Tax-free retirement income refers to the funds that retirees receive without owing any federal or state taxes. This type of income allows retirees to maximize their earnings during retirement and helps to maintain financial stability. It is a critical component of financial planning for retirement. By minimizing the tax burden, retirees can maximize the value of their savings, providing a more comfortable and secure lifestyle during their golden years. There are various sources of tax-free retirement income, including Roth IRAs, Roth 401(k)s, Health Savings Accounts (HSAs), municipal bonds, Treasury bonds, and certain life insurance policies. Each source has its own rules and benefits, making it essential to understand the differences to optimize one's retirement income.
I'm Taylor Kovar, a Certified Financial Planner (CFP), specializing in helping business owners with strategic financial planning. I recently guided a couple towards tax-free retirement income using a strategic Roth IRA conversion plan. They were concerned about maximizing their retirement savings while minimizing tax liabilities. By gradually converting a portion of their traditional IRA into a Roth IRA over several years, they unlocked tax-free income streams in retirement. Maximize your retirement savings with strategic Roth IRA conversions now. Contact me at (936) 899 - 5629 or [email protected] to discuss how we can achieve your financial objectives. WHY WE RECOMMEND: IDEAL CLIENTS: Business Owners, Executives & Medical Professionals FOCUS: Strategic Planning, Alternative Investments, Stock Options & Wealth PreservationWhat Is Tax-Free Retirement Income?
Read Taylor's Story

Fee-Only Financial Advisor
Certified Financial Planner™
3x Investopedia Top 100 Advisor
Author of The 5 Money Personalities & Keynote Speaker
Tax-Free Retirement Savings Accounts
Roth IRA
Contribution Limits
A Roth IRA is an individual retirement account that allows taxpayers to save for retirement on an after-tax basis. The annual contribution limits for Roth IRAs are $7,000 for individuals under 50 and $8,000 for individuals 50 and older (as of 2024).
Withdrawal Rules
Roth IRAs have specific withdrawal rules that must be followed to avoid penalties. Qualified withdrawals can be made tax-free and penalty-free after the age of 59 ½ and when the account has been open for at least five years.
Tax Benefits
The main tax benefit of a Roth IRA is that qualified withdrawals are tax-free during retirement. Additionally, there are no required minimum distributions, providing more flexibility for retirees when managing their income.
Roth 401(k)
Contribution Limits
A Roth 401(k) is an employer-sponsored retirement plan that allows employees to contribute after-tax dollars. The annual contribution limits for Roth 401(k)s are $23,000 for individuals under 50 and $30,500 for individuals 50 and older (as of 2024).
Withdrawal Rules
Similar to Roth IRAs, Roth 401(k) withdrawals are tax-free if made after the age of 59 ½ and when the account has been open for at least five years. Required minimum distributions apply after the age of 73, but they can be avoided by rolling the account into a Roth IRA.
Tax Benefits
Roth 401(k)s offer tax-free withdrawals during retirement, allowing retirees to avoid taxes on their savings. While contributions are made with after-tax dollars, the earnings grow tax-free, providing a significant advantage over time.
Health Savings Account (HSA)
Contribution Limits
A Health Savings Account (HSA) is a tax-advantaged account designed to help individuals save for medical expenses. The annual contribution limits for HSAs are $4,150 for individuals and $8,300 for families (as of 2024).
Withdrawal Rules for Medical Expenses
HSA withdrawals for qualified medical expenses are tax-free at any age. However, if funds are withdrawn for non-medical expenses before the age of 65, a 20% penalty and income tax apply.
Tax Benefits
HSAs offer triple tax benefits: contributions are tax-deductible, earnings grow tax-free, and withdrawals for qualified medical expenses are tax-free. After the age of 65, HSA funds can be withdrawn for any purpose without penalty, making them a valuable retirement income source.
Comparing Roth IRA, Roth 401(k), and HSA
Roth IRAs, Roth 401(k)s, and HSAs each offer unique tax benefits and withdrawal rules. Understanding the differences and choosing the best option for individual circumstances can maximize tax-free retirement income and provide financial security during retirement.

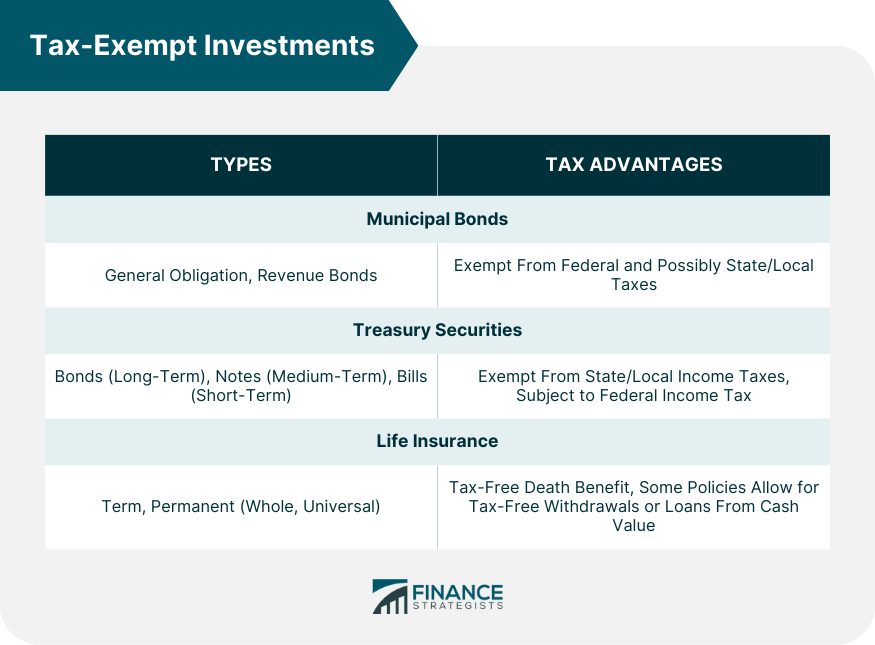
Tax-Exempt Investments
Municipal Bonds
Types of Municipal Bonds
Municipal bonds are debt securities issued by state and local governments to finance public projects.
There are two main types of municipal bonds: general obligation bonds, which are backed by the issuer's full faith and credit, and revenue bonds, which are repaid from the revenue generated by a specific project.
Tax Advantages
Interest income from municipal bonds is generally exempt from federal income tax and may also be exempt from state and local taxes if the investor resides in the issuing state. This tax exemption makes municipal bonds attractive to investors seeking tax-free retirement income.
Risks and Considerations
While municipal bonds are considered relatively low-risk investments, they are not without risk. Factors such as interest rate fluctuations, credit risk, and potential changes to tax laws can impact the bond's value and income generated.
Treasury Bonds, Notes, and Bills
Types of Treasury Securities
Treasury securities are debt instruments issued by the U.S. Department of the Treasury.
They come in three main forms: Treasury bonds (long-term), Treasury notes (medium-term), and Treasury bills (short-term). These securities are backed by the full faith and credit of the U.S. government, making them very low-risk investments.
Tax Advantages
Interest income from Treasury securities is exempt from state and local income taxes, though it is subject to federal income tax. This partial tax exemption can still provide significant tax savings for retirees, especially those in high-tax states.
Risks and Considerations
While Treasury securities are considered very low-risk investments, they are still subject to interest rate risk, which can impact their value. Additionally, inflation risk can erode the purchasing power of the income generated by these securities over time.
Life Insurance
Types of Life Insurance Policies
There are several types of life insurance policies, but the two most common are term life insurance, which provides coverage for a specified term, and permanent life insurance, which provides coverage for the insured's entire life.
Permanent life insurance policies, such as whole life and universal life, often include a cash value component that can grow over time.
Tax-Free Income Benefits
The death benefit from a life insurance policy is generally tax-free for beneficiaries. Additionally, some permanent life insurance policies allow for tax-free withdrawals or loans from the cash value, which can provide tax-free retirement income.
Risks and Considerations
Life insurance policies can be complex and may not be the most suitable option for every individual.
Factors to consider include the cost of premiums, the need for a death benefit, and the potential growth of the cash value. It is essential to carefully evaluate the benefits and risks before using life insurance as a tax-free retirement income source.
Social Security Benefits
Eligibility and Claiming Strategies
Social Security benefits are a critical component of retirement income for many Americans. Eligibility for benefits is based on earning enough work credits, which are typically earned over 10 years of employment.
The age at which benefits are claimed can significantly impact the amount received, with strategies such as delaying benefits to increase monthly payouts.
Taxation of Social Security Benefits
While Social Security benefits can be partially or fully tax-free, depending on an individual's income level, up to 85% of benefits may be subject to federal income tax. State taxation of benefits varies, with some states exempting Social Security income from taxes.
Maximizing Tax-Free Social Security Income
To maximize tax-free Social Security income, retirees should consider strategies such as minimizing taxable income from other sources, timing withdrawals from retirement accounts, and consulting with a tax professional to understand income stream tax implications.
Real Estate and Other Tax-Free Income Sources
Real Estate Investments
Types of Real Estate Investments
Real estate investments can provide tax-free income through strategies such as rental properties, real estate investment trusts (REITs), and tax-deferred real estate exchanges.
These investments offer various benefits and risks, with the potential for tax-free cash flow and long-term appreciation.
Tax Advantages
Real estate investments can offer tax advantages such as depreciation deductions, capital gains tax exclusions, and tax-deferred exchanges.
These tax benefits can help maximize tax-free income during retirement, making real estate a valuable component of a diversified investment portfolio.
Risks and Considerations
Real estate investments carry risks, such as market fluctuations, property management responsibilities, and potential liquidity issues.
It is essential to carefully evaluate each investment opportunity and consider the potential risks and rewards before incorporating real estate into a retirement income strategy.
Reverse Mortgage
Eligibility and Requirements
A reverse mortgage is a financial product that allows homeowners aged 62 and older to convert a portion of their home equity into tax-free income.
Eligibility requirements include owning the home outright or having a low mortgage balance, occupying the home as a primary residence, and meeting financial and property maintenance criteria.
Tax-Free Income Benefits
Reverse mortgage proceeds can be received as a lump sum, monthly payments, or a line of credit, providing tax-free income for retirees.
This income can be used to supplement other retirement income sources, pay off debt, or cover healthcare costs.
Risks and Considerations
While reverse mortgages can provide tax-free income, they also come with risks, such as high upfront costs, potential loss of home equity, and the possibility of foreclosure.
Homeowners should carefully weigh the benefits and risks and consult with a financial professional before pursuing a reverse mortgage.
Strategies for Maximizing Tax-Free Retirement Income

Diversifying Income Sources
To maximize tax-free retirement income, retirees should consider diversifying their income sources by investing in a mix of tax-advantaged accounts, tax-exempt investments, and other tax-free income opportunities.
This diversification can help minimize tax exposure and provide a more stable retirement income stream.
Tax-Efficient Withdrawal Strategies
Employing tax-efficient withdrawal strategies during retirement can help minimize taxes and maximize tax-free income.
These strategies may include withdrawing from tax-deferred accounts first, strategically timing withdrawals from taxable accounts, and managing required minimum distributions.
Roth Conversions and Other Tax Planning Techniques
Roth conversions, which involve transferring funds from a traditional IRA or 401(k) to a Roth IRA, can help retirees minimize future taxes by paying taxes on the conversion amount today.
Other tax planning techniques, such as tax-loss harvesting and charitable giving, can also be used to optimize tax-free retirement income.
Final Thoughts
Maximizing tax-free retirement income is a critical component of financial planning for retirement.
By minimizing the tax burden, retirees can maximize the value of their savings, providing a more comfortable and secure lifestyle during their golden years.
There are various sources of tax-free retirement income, including Roth IRAs, Roth 401(k)s, Health Savings Accounts, municipal bonds, Treasury bonds, certain life insurance policies, and Social Security benefits.
Each source has its own rules and benefits, making it essential to understand the differences to optimize one's retirement income.
Real estate investments and reverse mortgages also provide tax-free income opportunities.
Diversifying income sources, using tax-efficient withdrawal strategies, and employing tax planning techniques such as Roth conversions can further maximize tax-free retirement income.
By taking advantage of these strategies and sources of income, retirees can ensure a more financially stable retirement.
Tax-Free Retirement Income FAQs
Some common sources of tax-free retirement income include Roth IRAs, Roth 401(k)s, Health Savings Accounts (HSAs), municipal bonds, Treasury bonds, life insurance policies, Social Security benefits, and real estate investments. Each source has its own rules and benefits, so it's important to understand the differences to optimize your retirement income.
To maximize tax-free retirement income from tax-advantaged accounts, consider contributing to a Roth IRA or Roth 401(k) during your working years, as these accounts allow for tax-free withdrawals during retirement. Additionally, you can use a Health Savings Account (HSA) for tax-free income to cover medical expenses or supplement your income after age 65.
Municipal bonds and Treasury bonds are popular tax-exempt investments that can generate tax-free retirement income. Interest income from municipal bonds is typically exempt from federal, state, and local taxes, while interest income from Treasury bonds is exempt from state and local taxes.
Real estate investments, such as rental properties and real estate investment trusts (REITs), can provide tax-free retirement income through strategies like depreciation deductions, capital gains tax exclusions, and tax-deferred exchanges. These tax benefits can help maximize tax-free income during retirement and contribute to a diversified investment portfolio.
To maximize your tax-free retirement income, consider diversifying your income sources, employing tax-efficient withdrawal strategies, and utilizing tax planning techniques such as Roth conversions. Additionally, working with a financial planner or professional advisor can help you navigate the complexities of tax-free retirement income and develop a personalized plan to meet your financial goals.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.













