Capital gains are the profits made from the sale of an asset like stocks, bonds, or real estate. These gains are subject to taxes, which vary depending on your income level and how long you've held the asset. Long-term capital gains, which apply to assets held for more than a year, are taxed at a lower rate than short-term gains. The mechanism of tax loss harvesting involves strategically selling off investments that have experienced a loss to reduce the taxable income generated by capital gains from other investments. By doing this, investors can lower their overall tax liability. The capital losses incurred can offset capital gains, which effectively reduces the investor's taxable income. For instance, if an investor has $10,000 in capital gains and $8,000 in capital losses, they can offset the gains with the losses. This means they'll only be taxed on $2,000 of capital gains ($10,000 - $8,000). This strategy can provide significant tax savings, especially for investors in high tax brackets. The first step in the tax loss harvesting process is to identify which investments in your portfolio have unrealized losses. This step requires a comprehensive review of your portfolio and the performance of your assets. Once you have identified potential investments for tax loss harvesting, the next step is to sell these investments to realize the losses. After selling, you can immediately repurchase a similar but not "substantially identical" investment to maintain your preferred asset allocation and expected returns. This process is known as "switching." Strategic timing is crucial when it comes to tax loss harvesting. Generally, this strategy is most beneficial when executed near the end of the tax year. However, investors should also monitor market conditions and their portfolio's performance regularly throughout the year. The wash-sale rule is a regulation set by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) that prevents investors from claiming a loss on the sale of an investment if a "substantially identical" investment was purchased within 30 days before or after the sale. This rule can limit the effectiveness of tax loss harvesting if not properly managed. While tax loss harvesting can be beneficial, it's also crucial to consider its potential impact on your long-term investment strategy. Making trades solely for tax reasons may not always align with your overall investment goals and could disrupt your long-term plans. There are limitations on how much you can deduct in capital losses each year. As of 2024, the IRS allows investors to deduct up to $3,000 in capital losses against their income each year. Any losses above this amount can be carried forward to future years. To maximize the benefits of tax loss harvesting, you must keep a balanced portfolio. This means holding a mix of assets that can help smooth out returns over time. Diversification can also provide more opportunities for tax loss harvesting, as not all investments will move in the same direction at the same time. Implementing strategic timing for realizing losses and gains can also enhance the benefits of tax loss harvesting. Generally, it's beneficial to realize losses in years when you have high-income or capital gains and to realize gains in years when you have low-income or capital losses. Tax loss harvesting should be considered as part of a broader tax planning strategy. This might involve coordinating with other tax strategies, such as maximizing contributions to tax-advantaged accounts, gifting strategies, and estate planning. In a bull market, where prices are rising, opportunities for tax loss harvesting might be limited. However, not all investments will perform well at the same time, so there might still be opportunities to harvest losses from certain underperforming assets. Bear markets, where prices are falling, often provide ample opportunities for tax loss harvesting. These market conditions can allow investors to realize losses that can offset gains realized either in the current year or in future years. Tax loss harvesting can also be applied to mutual funds and ETFs. However, it's important to understand the unique characteristics and tax implications of these investment types to effectively implement this strategy. Capital losses and gains should be reported on Schedule D of your tax return. Detailed records of your transactions, including purchase and sale dates, costs, and proceeds, will be necessary to accurately report these figures. Keeping track of your investment transactions and maintaining detailed records are critical to effectively implementing tax loss harvesting and accurately reporting capital gains and losses. These records will also be crucial in case of an audit by the IRS. Tax loss harvesting is a critical strategy for investors, allowing them to offset capital gains tax liability by selling securities at a loss. This approach can minimize the tax burden and effectively lower the total cost of investments. For effective implementation, the investor must consider the IRS' wash-sale rule, which prevents claiming a loss on the sale of an investment if a "substantially identical" one was purchased within 30 days. Strategic timing of realizing losses and gains and maintaining a balanced, diversified portfolio can optimize the benefits of tax loss harvesting. Furthermore, viewing this tactic as part of a broader tax planning strategy can lead to significant long-term advantages. This strategy can be employed in both bull and bear markets and extends to mutual funds and ETFs. Proper record-keeping is essential for accurate reporting of capital losses and gains, aiding in effective tax loss harvesting while ensuring compliance with tax laws.Capital Gains and Their Tax Implications
Mechanism of Using Tax Loss Harvesting to Offset Capital Gains
Illustrating the Offset Process
Process of Tax Loss Harvesting
Identifying Investments for Tax Loss Harvesting
Executing Tax Loss Harvesting: Selling and Repurchasing Assets
Observing Strategic Timing for Tax Loss Harvesting

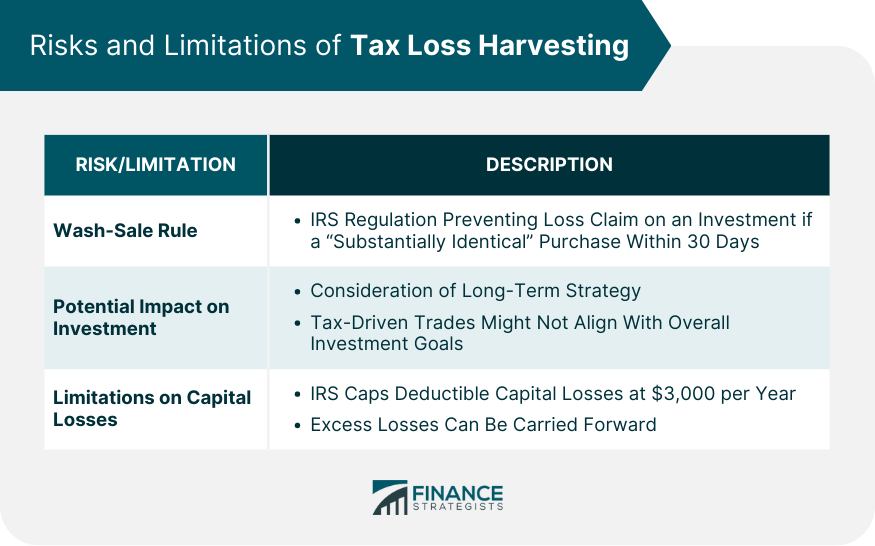
Risks and Limitations of Tax Loss Harvesting
Wash-Sale Rule
Potential Impact on Long-Term Investment Strategy
Limitations on Deducting Capital Losses
Strategies to Maximize Benefits From Tax Loss Harvesting
Balancing Portfolio Composition
Timing Strategies for Loss and Gain Realization
Considering Tax Loss Harvesting as Part of a Broader Tax Planning Strategy

Tax Loss Harvesting in Different Investment Scenarios
Bull Markets
Bear Markets
Mutual Funds and ETFs
Tax Reporting for Tax Loss Harvesting
How to Report Capital Losses and Gains
Tracking and Documenting for Tax Loss Harvesting
Conclusion
Using Tax Loss Harvesting to Offset Capital Gains FAQs
Tax loss harvesting is a strategy that involves selling securities at a loss to offset a capital gains tax liability. It's important because it can minimize your tax burden, effectively lower the total cost of your investments, and ensure that market movements do not negatively impact your after-tax returns.
Tax loss harvesting works by selling off investments that have experienced a loss. These capital losses can then be used to offset capital gains from other investments, effectively reducing the investor's taxable income.
The wash-sale rule is an IRS regulation that prevents investors from claiming a loss on the sale of an investment if a "substantially identical" investment was purchased within 30 days before or after the sale. This rule can limit the effectiveness of tax loss harvesting if not properly managed.
To maximize the benefits of tax loss harvesting, keep a balanced and diversified portfolio, implement strategic timing for realizing losses and gains, and consider tax loss harvesting as part of a broader tax planning strategy.
Capital losses and gains should be reported on Schedule D of your tax return. It's important to keep detailed records of your transactions, including purchase and sale dates, costs, and proceeds, to accurately report these figures and effectively implement tax loss harvesting.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.















