Retirement gap analysis assesses the difference between an individual's expected retirement income and the amount they will need to live comfortably in retirement. This analysis helps individuals identify any gaps in their retirement plan and take steps to bridge those gaps before retirement. Factors that are considered in retirement gap analysis include current income, anticipated expenses, investment portfolios, and retirement benefits, among others. By conducting a retirement gap analysis, individuals can gain a clear understanding of their retirement income needs and make informed decisions about savings, investments, and retirement planning. An individual's current income plays a vital role in determining their capacity to save for retirement. Higher incomes often enable greater savings and contributions to retirement accounts. Developing disciplined saving habits and employing effective strategies, such as automatic payroll deductions or budgeting, can significantly impact an individual's ability to accumulate wealth for retirement. Understanding current expenses provides insight into an individual's spending habits, allowing them to make adjustments and better prepare for future financial needs. Estimating future expenses during retirement, including housing, healthcare, and leisure, is essential to accurately assess the retirement gap. Social Security and pension benefits are vital sources of retirement income. Accurate estimates of these benefits can help individuals determine their retirement gap more precisely. Projected investment returns and an individual's risk tolerance can affect the growth of retirement savings and impact the retirement gap. Inflation erodes purchasing power over time, so factoring in its impact on both income and expenses is crucial in calculating the retirement gap. Longer life expectancies and potential healthcare costs must be considered when determining the retirement gap, as they can significantly influence retirement expenses. Working part-time or delaying retirement can help close the retirement gap by supplementing retirement income and allowing more time for savings to grow. Social security benefits serve as a primary source of retirement income for many individuals. The amount received depends on the person's earnings history, age at retirement, and other factors. Pension plans, whether provided by an employer or the government, can offer a steady stream of income during retirement. The benefits typically depend on factors such as years of service, salary, and the specific plan's provisions. Retirement savings accounts like 401(k) plans and Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs) allow individuals to accumulate savings for their post-working years. The amount available during retirement depends on the contributions made, investment performance, and withdrawal strategies. Annuities and certain insurance policies can provide a guaranteed income stream during retirement. These financial products can be tailored to meet specific needs, such as inflation protection or guaranteed lifetime income. Investments in stocks, bonds, mutual funds, and other securities can generate income through dividends, interest, and capital gains. The amount of income generated depends on the size of the investment portfolio and its performance. Owning real estate properties and collecting rental income can serve as a significant source of income during retirement. The income depends on property values, rental rates, and occupancy levels. Some retirees may choose to work part-time or pursue passive income sources like royalties, business ownership, or peer-to-peer lending to supplement their retirement income. Mortgage payments, rent, property taxes, and insurance are some of the housing costs that retirees need to consider. Electricity, water, heating, and other utilities, as well as home maintenance and repairs, are essential expenses during retirement. Food and grocery costs should be considered in retirement expenses, taking into account potential changes in dietary needs and preferences. Transportation costs, including vehicle maintenance, fuel, and public transportation, are necessary expenses to account for in retirement. Medicare premiums are a significant healthcare expense for retirees, and individuals should factor these costs into their retirement planning. Many retirees purchase supplemental insurance policies to cover gaps in Medicare coverage, which should be included in healthcare expense calculations. Retirees should also consider out-of-pocket healthcare costs, such as prescription medications, copayments, and other uncovered services. Travel, vacations, and leisure activities are discretionary expenses that can significantly impact retirement budgets. The cost of hobbies, clubs, and entertainment should also be factored into retirement expenses. Individuals who plan to donate to charitable organizations during retirement should include these expenses in their calculations. Inflation can have a substantial impact on retirement expenses, as the cost of living typically rises over time. Planning for inflation is essential to ensure an accurate estimate of future expenses. To estimate the retirement income gap, compare your projected income from all sources with your projected expenses during retirement. This will help you determine if there is a shortfall or surplus in your retirement funds. When estimating the income gap, it's crucial to adjust for inflation. This ensures that both income and expense projections accurately reflect the future purchasing power of your money. After comparing projected income and expenses, you can identify potential shortfalls or surpluses in your retirement funds. This information will help guide your strategies for closing the income gap. Regularly monitoring your retirement income gap and making necessary adjustments are essential to achieving your financial goals. As your circumstances change, your income and expense projections may need to be updated. One way to close the income gap is by increasing contributions to retirement savings accounts like 401(k)s and IRAs. This will help accumulate more savings to fund your retirement expenses. Delaying retirement or working part-time during retirement can provide additional income, reducing the income gap. This strategy also allows your retirement savings to grow for a more extended period. Reevaluating your investment strategies can help increase retirement income. This may involve adjusting your asset allocation or focusing on investments with higher income potential. Reducing housing costs by downsizing or moving to a more affordable area can help close the income gap. This strategy may also result in lower property taxes, utilities, and other expenses. Tapping into your home equity, taking out a reverse mortgage, or purchasing an annuity can provide additional income during retirement, helping to close the income gap. Cutting back on discretionary expenses, such as travel and leisure activities, can help you save more for retirement and reduce the income gap. Implementing tax planning strategies, such as optimizing withdrawal strategies from retirement accounts, can help minimize your tax burden during retirement and contribute to closing the income gap. Retirement income gap analysis is a crucial step in retirement planning. By assessing factors such as income sources, expenses, inflation, and risk tolerance, individuals can identify potential shortfalls in their retirement savings and implement strategies to close the gap. These strategies include increasing retirement savings contributions, delaying retirement or working part-time, adjusting investment strategies, downsizing, utilizing home equity or annuities, reducing discretionary spending, and implementing tax planning strategies. Ongoing monitoring and adjustments are necessary to ensure that retirement income goals are met. It is essential to estimate the income gap accurately by comparing projected income with projected expenses and adjusting for inflation. By taking these steps, individuals can achieve a secure and comfortable financial future in retirement.What Is Retirement Income Gap Analysis?
Factors Affecting the Retirement Gap
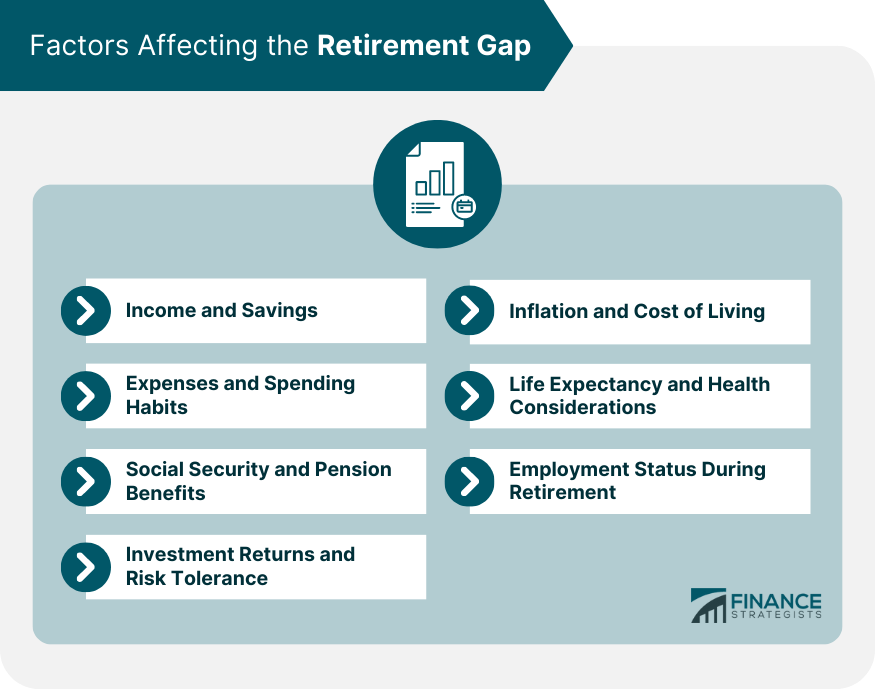
Income and Savings
Expenses and Spending Habits
Social Security and Pension Benefits
Investment Returns and Risk Tolerance
Inflation and Cost of Living
Life Expectancy and Health Considerations
Employment Status During Retirement
Identifying Sources of Retirement Income

Social Security Benefits
Pension Plans
401(k), IRA, and Other Retirement Savings Accounts
Annuities and Insurance Policies
Investment Income
Real Estate and Rental Income
Part-Time Work or Passive Income Sources
Assessing Retirement Expenses
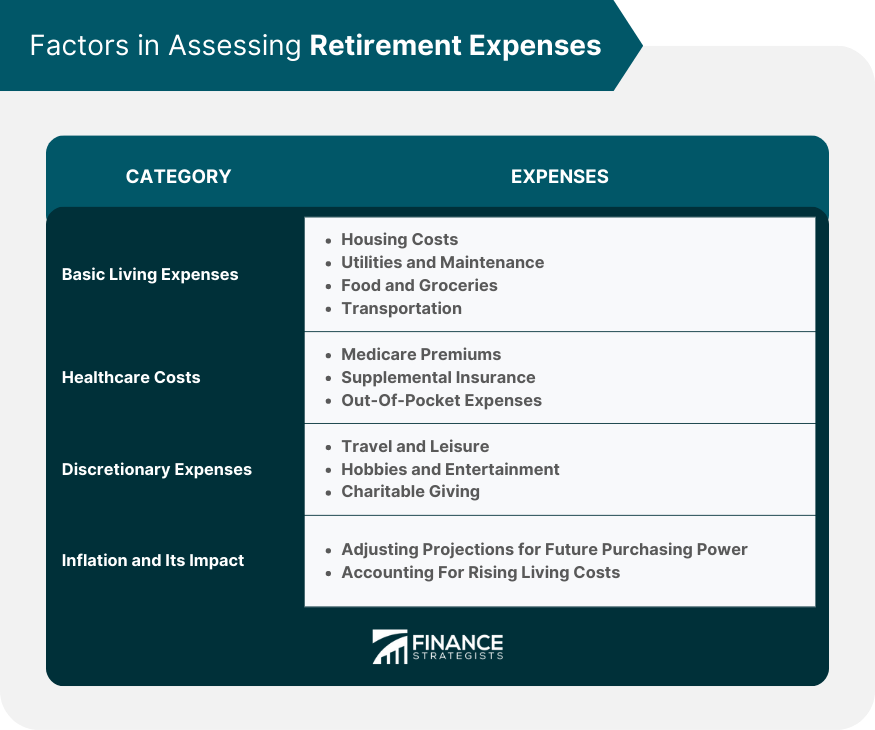
Basic Living Expenses
Housing Costs
Utilities and Maintenance
Food and Groceries
Transportation
Healthcare Costs
Medicare Premiums
Supplemental Insurance
Out-Of-Pocket Expenses
Discretionary Expenses
Travel and Leisure
Hobbies and Entertainment
Charitable Giving
Inflation and Its Impact on Expenses
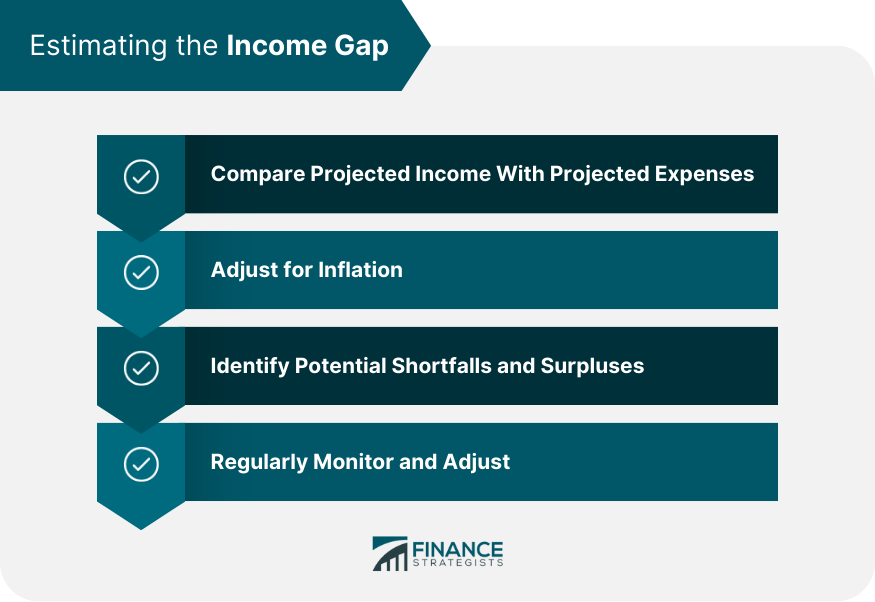
Estimating the Income Gap
Comparing Projected Income With Projected Expenses
Adjusting for Inflation
Identifying Potential Shortfalls and Surpluses
Ongoing Monitoring and Adjustments
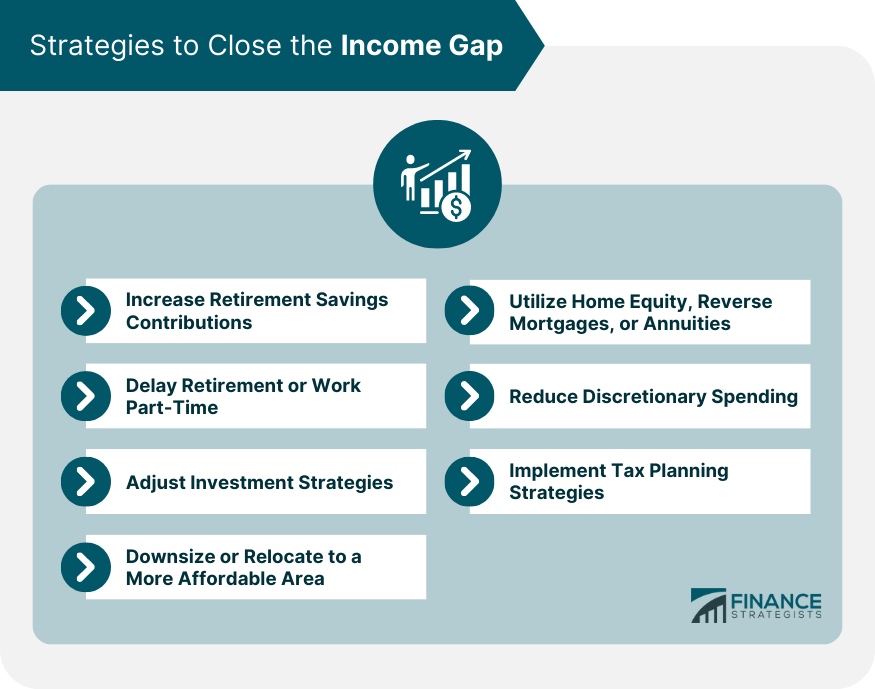
Strategies to Close the Income Gap
Increasing Retirement Savings Contributions
Delaying Retirement or Working Part-Time
Adjusting Investment Strategies
Downsizing or Relocating to a More Affordable Area
Utilizing Home Equity, Reverse Mortgages, or Annuities
Reducing Discretionary Spending
Tax Planning Strategies to Minimize Tax Burden
Bottom Line
Retirement Income Gap Analysis FAQs
Retirement income gap analysis is a process that helps individuals assess the difference between their projected income during retirement and their expected expenses. By conducting a retirement income gap analysis, you can identify potential shortfalls in your retirement funds and develop strategies to ensure a comfortable and financially secure retirement.
Retirement income gap analysis involves evaluating all potential income sources during retirement, including Social Security benefits, pension plans, retirement savings accounts, annuities, investment income, real estate, and part-time work. This comprehensive approach helps you estimate your total retirement income and identify any potential gaps that may need to be addressed.
Yes, a retirement income gap analysis takes into account both basic living expenses and discretionary expenses during retirement. This includes housing costs, utilities, food, transportation, healthcare costs, travel, hobbies, and charitable giving. By estimating these expenses, you can better understand how much income you will need to maintain your desired lifestyle in retirement.
There are several strategies you can employ to close the retirement income gap, such as increasing your retirement savings contributions, delaying retirement, adjusting your investment strategies, downsizing or relocating to a more affordable area, utilizing home equity or annuities, reducing discretionary spending, and implementing tax planning strategies. The best approach will depend on your individual circumstances and financial goals.
A financial advisor can provide expert guidance and personalized advice throughout the retirement income gap analysis process. They can help you evaluate your income sources, estimate your retirement expenses, identify potential shortfalls, and develop strategies to close the income gap. Additionally, a financial advisor can provide ongoing monitoring and adjustments to ensure your financial goals are met throughout your retirement.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.













