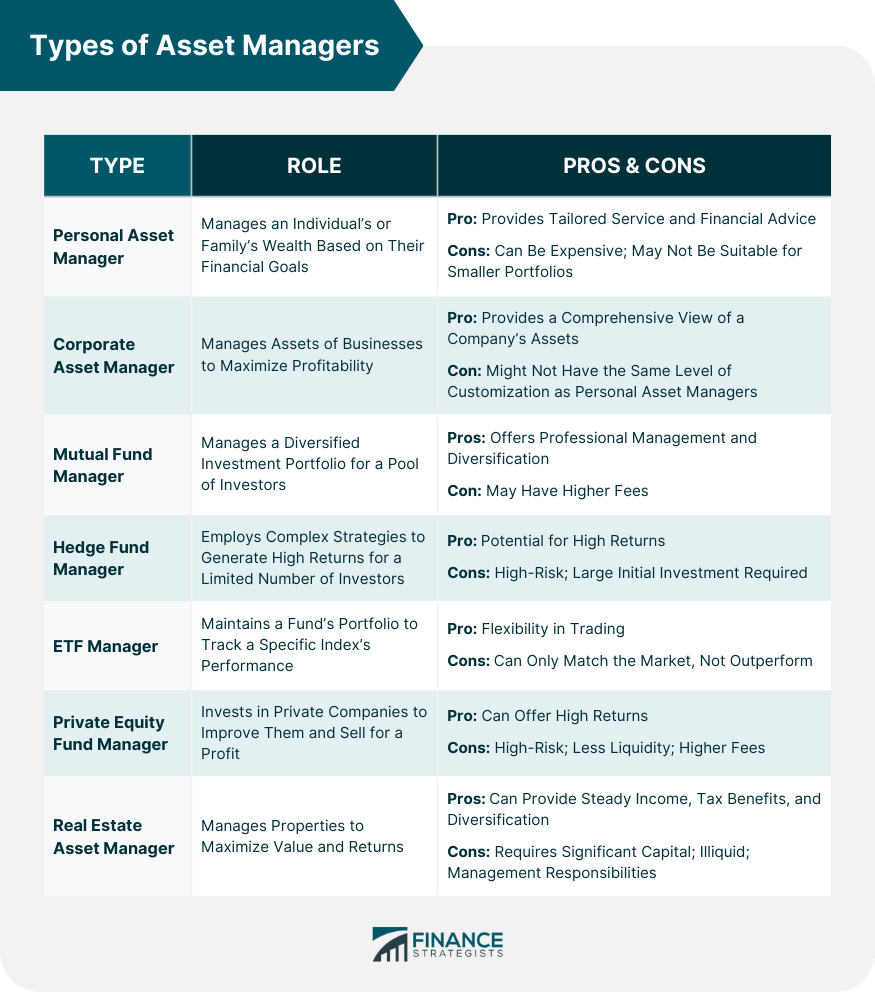
Asset managers play a crucial role in the financial sector, tasked with managing, investing, and overseeing funds for both individuals and corporations. Their responsibilities include allocating capital to diverse asset classes like stocks, bonds, or real estate based on the client's risk tolerance and investment goals. Asset managers use their expertise to identify suitable investment opportunities, monitor market trends, and formulate investment strategies that maximize returns while minimizing risk. They maintain regular communication with clients to discuss investment performance and adjust strategies as per changes in market conditions or client needs. Asset managers also ensure regulatory compliance and adherence to ethical standards. By providing these services, asset managers help individuals and corporations navigate complex financial markets, grow their wealth, and achieve their financial goals. Their role contributes significantly to the overall stability and efficiency of financial markets. These are asset managers who focus on managing the investments of individuals or families. They work closely with their clients, understanding their financial goals, risk tolerance, and time horizons to create a tailored investment strategy. Personal asset managers assess a client's financial needs, goals, risk tolerance, and investment timeline. Based on this assessment, they devise a customized investment strategy, selecting suitable financial products such as stocks, bonds, and mutual funds. The main benefit of personal asset managers is the customized service and financial advice tailored to your unique circumstances. However, the cost of this service can be high, and may not be suitable for those with smaller investment portfolios. Unlike personal asset managers, corporate asset managers work with businesses and corporations. They manage assets like cash, investments, property, and other corporate holdings. Their goal is to ensure these assets contribute to the corporation's overall growth and profitability. Corporate asset managers handle a wide range of assets, including cash, property, equipment, and investments. They optimize the use of these assets to improve operational efficiency, minimize risks, and increase returns. The advantage of corporate asset managers is their ability to provide a comprehensive view of a company's assets and how best to utilize them. However, they might not have the same level of personal touch or customization as personal asset managers. Mutual fund managers, hedge fund managers, and ETF managers have distinct roles and responsibilities in the finance world, each offering different investment strategies. These asset managers handle mutual funds, which pool money from numerous investors to invest in a diversified portfolio of stocks, bonds, or other assets. Mutual fund managers decide which securities to buy or sell within the fund's portfolio based on rigorous research and analysis. Hedge fund managers oversee hedge funds, which are typically available to a limited number of accredited or institutional investors. They employ more complex strategies than traditional investment funds, including short selling, leverage, and derivatives, to generate high returns. ETF managers run ETFs, which are investment funds traded on stock exchanges. An ETF holds assets like stocks, bonds, or commodities. ETF managers are responsible for maintaining the fund's portfolio to track a specific index's performance. Mutual fund managers oversee the investment strategy for a mutual fund, which involves diversified investments in various asset classes. Hedge fund managers, on the other hand, employ aggressive strategies to generate high returns, regardless of the overall market situation. ETF managers aim to replicate the performance of a specific index, sector, commodity, or asset class. Mutual funds offer diversification and professional management but may have higher fees. Hedge funds can potentially deliver high returns but are risky and usually require a large initial investment. ETFs offer flexibility, as they can be traded like stocks, but they can only match, not outperform, the market. These asset managers deal with private equity funds, which are pools of capital from investors used to directly invest in private companies or conduct buyouts of public companies. The ultimate goal is to improve the companies and sell them for a profit. Private Equity Fund Managers analyze potential investment opportunities, perform due diligence, acquire equity ownership in private firms, and then work to increase the value of those firms. This process often involves strategic changes, operational improvements, and financial restructuring. Investing in private equity funds can offer significant returns, often outperforming traditional investment vehicles. However, they also come with a high level of risk, and they require a long-term investment commitment. They are also less liquid than publicly traded investments and usually have higher fees. Real estate asset managers specialize in managing properties as investments. They make decisions about property purchases, sales, rentals, and renovations to maximize the property's value and returns. These managers handle property acquisition, maintenance, tenant relations, and property disposal. They aim to increase the property’s value and ensure it provides a steady revenue stream through rent or price appreciation. Real estate investment can provide a steady income, tax benefits, and diversification. However, it requires significant capital, is illiquid, and comes with responsibilities like maintenance and dealing with tenants. These include the type and size of your investment portfolio, your financial goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon. For instance, individual investors may opt for personal asset managers or mutual fund managers, while large corporations may benefit from corporate asset managers. Your financial goals, whether they involve saving for retirement, accumulating wealth, or preserving your wealth for future generations, will also influence your choice of asset manager. Risk tolerance is another key factor. More risk-averse investors may prefer the diversification of mutual funds, while those willing to take on more risk might consider hedge funds or private equity. The type of asset manager one opts for depends heavily on individual or corporate investment goals, risk tolerance, financial capacity, and the nature of the assets involved. With a personal, corporate, mutual fund, hedge fund, ETF, private equity, and real estate asset managers, there's a vast spectrum of specialized professionals geared toward diverse investment needs. Each type brings along its unique benefits and drawbacks, and understanding these can help in making an informed decision. Remember, choosing the right asset manager can significantly influence your financial journey, helping navigate the intricacies of financial markets and effectively driving towards wealth accumulation and financial stability. Be proactive in your pursuit of financial growth. Start exploring your options and consider engaging the expertise of a wealth management service to guide your investment decisions today.Understanding the Roles of Asset Managers
Various Types of Asset Managers
Individual or Personal Asset Managers
Role and Responsibilities
Benefits and Drawbacks
Corporate Asset Managers
Role and Responsibilities
Benefits and Drawbacks
Mutual Fund, Hedge Fund, ETF Managers
Differences in Their Roles and Responsibilities
Benefits and Drawbacks of Each
Private Equity Fund Managers
Role and Responsibilities
Benefits and Drawbacks
Real Estate Asset Managers
Role and Responsibilities
Benefits and Drawbacks
Choosing the Right Type of Asset Manager
Consider Relevant Factors
Understand Financial Goals
Assess Your Risk Tolerance
Bottom Line
Types of Asset Managers FAQs
Personal asset managers create tailored investment strategies based on an individual's financial goals, risk tolerance, and investment timeline.
Corporate asset managers handle a company's assets, optimizing their use to improve operational efficiency, minimize risks, and increase returns.
Mutual fund managers oversee diversified investments, hedge fund managers employ aggressive strategies for high returns, while ETF managers replicate specific index performance.
Private Equity Fund Managers perform due diligence, acquire equity in private firms, and work to enhance those firms' value.
Real Estate Asset Managers manage properties as investments, handling property acquisition, maintenance, tenant relations, and property disposal to maximize value.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











