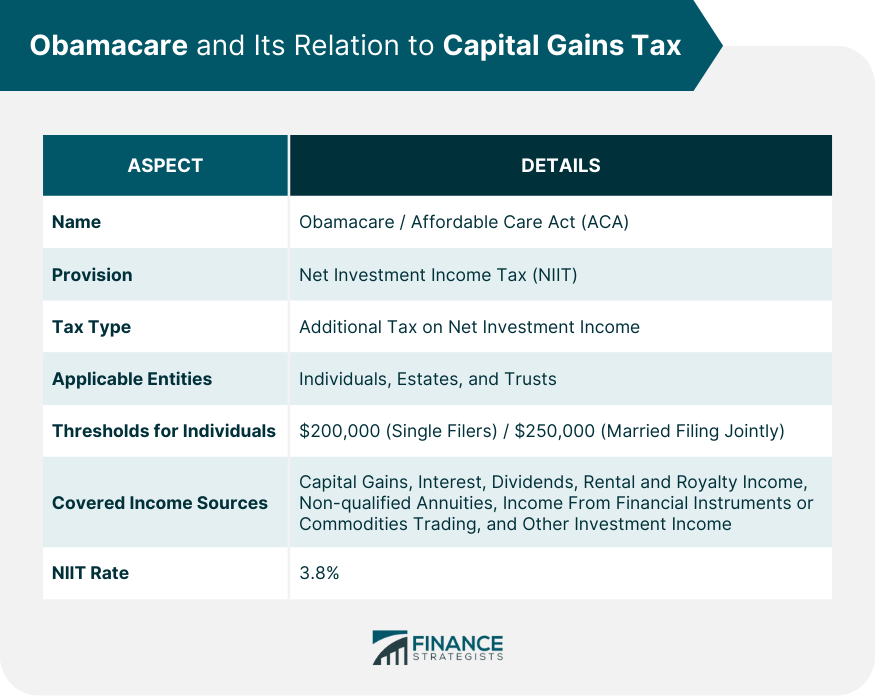
Capital gains tax is charged on profits from selling assets like stocks, bonds, or real estate. The duration you hold an asset determines the tax rate: assets held under a year incur short-term capital gains tax, generally equivalent to an individual's regular income tax rate. In contrast, assets held over a year benefit from the typically lower long-term capital gains tax rates. This system promotes long-term investment. The tax has individual and economic implications. For investors, it affects returns on investment, while for the government, it's a crucial revenue source. The amount owed varies based on factors such as income level, asset type, holding duration, and tax bracket. Some situations may also lead to unique tax treatments. Obamacare, officially known as the Affordable Care Act (ACA), brought about many changes in the healthcare landscape when it was implemented. One lesser-known provision of Obamacare is the Net Investment Income Tax (NIIT), which has implications for capital gains tax. The NIIT is a 3.8% tax that applies to individuals, estates, and trusts that have net investment income above certain threshold amounts. For individuals, these thresholds are $200,000 for single filers and $250,000 for married couples filing jointly. The NIIT applies to taxpayers with modified adjusted gross income above the thresholds mentioned earlier. Importantly, it's not just capital gains that count towards this. Interest, dividends, rental and royalty income, non-qualified annuities, income from businesses involved in trading of financial instruments or commodities, and other investment income are also included. The 3.8% NIIT applies to the lesser of the net investment income or the excess of modified adjusted gross income over the threshold. For example, if a single filer has a modified adjusted gross income of $220,000, including $30,000 in net investment income, the NIIT would apply to the $20,000 that's over the threshold. For taxpayers subject to the NIIT, the effective tax rate on long-term capital gains and qualified dividends can rise from the base 15% or 20% rate to 18.8% or 23.8%—including the 3.8% NIIT. For short-term capital gains, which are taxed as ordinary income, the top effective rate can be as high as 43.4% when including the top ordinary income tax rate and the NIIT. Consider a high-income individual with $500,000 in salary and an additional $100,000 in long-term capital gains. This individual would be subject to the 20% long-term capital gains tax rate, as well as the 3.8% NIIT. This means that instead of paying $20,000 in capital gains tax, they would pay an additional $3,800 due to the NIIT, for a total of $23,800. There are several strategies that high-income taxpayers can use to minimize their tax liability under Obamacare. These include tax-efficient investing, tax-loss harvesting, and strategic asset location. For example, holding onto assets for more than a year can ensure they qualify for the lower long-term capital gains rate. Additionally, tax-loss harvesting, which involves selling losing investments to offset gains, can also help reduce tax liability. The NIIT (Net Investment Income Tax) does not burden the majority of the population, specifically those who fall into the low to middle-income brackets. This ensures that the tax doesn't disproportionately affect individuals who aren't earning high incomes, hence not burdening those who are less financially secure. One of the major goals of Obamacare was to expand healthcare access. The revenue collected from this tax specifically targets providing subsidies for healthcare. By channeling the funds in this manner, it enhances the feasibility for more people to access essential health services, bridging the gap between the economically disadvantaged and proper healthcare. By influencing the investment dynamics, the tax promotes the holding of assets for a longer period of time. This approach can lead to more stable financial markets, as rapid selling and buying (often leading to speculation) can be deterred. Long-term investments can contribute to economic stability and growth. High earners, certain estates, and trusts are now facing a significant increase in their tax liabilities due to the NIIT, especially if they have substantial investment income. This might make them reconsider the viability of certain investments, potentially limiting the capital flow into various sectors of the economy. With the introduction of the NIIT, certain investments might become less appealing to high-income individuals. This could lead to a decrease in investments, which can have cascading effects on businesses seeking capital, employment rates, and overall economic growth. The NIIT introduces additional layers of complexity in tax planning. This can lead to increased expenditure for taxpayers in terms of hiring professionals for tax preparation and financial planning. This not only results in direct costs but also could deter efficient investment planning due to the intricacies involved. While the primary target might seem to be the ultra-wealthy, the ripple effect of the tax can also touch upon retirees who rely on their investments for sustenance. Additionally, individuals looking to sell properties or businesses might find themselves facing this additional tax, which could affect their net gains and financial planning. Tax-efficient investing involves strategies that aim to maximize after-tax returns. This could mean prioritizing investments that qualify for the lower long-term capital gains rates, such as stocks, bonds, and real estate held for more than a year. It can also mean taking advantage of tax-advantaged accounts like IRAs and 401(k)s, which allow for tax-free or tax-deferred growth. Another strategy is tax-loss harvesting, which involves selling securities at a loss to offset capital gains from other investments. By doing this, you can lower your overall taxable capital gains, reducing the amount subject to the NIIT. Strategic asset location is the practice of placing investments in the type of account (taxable or tax-advantaged) that will provide the most tax benefit. For example, investments that generate significant income, like bonds, may be better placed in tax-advantaged accounts, while investments that qualify for the long-term capital gains rate might be placed in taxable accounts. Given the complexity of the tax code and the significant potential impact on your finances, it's advisable to consult with a tax professional or financial advisor. They can help you understand your specific situation and design a strategy that minimizes your tax liability while meeting your financial goals. Understanding the capital gains tax and its implications due to Obamacare is vital for all individuals, especially those who hold significant investments or assets. The introduction of the Net Investment Income Tax (NIIT) under Obamacare has both positive and negative implications. While it ensures that the majority of low- to middle-income individuals remain unaffected, it presents a higher tax liability for high-income individuals, potentially influencing their investment behaviors. The revenue generated from this tax is crucial in providing healthcare subsidies, making healthcare more accessible for many. At the same time, it's undeniable that the added complexities might deter efficient investment and financial planning. Given the intricate nature of these tax regulations and their profound impact on financial planning, it's paramount to seek informed advice. To navigate these complexities and optimize your financial strategy, consider seeking professional tax planning services.Understanding Capital Gains Tax
Obamacare and Its Relation to Capital Gains Tax
Net Investment Income Tax Under Obamacare
Who It Applies To
Rates and Income Thresholds
Impact of Obamacare on Capital Gains Tax
How Obamacare Affects the Taxation of Capital Gains
Scenarios to Illustrate the Impact
Possible Strategies to Minimize Tax Liability
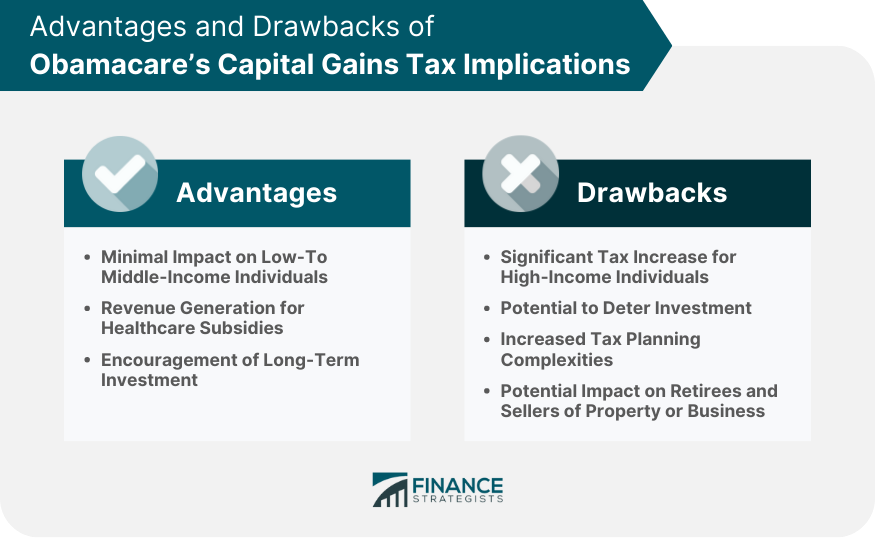
Advantages of Obamacare’s Capital Gains Tax Implications
Minimal Impact on Low- to Middle-Income Individuals
Revenue Generation for Healthcare Subsidies
Encouragement of Long-Term Investment
Drawbacks of Obamacare’s Capital Gains Tax Implications
Significant Tax Increase for High-Income Individuals
Potential to Deter Investment
Increased Tax Planning Complexities
Potential Impact on Retirees and Sellers of Property or Business
Strategies for Managing the Capital Gains Tax Under Obamacare
Tax-Efficient Investing
Tax-Loss Harvesting
Strategic Asset Location
Professional Consultation

Bottom Line
Impact of Obamacare on Capital Gains Tax FAQs
Obamacare introduced the Net Investment Income Tax (NIIT), which can increase capital gains tax for high-income individuals.
Under Obamacare, high-income taxpayers can face increased capital gains tax due to the 3.8% NIIT on top of their usual rates.
The NIIT can effectively raise the capital gains tax rate to nearly 20%, affecting investment decisions for high-income individuals.
Strategies include tax-efficient investing, tax-loss harvesting, strategic asset location, and consulting a tax professional.
High-income individuals, estates, and trusts are most affected as they may face higher tax rates due to the introduction of the NIIT.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











