Buying savings bonds is a process that begins with understanding what a savings bond is. It is a type of debt security issued by the U.S. Treasury to support government spending. Investors lend money to the government by purchasing the bond, and in return, the government promises to pay the investor back with interest after a specific period. Savings bonds hold immense importance as low-risk investments, making them ideal for conservative investors or those seeking to diversify their portfolios. They offer guaranteed returns and certain tax advantages, making them a practical saving option. You can buy savings bonds online via TreasuryDirect, a secure government platform. Alternatively, they can be purchased through certain financial institutions such as banks and credit unions. The process entails deciding on the type of bond (Series EE or Series I), determining the investment amount, and completing the transaction. Buying savings bonds is not just an investment strategy; it contributes to the nation's financial health. Unlike stocks and other volatile investment options, savings bonds present virtually no risk to your principal amount. This is because they are not subject to market fluctuations, and their return rate does not change once the bond is issued. Moreover, savings bonds are backed by the full faith and credit of the U.S. government, the issuer of these bonds. This means that the U.S. government guarantees the bond's face value payment plus the stated interest to the bondholder, offering unparalleled security for your investment. This assurance makes savings bonds an excellent choice for conservative investors seeking to preserve their capital while still earning a reliable return. Many investment options in the market may promise high returns, but they often come with a level of risk and uncertainty. With savings bonds, however, you're assured a fixed rate of return. Savings bonds earn interest monthly and compounded semiannually. This means that the interest earned is added to the principal amount, and then interest is calculated on this new amount, maximizing your earning potential over time. Whether it's a Series EE bond, which offers a fixed rate of interest, or a Series I bond, which provides a composite rate of fixed and inflation-adjusted interest, the return on your investment is guaranteed. The interest earned from savings bonds is exempt from state and local income taxes, which can lead to substantial savings, especially for those in high tax brackets or living in high-tax states. On the federal level, taxes on the interest can be deferred until you redeem the bond or it reaches final maturity, typically 30 years from the issue date. This tax deferral means that you will only owe federal income tax on the interest earned once you receive it, allowing the interest to compound tax-free in the meantime. The interest may be entirely exempt from federal income tax if the bonds are used for qualified education expenses and meet other criteria. This feature can make savings bonds an attractive investment option for parents or grandparents planning to contribute to a child's or grandchild's education costs. Series EE bonds are savings bonds issued by the U.S. Department of the Treasury. These bonds are known for their reliability and low-risk nature. They have a fixed interest rate that is set at the time of purchase and remains the same throughout the bond's 30-year term. When you buy a Series EE bond, you pay the face value of the bond, which is its full denomination. For example, if you purchase a $50 Series EE bond, you pay $50 upfront. The bond accrues interest over time, and you can redeem it for its full face value plus any earned interest when it reaches maturity. One notable feature of Series EE bonds is that they have a guarantee to double in value if held to maturity, which effectively gives them a guaranteed interest rate. However, this doubling period may take longer than the initial 30-year term, depending on the bond's specific issue date. Series I bonds are also savings bonds issued by the U.S. Department of the Treasury. These bonds are designed to protect against inflation and offer a return composed of both a fixed interest rate and an inflation rate. Similar to Series EE bonds, Series I bonds are sold at face value. The interest rate for Series I bonds consists of two components: a fixed rate that remains constant throughout the bond's term and an inflation rate that is adjusted twice a year based on changes in the Consumer Price Index for All Urban Consumers (CPI-U). The combination of the fixed rate and inflation rate determines the bond's overall interest rate. This means that the return on Series I bonds can adjust to keep pace with inflation, providing a measure of protection against the eroding effects of rising prices. Series I bonds have a minimum holding period of one year, and if you redeem them before five years, you forfeit the most recent three months of interest. They reach final maturity after 30 years, and you can redeem them for their face value plus any earned interest. Only some people are eligible to purchase U.S. savings bonds. The U.S. Treasury has set specific requirements that potential buyers must meet. First, you must have a Social Security Number (SSN) to buy savings bonds. This number is used for tax reporting and tracking your bond ownership. Secondly, you must be a U.S. resident, a U.S. citizen living abroad, or a civilian employee of the U.S., regardless of your residence. This requirement ensures that savings bonds remain a domestic investment tool, with the proceeds used to fund U.S. government operations. The good news is that there's no age limit for buying savings bonds. Parents or guardians can purchase bonds for minors, making them a popular gift option for children's birthdays, graduations, or other special occasions. Once you meet the eligibility criteria, the next step is to decide where to buy the savings bonds. The most common and convenient method is through the U.S. Treasury's online platform, TreasuryDirect. This site offers a secure environment for buying, managing, and redeeming savings bonds. The advantage of this approach is that you can access and manage your bonds anytime, anywhere, without the need to keep track of paper certificates. In addition to TreasuryDirect, savings bonds can also be purchased through various financial institutions. While this option has become less common with the rise of online purchasing, some banks and credit unions still facilitate the purchase of savings bonds for their customers. Similarly, some brokerage firms may allow clients to purchase savings bonds as part of a broader investment portfolio. TreasuryDirect is an online platform run by the U.S. Department of the Treasury that allows individuals to purchase U.S. government securities, including savings bonds, directly from the source. This reliable and secure online portal directly links the U.S. government and individual investors. The TreasuryDirect platform offers various benefits. It eliminates the need for physical paper bonds, reducing the risk of loss or damage. It also allows for easy management of your bond portfolio from anywhere with an internet connection. You can buy, hold, and redeem Series EE and Series I savings bonds and other treasury securities at any time and from anywhere. Once you set up a TreasuryDirect account, you have full control over your savings bond investments. You can view the current value of your bonds, see how much interest your bonds have earned, and redeem your bonds when necessary. Additionally, TreasuryDirect offers helpful tools and resources, such as a savings bond calculator and detailed information about current interest rates. 1. Open a TreasuryDirect Account: To purchase a savings bond online, you first need to open an account on TreasuryDirect. To complete this process, you'll need your Social Security Number, a U.S. address, and a checking or savings account. 2. Navigate to the Purchase Page: Once you have your account set up, you can navigate to the "BuyDirect" page and select the type of bond you wish to purchase (Series EE or Series I). 3. Enter Purchase Details: You must enter the amount you wish to purchase, the bond series, and the ownership type. 4. Review and Submit: Review your purchase and submit it. Your account will be debited for purchase, and the bond will be issued electronically. 1. Find a Participating Institution: Identify banks, credit unions, or brokerage firms that offer the option to purchase savings bonds. 2. Complete the Necessary Forms: Obtain and complete the purchase request form provided by the financial institution. This form will require information such as your personal details and the amount of savings bonds you wish to purchase. 3. Provide Payment: Submit the required payment for the savings bonds you want to buy. The financial institution will specify the accepted payment methods, such as cash, check, or electronic transfer. 4. Registration and issuance: The financial institution will handle the registration process and facilitate the purchase of the savings bonds from the U.S. Treasury on your behalf. 5. Recordkeeping: Keep a copy of the purchase confirmation or receipt provided by the financial institution for your records. While savings bonds offer secure investment and guaranteed returns, they're not meant for short-term investment. If you redeem a bond within the first five years, you will lose the last three months' worth of interest. Series I Bonds provide inflation protection. However, Series EE bonds do not. If inflation rates exceed the fixed interest rate of Series EE bonds, the real return might be less than anticipated. There is an annual purchase limit for savings bonds. You could buy a maximum of $10,000 in each series (EE and I) per Social Security Number in one calendar year. Savings bonds can play an essential role in creating a diversified investment portfolio. Their low-risk nature balances higher-risk investments, ensuring some degree of safety for your capital. Savings bonds are popular for long-term goals like education and retirement planning. The Education Savings Bond Program allows interest earnings from certain savings bonds to be excluded from federal income tax when the bonds are redeemed to pay qualified higher education expenses. Buying savings bonds involves understanding the basics and benefits of these debt securities issued by the U.S. Treasury. Savings bonds are low-risk investments with guaranteed returns and tax advantages, making them an attractive option for conservative investors. They can be purchased online through TreasuryDirect or through financial institutions such as banks and credit unions. Savings bonds offer secure investments backed by the U.S. government, providing a constant return and protection against market fluctuations. There are two types of savings bonds: Series EE bonds with a fixed interest rate over a 30-year term and the potential to double in value, and Series I bonds with a fixed interest rate combined with an inflation rate adjustment based on the CPI-U. To purchase savings bonds online, you need to open a TreasuryDirect account, select the bond type, enter purchase details, and submit the transaction. Buying through financial institutions involves finding participating institutions, completing forms, providing payment, and keeping records. There are certain limitations to consider, such as early redemption penalties within the first five years, inflation risks for Series EE bonds, and annual purchase limits. Savings bonds can contribute to a diversified portfolio and are often used for long-term goals like education and retirement planning, with some bonds eligible for tax exclusions when redeemed for qualified education expenses.How to Buy Savings Bonds: Overview
Reasons to Buy Savings Bonds
Secure Investment
Guaranteed Interest
Tax Advantages

Types of Savings Bonds
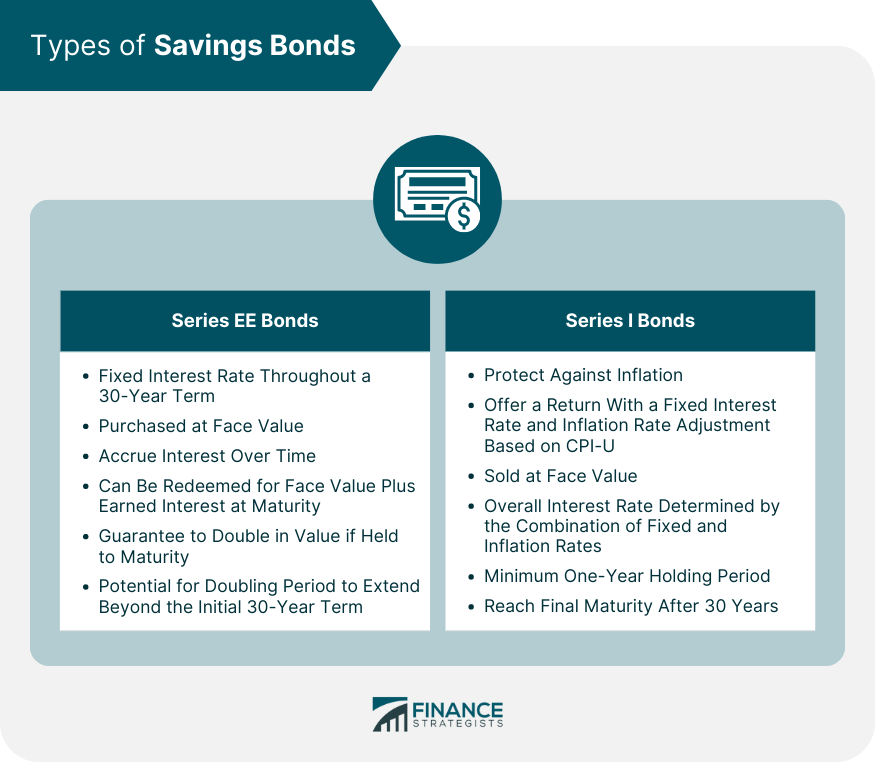
Series EE Bonds
Series I Bonds
Understanding the Process of Buying Savings Bonds
Eligibility
Where to Buy Savings Bonds
How to Buy Savings Bonds Online
Overview of the TreasuryDirect Platform
Steps to Purchasing Online

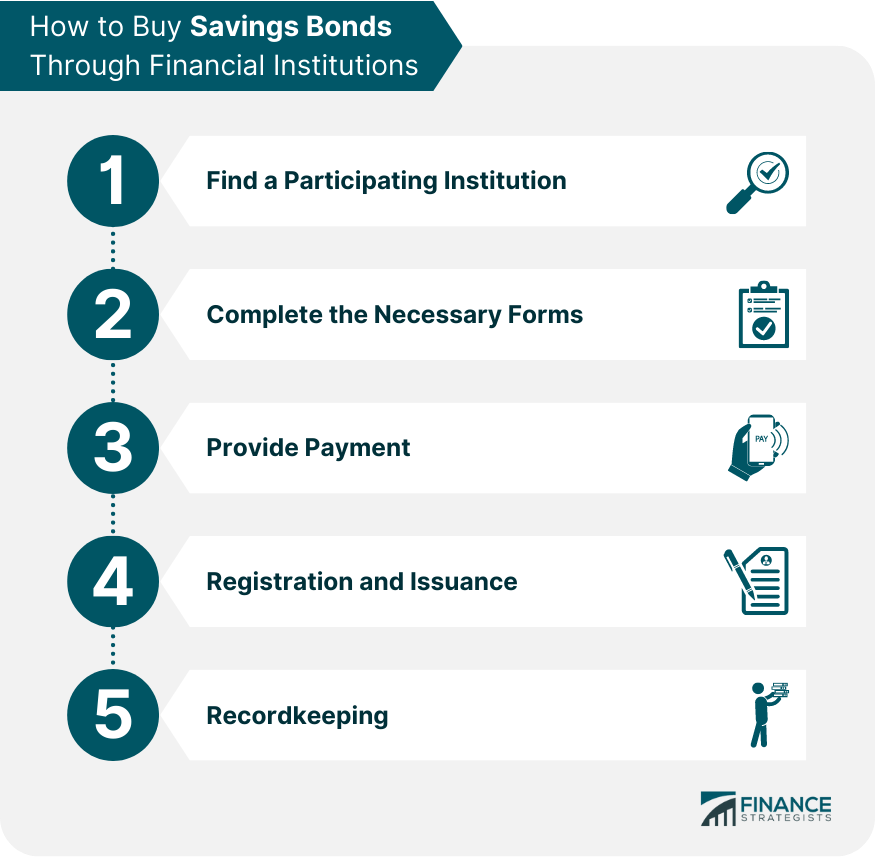
How to Buy Savings Bonds Through Financial Institutions
Risks and Limitations of Buying Savings Bonds
Early Redemption Penalties
Inflation Risks
Annual Purchase Limits
Financial Planning and Buying Savings Bonds
Role of Savings Bonds in a Diversified Portfolio
Savings Bonds for Education and Retirement Planning
Conclusion
How to Buy Savings Bonds FAQs
The principal investment in savings bonds is secure because the U.S. government supports them. This ensures that the initial amount invested can be recovered.
Savings bonds cease earning interest upon reaching maturity. To prevent losing potential returns, it is recommended to redeem them at this time.
Absolutely, savings bonds are suitable gifts and can be procured for children or grandchildren.
Savings bonds can be purchased for $25 or more, up to the annual limit.
The Treasury Department determines interest rates for both Series EE and Series I savings bonds, which may fluctuate every six months. As of May 2023 through October 2023 issuance period, Series EE savings bonds have been set to earn a fixed annual interest rate of 2.50%. Series I savings bonds, on the other hand, are accruing a composite rate of 4.30% during the same period. This rate comprises a fixed component and an additional part indexed to inflation, which is adjusted semi-annually.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.













