The 1040EZ form was a simplified version of the IRS 1040 form used to file individual federal income tax returns. The "EZ" in 1040EZ stood for "easy" because it was designed to simplify the process of filing a tax return for taxpayers with straightforward financial situations. To qualify for the 1040EZ, taxpayers needed to meet certain conditions, such as taxable income less than $100,000, filing status of single or married filing jointly, no dependents, and interest income of $1,500 or less, among others. However, as of the 2018 tax year, the IRS has discontinued the 1040EZ (as well as the 1040A form) and replaced them with a redesigned 1040 form to simplify the tax filing process for all taxpayers, regardless of their financial situation. The new 1040 form is intended to be used by all individual taxpayers and can be supplemented with additional schedules if needed for more complex tax situations. Before deciding to use the 1040EZ Form, it is essential to understand the eligibility criteria. Not all taxpayers qualify to use this simplified form. The following sections outline the requirements that must be met. Taxpayers can only use the 1040EZ Form with a filing status of "single" or "married filing jointly." Those who are "married filing separately," "head of household," or "qualifying widow(er)" must use a different form. Taxpayers must have a taxable income of less than $100,000 to use the 1040EZ Form. This includes wages, salaries, tips, taxable interest, and unemployment compensation. It is important to note that this form cannot be used to report income from self-employment, dividends, or capital gains. To be eligible for the 1040EZ Form, taxpayers cannot claim any dependents or exemptions. This means that those with children or other qualifying relatives must use a different form. The 1040EZ Form can only be used to report specific types of income. These include wages, salaries, tips, taxable interest, and unemployment compensation. Other types of income, such as self-employment, dividends, or capital gains, are not allowed. Before beginning the process of completing the 1040EZ Form, it is important to gather all necessary information. The following sections outline the personal information and income details required for this form. Taxpayers must provide their name, address, and Social Security Number (SSN). They must also indicate their filing status, either "single" or "married filing jointly." The 1040EZ Form requires reporting of wages, salaries, and tips, as well as taxable interest and unemployment compensation. This information can be found on the W-2 and 1099-INT forms provided by employers and financial institutions. The 1040EZ Form allows taxpayers to claim the Earned Income Credit (EIC), a refundable credit for low- to moderate-income individuals and families. Additionally, federal income tax withheld, as reported on the W-2 form, should be entered on the 1040EZ Form. Filling out the 1040EZ Form requires attention to detail and accuracy. The following sections provide step-by-step instructions for completing the form correctly. Enter your name, address, and SSN in the designated fields. If you are married and filing jointly, provide your spouse's name and SSN as well. Indicate your filing status by checking the appropriate box. Report your wages, salaries, and tips on Line 1 of the form. This information can be found in Box 1 of your W-2 form. On-Line 2, enter any taxable interest income reported on your 1099-INT form. If you received unemployment compensation, report this amount on Line 3. Once you have reported your income, calculate your adjusted gross income (AGI) on Line 4. To do this, simply add the amounts from Lines 1, 2, and 3. You must subtract the standard deduction and personal exemption from your AGI to determine your taxable income. The standard deduction for the 2024 tax year is $14,600 for single filers and $29,200 for married filing jointly. Enter this amount on Line 5 and subtract it from your AGI (Line 4). The result is your taxable income, which should be entered on Line 6. Use the tax table provided in the 1040EZ instructions to calculate your total tax liability. Find the row corresponding to your taxable income (Line 6) and enter the amount in the "tax" column on Line 10. Once you have calculated your total tax liability, it's time to determine if you owe a refund or additional taxes. Enter the total federal income tax withheld (as reported on your W-2) on Line 7. If you are eligible for the Earned Income Credit (EIC), enter the amount on Line 8a. Add Lines 7 and 8a to determine your total payments and credits. Compare this amount to your total tax liability (Line 10). You are entitled to a refund if your total payments and credits exceed your tax liability. Subtract Line 10 from the sum of Lines 7 and 8a and enter the difference on Line 13. You owe additional taxes if your tax liability exceeds your total payments and credits. Subtract the sum of Lines 7 and 8a from Line 10 and enter the difference on Line 12. After completing the 1040EZ Form, you can file electronically or by mail. The following sections outline the electronic filing options and the process for mailing your completed form. There are several options for electronically filing your 1040EZ Form. The IRS offers a free electronic filing service called "Free File" for taxpayers who meet certain income requirements. Additionally, commercial tax software is available for purchase, which can simplify the filing process and provide guidance on tax deductions and tax credits. If you choose to file your 1040EZ Form by mail, be sure to send it to the appropriate mailing address, as listed in the form's instructions. Include any necessary documentation, such as your W-2 form. The deadline to file your tax return is typically April 15th. If you need more time to prepare your return, you can request an extension by filing Form 4868. However, it is important to note that an extension only grants additional time to file your return, not to pay any taxes owed. Any unpaid taxes will be subject to interest and penalties. Avoiding common mistakes on the 1040EZ Form is crucial for accurate and timely tax return processing. Some of the most common errors include: Double-check your name, address, and SSN to ensure they are accurate. Any discrepancies can cause delays in processing your return. Verify that the income reported on Lines 1, 2, and 3 is correct. This includes accurately reporting wages, salaries, tips, taxable interest, and unemployment compensation. Using the correct tax table and double-checking your calculations can help prevent errors in determining your tax liability. Additionally, ensure that you have accurately calculated your taxable income (Line 6) before using the tax table. You must meet the eligibility criteria for the 1040EZ Form to file a different form, such as the 1040 or 1040-SR. Filing the incorrect form can result in processing delays and potential inaccuracies in your tax return. You may need to amend your tax return if you discover errors or omissions on your filed 1040EZ Form. The following sections outline the reasons for amending, the process for doing so, and the associated deadlines. There are several reasons you may need to amend your tax return, including: Reporting additional income Correcting errors in deductions or credits Changing your filing status Adding or removing dependents You must file Form 1040X, Amended U.S. Individual Income Tax Return, to amend your tax return. This form is used to correct previously filed Forms 1040, 1040-SR, 1040A, 1040EZ, or 1040NR. When completing Form 1040X, you will need to provide an explanation of the changes being made and attach any relevant documentation. Form 1040X can be filed electronically or by mail. The deadline for amending your tax return is typically within three years of filing your original return or within two years of the date you paid the tax, whichever is later. Filing your taxes can be daunting, but resources are available to help simplify the process and ensure accuracy. Some of these resources include: The IRS provides a variety of publications and online resources to assist taxpayers with completing and filing their tax returns. These include the 1040EZ instructions, tax tables, and helpful articles on common tax topics. The VITA program offers free tax help to low- to moderate-income individuals, persons with disabilities, and limited English-speaking taxpayers. IRS-certified volunteers provide assistance with tax return preparation and electronic filing. If you need additional assistance with your tax return or have questions about your specific tax situation, consider consulting with a tax professional or advisor. These experts can provide personalized guidance and help ensure your tax return is accurate and compliant with IRS regulations. Tax laws are constantly evolving, and taxpayers must stay informed about any changes that may affect their tax returns. Some potential sources of information include: The IRS regularly publishes news releases and tax tips on its website. These updates cover a wide range of tax-related topics, including changes to tax laws, filing deadlines, and new tax initiatives. Organizations like the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA) and the National Association of Enrolled Agents (NAEA) often provide updates and analyses on tax law changes. These organizations can be valuable resources for taxpayers seeking expert insights into how changes may affect their tax situation. Financial news sources such as CNBC, Bloomberg, and The Wall Street Journal frequently report on tax law changes and their potential impact on taxpayers. Staying informed through these sources can help taxpayers prepare for any changes affecting their tax returns. Consulting with a tax professional or advisor can help taxpayers stay up-to-date on the latest tax law changes. These experts know current tax laws and can provide personalized guidance on how changes may impact an individual's tax situation. The 1040EZ Form was a simplified version of the IRS 1040 form used for individual federal income tax returns. However, as of the 2018 tax year, the IRS discontinued the 1040EZ Form and replaced it with a redesigned 1040 form. To use the 1040EZ Form, taxpayers needed to meet specific eligibility criteria, including filing status limitations, income limitations, and restrictions on dependents and types of income. Understanding the required information and steps for completing the form accurately is crucial to avoid common mistakes. Taxpayers have the option to file electronically or by mail, and resources such as IRS publications, volunteer assistance programs, and tax professionals are available to provide guidance. Staying updated on tax law changes is also important to ensure compliance with current regulations.What Is the 1040EZ Form?
Eligibility Criteria for Using the 1040EZ Form
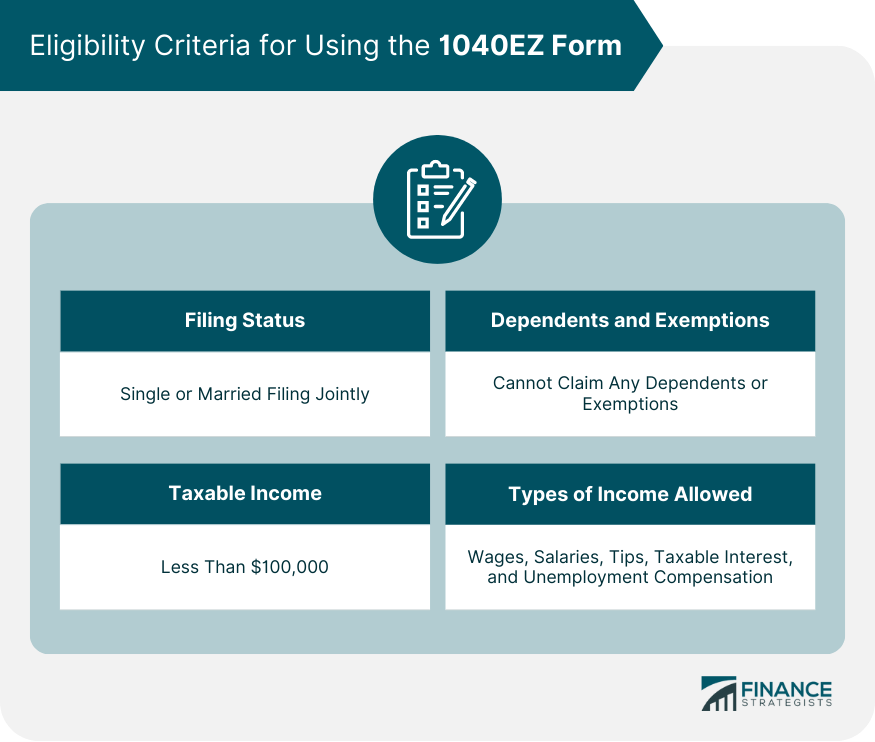
Filing Status Requirements
Income Limitations
Dependents and Exemptions
Types of Income Allowed
Required Information for Completing the 1040EZ Form
Personal Information
Income Details
Tax Credits and Adjustments
How to Fill Out the 1040EZ Form
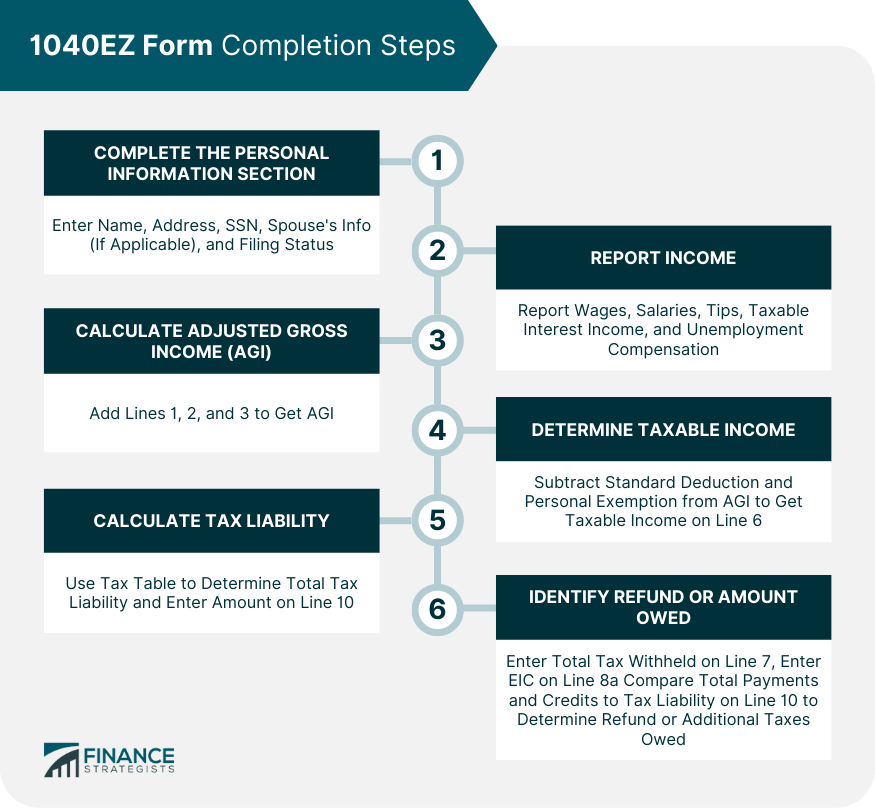
Completing the Personal Information Section
Reporting Income
Calculating Adjusted Gross Income (AGI)
Determining Taxable Income
Calculating Total Tax Liability
Identifying Refund or Amount Owed
Filing the 1040EZ Form
Electronic Filing Options
Paper Filing
Deadlines and Extensions
Common Mistakes on the 1040EZ Form
Incorrect Personal Information
Misreporting Income
Miscalculating Tax Liability
Filing the Wrong Form
Amending a 1040EZ Form
Reasons for Amending
Using Form 1040X
Filing Process and Deadlines
Resources for Assistance With the 1040EZ Form
IRS Publications and Online Resources
Volunteer Income Tax Assistance (VITA) Program
Tax Professionals and Advisors
Staying Updated on Tax Law Changes
IRS News Releases and Tax Tips
Professional Tax Organizations
Financial News Sources
Tax Professionals and Advisors
Conclusion
1040EZ Form FAQs
The 1040EZ Form is a simplified tax form used for filing individual federal income taxes. It can be used by taxpayers with a simple tax situation and meet certain eligibility criteria, such as having no dependents and taxable income below a certain threshold.
You will need to provide your personal information, such as your name, address, and Social Security Number, as well as details about your income and tax credits. Ensure you have your W-2 forms and other necessary documents before you start.
Yes, you can file your 1040EZ Form electronically using the IRS Free File or commercial tax software. Electronic filing is faster, more accurate, and allows you to receive your refund faster.
Some common mistakes include entering incorrect personal information, misreporting income, miscalculating tax liability, and filing the wrong form. Double-check your work and use the correct tax tables to avoid these errors.
Yes, you can amend your 1040EZ Form using Form 1040X if you made a mistake or need to make changes after filing. However, some specific rules and deadlines must be followed when amending a tax return.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.















