Social Security retirement benefits are a government-administered program designed to provide financial support to eligible individuals in their retirement years. These benefits play a crucial role in many retirees' financial plans. To optimize retirement planning, it is essential to understand how Social Security benefits work, the factors affecting these benefits, and the strategies available for maximizing them. Several factors influence Social Security benefits, including eligibility requirements, benefit calculations, retirement age, and taxation.
To qualify for Social Security retirement benefits, individuals must meet specific age requirements. Benefits can be claimed as early as age 62 or as late as age 70, with varying benefit amounts based on the age of retirement. Eligibility for Social Security benefits is also determined by the number of work credits earned during an individual's working years. Typically, 40 credits are required to qualify for benefits, with a maximum of four credits earned per year. Individuals must be U.S. citizens or legal residents to qualify for Social Security retirement benefits. The first step in calculating Social Security benefits is determining an individual's Average Indexed Monthly Earnings (AIME). This figure is based on the 35 highest-earning years of an individual's work history, adjusted for inflation. Next, the Primary Insurance Amount (PIA) is calculated using a formula applied to the AIME. The PIA is the base benefit amount an individual will receive upon reaching their Full Retirement Age (FRA). Finally, Social Security retirement benefits are adjusted based on the age at which the individual claims benefits. Benefits will be reduced for early retirement and increased for delayed retirement. The Full Retirement Age (FRA) is the age at which an individual can claim their full Social Security retirement benefits. The FRA varies based on an individual's birth year, ranging from 65 to 67. Claiming Social Security benefits before reaching FRA will result in reduced benefits. The reduction is permanent and can significantly impact an individual's overall retirement income. Conversely, delaying Social Security retirement benefits past FRA will result in increased benefits. Benefit amounts increase up until age 70, after which no further increases are available. Individuals should consider factors such as their health, financial needs, and life expectancy when deciding when to claim Social Security benefits. Spouses can claim their own benefits or up to half of their spouse's benefit amount, whichever is higher. Coordinating spousal benefits can help maximize overall retirement income. Surviving spouses are eligible for survivor benefits based on their deceased spouse's Social Security record. Understanding the rules and coordinating survivor benefits with other retirement income can help ensure financial stability. Divorced individuals may be eligible for spousal or survivor benefits based on their ex-spouse's Social Security record. Understanding the rules and claiming strategies can help divorced individuals maximize their benefits. A portion of Social Security retirement benefits may be subject to federal income tax, depending on an individual's income level. Understanding the tax implications can help retirees plan their income sources more effectively. Some states also tax Social Security benefits, while others do not. Retirees should be aware of their state's tax rules and consider the impact on their retirement income. There are strategies available to minimize the taxation of Social Security benefits, such as managing other income sources, timing withdrawals from retirement accounts, and considering state tax rules when choosing a retirement location. Social Security benefits should be considered in conjunction with other retirement income sources, such as pensions, retirement savings accounts, and investments, to ensure a well-rounded retirement plan. Higher-income individuals may be subject to higher Medicare premiums based on their Social Security benefits and other income. Understanding the relationship between Social Security and Medicare can help retirees manage their healthcare costs effectively. Careful coordination of Social Security benefits with other retirement income sources can help maximize overall retirement income and ensure financial security. To maximize Social Security benefits, individuals should stay informed about their benefits, the program's rules, and potential changes that could impact their retirement planning. Incorporating Social Security benefits into retirement planning can help ensure a more secure and comfortable retirement. This includes coordinating benefits with other income sources and considering tax implications. Working with financial professionals can help individuals navigate the complexities of Social Security benefits and develop strategies to maximize their retirement income. Social Security retirement benefits play a critical role in retirement planning, providing financial support for millions of retirees. To ensure a secure and comfortable retirement, it is crucial for individuals to understand the various aspects of these benefits, including eligibility requirements, benefit calculations, claiming strategies, and tax implications. By staying informed about potential changes to the Social Security system and coordinating benefits with other retirement income sources, individuals can create a well-rounded retirement plan that addresses their unique needs and goals. A proactive approach to retirement planning, which incorporates Social Security benefits, can help individuals maximize their overall retirement income and ensure financial stability during their golden years. Working with financial professionals and staying informed about the latest developments in Social Security benefits can further enhance one's ability to navigate the complexities of retirement planning. Ultimately, understanding and optimizing Social Security retirement benefits is essential for achieving a fulfilling and financially secure retirement.What Are Social Security Retirement Benefits?
Eligibility for Social Security Retirement Benefits
Age Requirements
Work Credit Requirements
Citizenship or Legal Residency Status
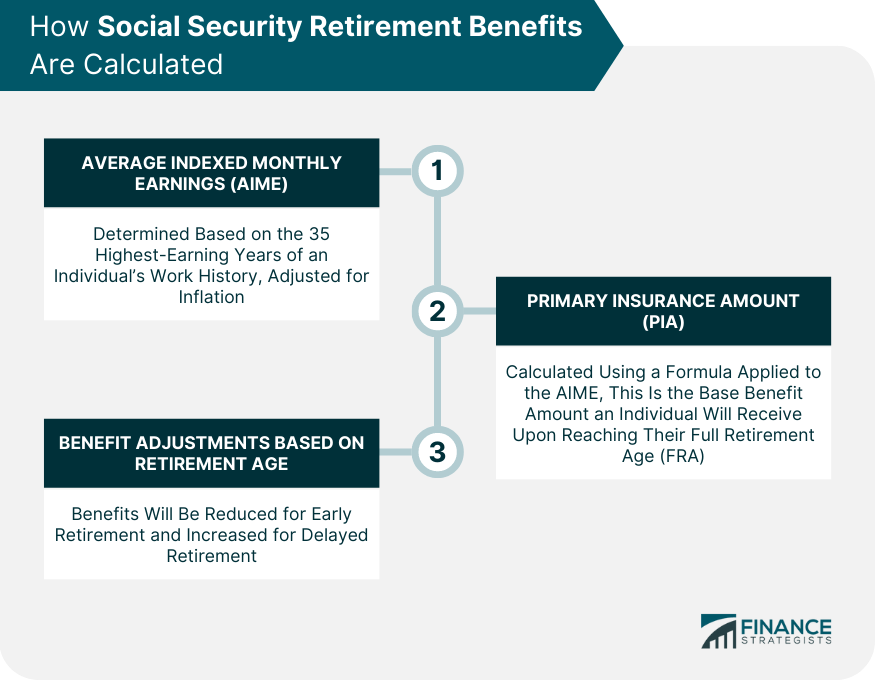
How Social Security Retirement Benefits Are Calculated
Average Indexed Monthly Earnings (AIME)
Primary Insurance Amount (PIA)
Benefit Adjustments Based on Retirement Age
Full Retirement Age and Benefit Adjustments
Definition of Full Retirement Age (FRA)
Early Retirement and Reduced Benefits
Delayed Retirement and Increased Benefits
Claiming Strategies for Social Security Retirement Benefits
Individual Claiming Strategies
Spousal Benefits and Strategies
Survivor Benefits and Strategies
Strategies for Divorced Individuals
Taxation of Social Security Retirement Benefits
Federal Income Tax Implications
State Income Tax Implications
Strategies to Minimize Taxation
Social Security Retirement Benefits and Other Retirement Income
Interaction With Pensions and Retirement Savings
Impact on Medicare Premiums
Coordinating Social Security Benefits With Other Retirement Income Sources
Tips for Maximizing Social Security Retirement Benefits
Staying Informed About Benefits and Changes to the Program
Planning for Retirement With Social Security Benefits in Mind
Coordinating With Financial Professionals to Optimize Benefits

Conclusion
Social Security Retirement Benefits FAQs
Social Security retirement benefits are monthly payments made to individuals who have reached retirement age and have contributed to Social Security throughout their working years.
Individuals can begin receiving Social Security retirement benefits as early as age 62, but benefits increase for each year that retirement is delayed up to age 70.
The amount of Social Security retirement benefits is based on an individual's lifetime earnings. The Social Security Administration calculates a benefit amount based on an individual's 35 highest-earning years, adjusting for inflation.
Yes, individuals can work and receive Social Security retirement benefits. However, if you start receiving benefits before your full retirement age and earn more than a certain amount, your benefits may be reduced. Once you reach your full retirement age, there is no limit on how much you can earn while receiving Social Security retirement benefits.
If you delay taking Social Security retirement benefits beyond your full retirement age, you can receive increased benefits. For each year that you delay receiving benefits, your benefit amount will increase by a certain percentage until you reach age 70.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











