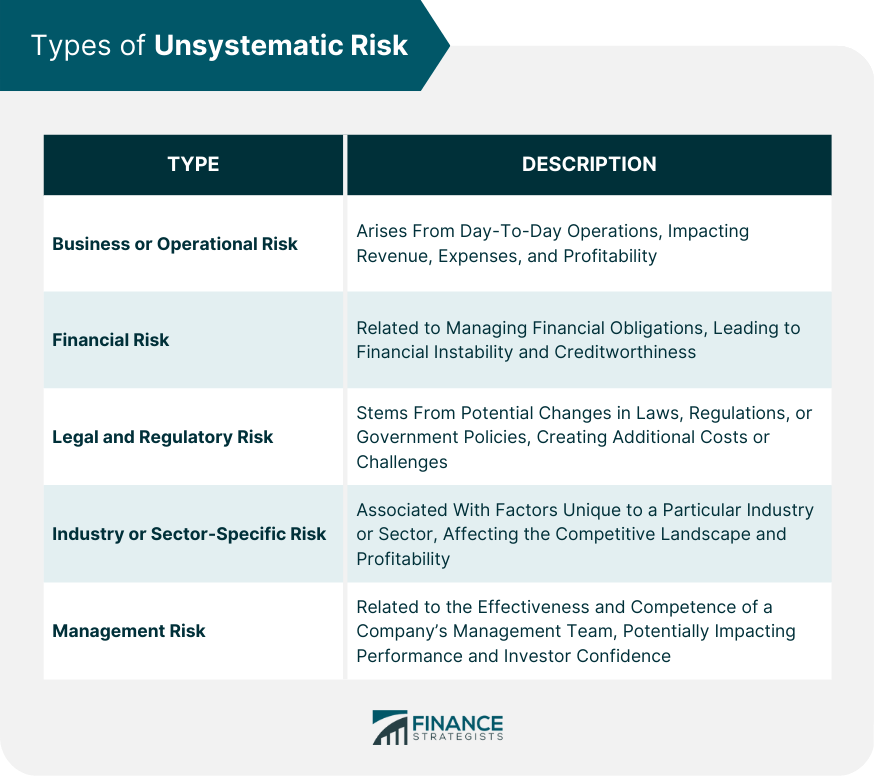
Unsystematic risk, or idiosyncratic or company-specific risk, refers to the uncertainties or risks unique to a particular company or industry. Unlike systematic risk, which affects the entire market or economy, unsystematic risk can be managed or reduced through proper diversification within an investment portfolio. While unsystematic risk is specific to a company or industry, systematic risk is the risk inherent to the entire market or economy. Systematic risk cannot be diversified away and affects all investments in the market, whereas unsystematic risk can be mitigated through diversification. Business or operational risk arises from the day-to-day operations of a company. It can result from factors such as inefficiencies in production, labor disputes, supply chain disruptions, or changes in customer demand. These risks can impact a company's revenue, expenses, and overall profitability. Financial risk is related to a company's ability to manage its financial obligations, such as debt repayment, interest payments, and dividend payouts. High levels of debt, poor cash flow management, or changes in interest rates can lead to financial risk, which may affect a company's financial stability and creditworthiness. Legal and regulatory risk stems from potential changes in laws, regulations, or government policies that could impact a company's operations or profitability. Examples include changes in tax laws, environmental regulations, or antitrust legislation. These risks can create additional costs or operational challenges for a company. Industry or sector-specific risk is associated with factors that are unique to a particular industry or sector. Examples include technological advancements that render a product or service obsolete, regulatory changes that disproportionately affect a specific industry or shifts in consumer preferences. These risks can affect the competitive landscape and profitability of companies within an industry. Management risk is related to the effectiveness and competence of a company's management team. Poor strategic decisions, corporate governance issues, or leadership turnover can create management risk, potentially impacting a company's performance and investor confidence. Quantitative methods for measuring unsystematic risk involve using financial metrics and statistical analysis to assess a company's risk exposure. Examples include calculating financial ratios, analyzing historical stock price volatility, or using regression analysis to isolate company-specific risk factors. Qualitative methods of measuring unsystematic risk involve assessing non-numerical factors that could impact a company's performance. These may include examining a company's competitive position, management quality, or potential exposure to regulatory changes. Qualitative analysis can provide valuable context and insights into a company's risk profile. Total risk is the combination of systematic and unsystematic risk within an investment portfolio. By comparing unsystematic risk to total risk, investors can better understand the proportion of risk within their portfolio that can be diversified away through proper asset allocation and investment selection. Diversification is the process of allocating investments across a variety of asset classes, industries, or geographic regions to reduce unsystematic risk. By diversifying, investors can minimize the impact of the company or industry-specific risks on their overall portfolio performance, as the negative performance of one investment can be offset by the positive performance of others. Conducting thorough due diligence is crucial for managing unsystematic risk. This involves researching and analyzing a company's financial health, management quality, competitive position, and potential legal or regulatory risk exposure. By performing due diligence, investors can make informed investment decisions and avoid companies with high levels of unsystematic risk. Active management involves constantly monitoring and adjusting an investment portfolio to minimize unsystematic risk. This may include regularly reviewing portfolio holdings, reassessing the risk profile of individual investments, and making strategic changes to the portfolio based on changes in the market or a company's circumstances. Risk transfer involves shifting the potential financial consequences of unsystematic risk to another party. Examples include using insurance to protect against business interruptions or purchasing financial derivatives to hedge against currency risk. Risk transfer can be a useful tool for managing unsystematic risk when used in conjunction with other strategies. Considering unsystematic risk when constructing a portfolio is essential to ensure proper diversification and risk management. Asset allocation decisions should be based on an investor's risk tolerance, investment goals, and time horizon, taking into account the potential impact of unsystematic risk on portfolio performance. Unsystematic risk can significantly impact the expected returns of individual investments within a portfolio. By effectively managing unsystematic risk, investors can optimize their portfolio's risk-adjusted returns, achieving a balance between risk and reward that aligns with their investment objectives. Different investor profiles, such as conservative, moderate, or aggressive investors, may have varying tolerances for unsystematic risk. Understanding and managing unsystematic risk is crucial to constructing a portfolio that aligns with an investor's risk tolerance and investment goals, ensuring the appropriate balance between risk and potential return. Value investing focuses on identifying and investing in undervalued companies with strong fundamentals. This investment strategy may expose investors to unsystematic risk, as undervalued companies may face specific challenges or risks that have led to their discounted valuation. Thorough due diligence is essential to manage unsystematic risk in a value investing strategy. Growth investing involves investing in companies with high growth potential, often characterized by rapidly expanding revenues or earnings. Growth companies can be subject to elevated levels of unsystematic risk due to factors such as heightened competition, reliance on new technologies, or regulatory challenges. Diversification and ongoing risk assessment are important to manage unsystematic risk in a growth investing strategy. Income investing focuses on generating regular income through investments in dividend-paying stocks or interest-bearing securities. While income investments may be less susceptible to market fluctuations, they can still be exposed to unsystematic risk related to the individual companies or industries from which they derive income. Diversification and due diligence are crucial to managing unsystematic risk in an income investing strategy. Understanding unsystematic risk is essential for successful investing, as it allows investors to make informed decisions about asset allocation, risk management, and investment strategies. Investors should recognize the importance of managing unsystematic risk through diversification, due diligence, and active portfolio management. Understanding the different types of unsystematic risk and their potential impact on investments is essential for constructing a well-balanced portfolio that aligns with an investor's risk tolerance and investment goals. Effective risk management is an ongoing process that requires regular monitoring, assessment, and adjustment of an investment portfolio. Investors should stay informed about changes in the market or their investments that could impact unsystematic risk and make strategic adjustments as necessary to maintain an optimal risk profile. Professional wealth management services can help investors effectively manage unsystematic risk and optimize their portfolio's risk-adjusted returns. What Is Unsystematic Risk?
Types of Unsystematic Risk
Business or Operational Risk
Financial Risk
Legal and Regulatory Risk
Industry or Sector-Specific Risk
Management Risk
Measuring Unsystematic Risk
Quantitative Methods
Qualitative Methods
Comparing Unsystematic Risk to Total Risk
Managing Unsystematic Risk

Diversification
Due Diligence
Active Management
Risk Transfer
Unsystematic Risk and Portfolio Construction
Role of Unsystematic Risk in Asset Allocation
Impact on Expected Returns
Considerations for Different Investor Profiles
Unsystematic Risk and Investment Strategies
Value Investing
Growth Investing
Income Investing
Final Thoughts
Unsystematic Risk FAQs
Unsystematic risk refers to the uncertainties or risks that are unique to a particular company or industry, as opposed to risks that affect the entire market or economy.
Investors can manage unsystematic risk through diversification, thorough due diligence, active portfolio management, and risk transfer strategies.
The main types of unsystematic risk include business or operational risk, financial risk, legal and regulatory risk, industry or sector-specific risk, and management risk.
Unsystematic risk plays a critical role in portfolio construction, as it influences asset allocation decisions, expected returns, and risk management strategies tailored to an investor's risk tolerance and investment goals.
Understanding unsystematic risk is essential for successful investing because it allows investors to make informed decisions about asset allocation, risk management, and investment strategies, ultimately optimizing their portfolio's risk-adjusted returns.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.













