A Unitized Endowment Pool is an investment strategy used by non-profit organizations and educational institutions to pool multiple endowment funds together, creating a larger and more diversified investment portfolio. The main purpose of a UEP is to improve investment performance, reduce administrative and investment costs, and maintain or increase the purchasing power of the endowment funds over time. This pooling enables greater economies of scale and efficiency in managing the funds. By unitizing the pool, each participating endowment's holdings are represented by units, providing transparency and ease of tracking performance. UEPs involve the combination of several endowment funds, each with its unique investment objectives and restrictions. By pooling these funds, the overall investment portfolio becomes larger and more diversified, benefiting all participating funds. In a UEP, each endowment fund owns a certain number of units, representing their share of the pool. The unit value is calculated by dividing the total market value of the pool by the number of outstanding units. Units are distributed to the participating endowment funds based on their initial investment or additional contributions. As the unit value fluctuates with the performance of the pool, each endowment fund's share of the pool changes accordingly. The investment committee is responsible for overseeing the UEP, setting investment objectives, and determining the overall investment strategy. This committee typically includes representatives from participating organizations and external experts. An investment policy statement (IPS) outlines the investment objectives, risk tolerance, asset allocation, and other guidelines for the UEP. The IPS provides a framework for investment decisions and helps ensure consistent and disciplined management. UEPs aim to achieve diversification across various asset classes, such as equities, fixed income, and alternative investments. This diversification helps reduce risk and enhance returns over the long term. The investment committee establishes the risk tolerance and return objectives for the UEP, considering the specific needs and objectives of the participating endowment funds. These factors guide asset allocation and overall investment strategy. UEPs may utilize a combination of active and passive investment management strategies. Active management involves selecting individual investments with the goal of outperforming a benchmark, while passive management involves tracking a market index. The investment committee conducts thorough due diligence when selecting investment managers, assessing their investment approach, performance, and risk management practices. This helps ensure the UEP is managed by skilled and experienced professionals. The investment committee regularly reviews the UEP's performance and asset allocation, making adjustments as needed to ensure alignment with the investment objectives and risk tolerance. The UEP's performance is benchmarked against relevant market indices and peer groups, providing a measure of success and identifying areas for potential improvement. A percentage-based spending rule involves distributing a fixed percentage of the UEP's market value each year, usually calculated as a trailing average over a specified number of years. This approach provides stability in spending but may not always protect the purchasing power of the endowment funds in the long term. The smoothing rule aims to stabilize annual spending by incorporating both the percentage-based spending and the previous year's spending adjusted for inflation. This approach helps mitigate fluctuations in spending and protects the purchasing power of the endowment funds over time. Some UEPs may adopt a hybrid spending policy that combines elements of both percentage-based and smoothing rules, aiming to achieve a balance between spending stability and the preservation of purchasing power. To maintain the endowment's long-term sustainability, it is essential to protect its purchasing power. This involves ensuring that the spending policy and investment strategy are designed to generate returns that at least match or exceed inflation. Intergenerational equity is the principle that each generation should benefit equally from an endowment. UEPs must balance current spending needs with the objective of preserving or growing the endowment for future generations. Non-profit organizations and educational institutions are generally tax-exempt. However, they may be subject to UBTI if they engage in activities unrelated to their primary purpose. UEPs must be managed to minimize UBTI exposure and maintain tax-exempt status. Many U.S. states have adopted the Uniform Prudent Management of Institutional Funds Act, which provides guidelines for the management and investment of endowment funds. UEPs must comply with UPMIFA requirements, including prudent investment practices and spending rules. The investment committee and other parties responsible for managing the UEP have fiduciary responsibilities to act in the best interests of the participating endowment funds. This involves adhering to best practices, such as conducting thorough due diligence, maintaining proper documentation, and ensuring transparency in decision-making. By pooling resources, UEPs can take advantage of economies of scale, leading to lower investment and administrative costs for the participating endowment funds. UEPs provide access to a broader range of investment opportunities, leading to better diversification and potentially higher returns. UEPs simplify the administration and reporting processes, as all participating endowment funds are managed together under a single investment strategy and policy. Each participating endowment fund may have unique objectives and restrictions, which can be challenging to balance within a UEP. The presence of representatives from different organizations on the investment committee may lead to potential conflicts of interest in decision-making. Maintaining transparency and accountability is essential for building trust among participating endowment funds and other stakeholders. A Unitized Endowment Pool (UEP) is a valuable investment strategy used by non-profit organizations and educational institutions. By pooling multiple endowment funds, UEPs create a larger and more diversified investment portfolio, aiming to improve performance and reduce costs. The structure of UEP involves unit ownership and valuation, with a unit value calculated based on the pool's market value. The management and governance of UEPs are overseen by an investment committee guided by an investment policy statement. Asset allocation, investment manager selection, and periodic rebalancing and monitoring are key strategies employed in UEPs. Distribution policies in UEPs include percentage-based spending, smoothing rules, and hybrid approaches. UEPs also face tax and legal considerations, fiduciary responsibilities, and challenges in balancing unique endowment objectives. While UEPs offer benefits such as economies of scale, enhanced diversification, and simplified administration, challenges include conflicts of interest and ensuring transparency and accountability. Thus, seeking professional services from experienced investment advisors and attorneys can help organizations navigate these challenges and achieve their long-term financial goals. Definition and Purpose of a Unitized Endowment Pool (UEP)
Structure of Unitized Endowment Pool
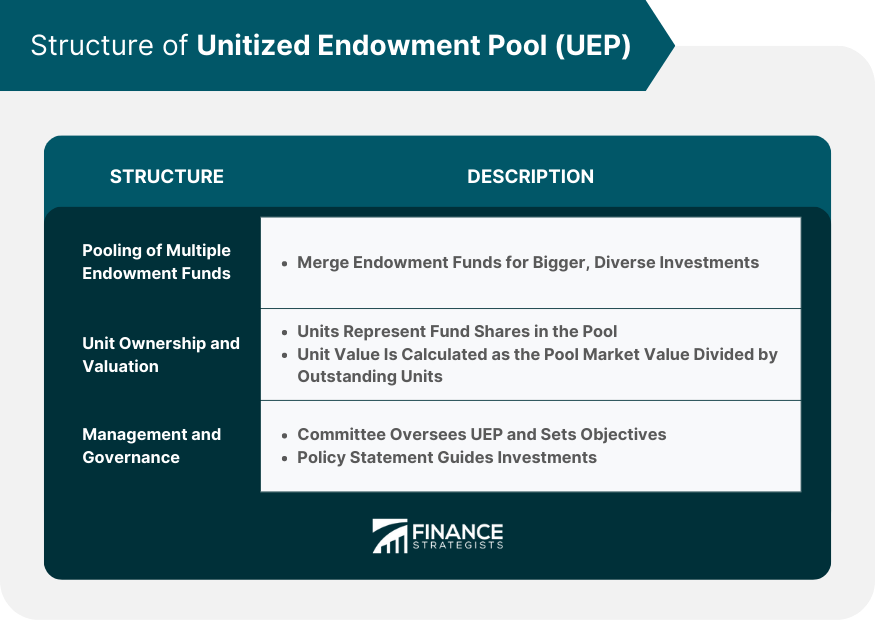
Pooling of Multiple Endowment Funds
Unit Ownership and Valuation
Calculation of Unit Value
Distribution of Units to Investors
Management and Governance
Investment Committee
Investment Policy Statement
Investment Strategies for Unitized Endowment Pool

Asset Allocation
Diversification of Assets
Risk Tolerance and Return Objectives
Investment Manager Selection
Active vs Passive Management
Manager Due Diligence
Rebalancing and Monitoring
Periodic Reviews
Performance Benchmarking
Distribution Policies in Unitized Endowment Pool
Spending Rule
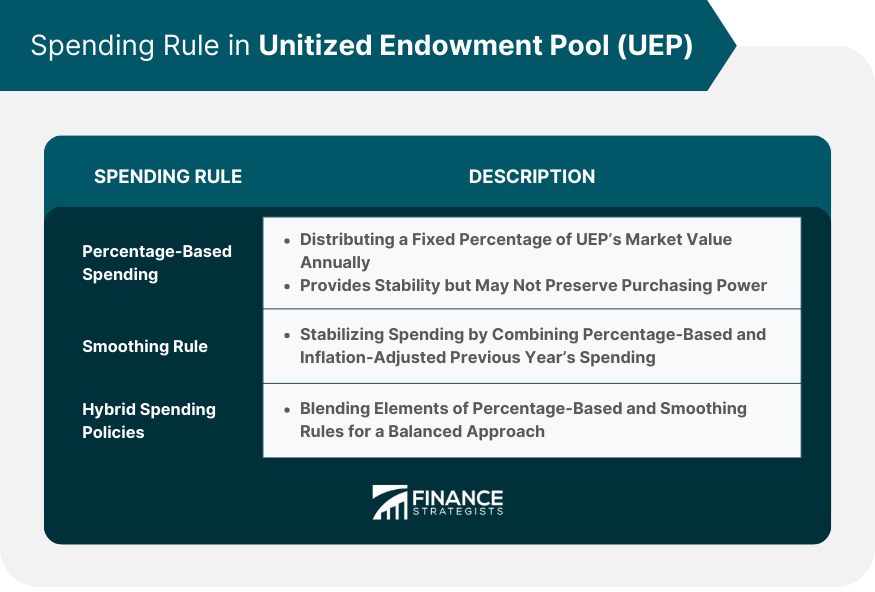
Percentage-Based Spending
Smoothing Rule
Hybrid Spending Policies
Impact on the Endowment's Long-Term Sustainability
Protecting the Purchasing Power
Ensuring Intergenerational Equity
Unitized Endowment Pool Tax and Legal Considerations
Tax-Exempt Status and Unrelated Business Taxable Income (UBTI)
Compliance With the Uniform Prudent Management of Institutional Funds Act (UPMIFA)
Fiduciary Responsibilities and Best Practices
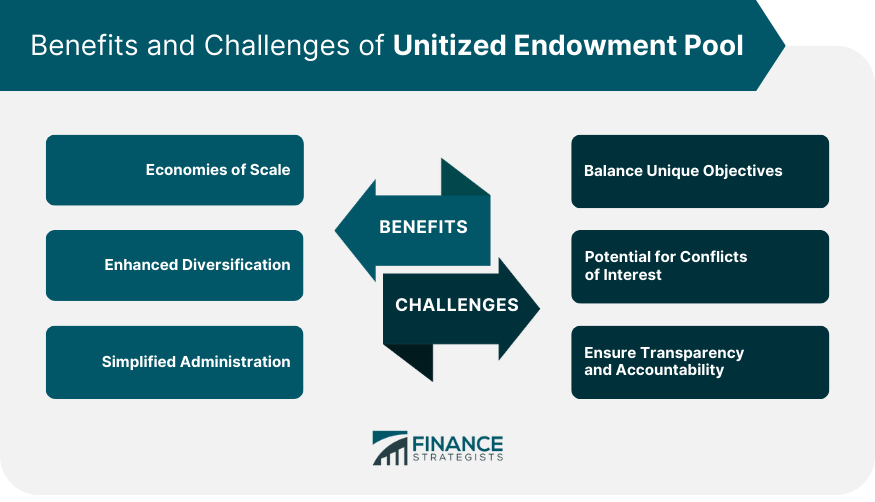
Benefits and Challenges of Unitized Endowment Pool
Benefits
Economies of Scale
Enhanced Diversification
Simplified Administration and Reporting
Challenges
Balancing Unique Endowment Objectives
Potential for Conflicts of Interest
Ensuring Transparency and Accountability
Conclusion
Unitized Endowment Pool (UEP) FAQs
A Unitized Endowment Pool (UEP) is an investment strategy that combines multiple endowment funds to create a larger and more diversified investment portfolio. UEPs benefit non-profit organizations and educational institutions by improving investment performance, reducing administrative and investment costs, and maintaining or increasing the purchasing power of their endowment funds.
In a UEP, each endowment fund owns a certain number of units, representing their share of the pool. The unit value is calculated by dividing the total market value of the pool by the number of outstanding units. Units are distributed to the participating endowment funds based on their initial investment or additional contributions.
The key investment strategies used in a UEP include asset allocation, investment manager selection, and rebalancing and monitoring. Asset allocation involves diversifying investments across various asset classes, while investment manager selection focuses on choosing skilled professionals to manage the pool. Rebalancing and monitoring involve periodic reviews and performance benchmarking to ensure alignment with the investment objectives and risk tolerance.
Spending rules in a UEP, such as percentage-based spending, smoothing rules, or hybrid policies, determine the annual distributions from the pool to support the participating organizations. The chosen spending rule should balance the need for stable funding with the goal of preserving the purchasing power of the endowment funds, ensuring intergenerational equity and long-term sustainability.
The main challenges associated with managing a UEP include balancing the unique objectives and restrictions of each participating endowment fund, addressing potential conflicts of interest among investment committee members, and ensuring transparency and accountability in decision-making and reporting.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.















