Investment advice refers to professional guidance provided by financial experts, such as financial planners or investment advisors, on how to invest your money in a way that aligns with your financial goals, risk tolerance, and other personal factors. The goal of investment advice is to help you make informed decisions about investing your money to maximize returns and minimize risks. Good investment advice takes into account various factors, such as your age, income, financial obligations, investment goals, and risk tolerance. An investment advisor will work with you to assess your financial situation, develop a personalized investment plan, and provide ongoing support to help you achieve your financial objectives. Before creating an investment strategy, it is crucial to assess one's risk tolerance. This involves evaluating an individual's willingness and capacity to accept losses in pursuit of potential gains. Risk tolerance varies based on factors such as age, income, financial goals, and personal values. Establishing clear short-term and long-term objectives is critical for creating an effective investment plan. Short-term goals might include funding a vacation or purchasing a car, while long-term objectives could encompass retirement savings or paying for a child's education. Aligning investment goals with personal values ensures that financial decisions are consistent with an individual's overall life vision. Diversification is the practice of spreading investments across various asset classes and industries to minimize risk. By holding a diverse mix of investments, investors can reduce the impact of poor performance in one area and potentially enhance overall returns. Investors can choose from several types of investment assets, including: Stocks: Shares of ownership in a corporation, providing potential for capital gains and dividends. Bonds: Debt securities issued by governments or corporations, offering interest payments and principal repayment at maturity. Mutual funds: Pooled investment vehicles that hold a diversified mix of assets, managed by professional fund managers. Exchange-traded funds (ETFs): Investment funds that track an index or sector, traded on stock exchanges like individual stocks. Real estate: Tangible property investments, such as residential or commercial properties, offering potential for income and appreciation. Alternative investments: Non-traditional assets, including commodities, private equity, and hedge funds. Asset allocation involves dividing investments among different asset classes based on an individual's risk tolerance and objectives. This strategy helps manage risk and optimize returns by ensuring exposure to a variety of investments. Growth investing focuses on companies with above-average growth potential, often in rapidly expanding industries. Investors in growth stocks anticipate higher returns through capital appreciation. Value investing seeks undervalued companies with strong fundamentals, offering the potential for capital appreciation when the market recognizes the company's true value. Income investing aims to generate regular income through dividends or interest payments. This strategy often involves investing in dividend-paying stocks, bonds, or real estate investment trusts (REITs). Passive investing involves tracking a market index or sector through index funds or ETFs. This low-cost approach seeks to replicate market performance with minimal active management. Active investing involves selecting individual securities or funds with the goal of outperforming the market. This approach typically requires more research and monitoring than passive investing. SRI emphasizes investments in companies that adhere to environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria, promoting ethical and sustainable business practices. Various risks can impact investment performance, including: Market risk: The risk of investments losing value due to market fluctuations. Credit risk: The risk of bond issuers defaulting on interest or principal payments. Interest rate risk: The risk of bond prices declining as interest rates rise. Inflation risk: The risk of investments losing purchasing power due to rising prices. Liquidity risk: The risk of being unable to sell an investment quickly and at a fair price. Investors can employ several strategies to manage and mitigate risks, such as diversification, asset allocation, periodic rebalancing, and investing in low-risk assets like treasury bonds or cash equivalents. Taxes can significantly impact investment returns. Different investment types have varying tax implications, such as capital gains tax on stock sales, interest income tax on bonds, and dividend tax on dividend-paying stocks. Tax-efficient investing strategies help minimize tax liabilities, thereby preserving more of the investment returns. These strategies may include investing in tax-advantaged accounts, utilizing tax-loss harvesting, and holding investments for longer periods to qualify for lower long-term capital gains tax rates. Tax-advantaged investment accounts, such as individual retirement accounts (IRAs) and 401(k) plans, offer tax-deferred or tax-free growth, allowing investors to save more for retirement and other long-term financial goals. Regularly monitoring and assessing investment performance is essential for making informed decisions. Investors should establish benchmarks and performance metrics to gauge the success of their investment strategies. Periodic portfolio reviews help investors ensure their asset allocation remains aligned with their risk tolerance and financial objectives. Rebalancing involves adjusting the portfolio by selling overperforming assets and purchasing underperforming ones to maintain the desired asset allocation. Investment strategies may need adjustments as personal circumstances, market conditions, or financial goals change. Staying flexible and adapting to these changes can help ensure long-term financial success. Some investors may benefit from seeking professional investment advice to navigate complex financial situations, ensure compliance with regulations, or optimize their investment strategies. Financial advisors come in several forms, including: Fee-only advisors: Advisors who charge a flat fee or a percentage of assets under management, without earning commissions from product sales. Fee-based advisors: Advisors who charge fees for their advice and may also earn commissions from product sales. Commission-based advisors: Advisors who primarily earn their income through commissions from product sales. Selecting the right financial advisor involves evaluating factors such as credentials, experience, fee structures, and investment philosophy. It is crucial to work with a trustworthy and competent advisor who understands an individual's unique financial needs. The importance of investment advice in guiding individuals towards their financial objectives cannot be overstated. It is crucial for investors to commit to ongoing education and stay up-to-date with relevant information to make well-informed decisions. As personal circumstances, market conditions, or financial goals evolve, adjusting investment strategies accordingly can help ensure enduring financial prosperity. When necessary, seeking professional advice from a trusted and experienced financial advisor can further enhance an investor's ability to navigate the complexities of the financial world and safeguard their future.What Is Investment Advice?
Establishing Investment Goals
Assessing Risk Tolerance
Identifying Short-Term and Long-Term Objectives
Building a Diversified Investment Portfolio
Importance of Diversification
Types of Investment Assets

Asset Allocation Strategies
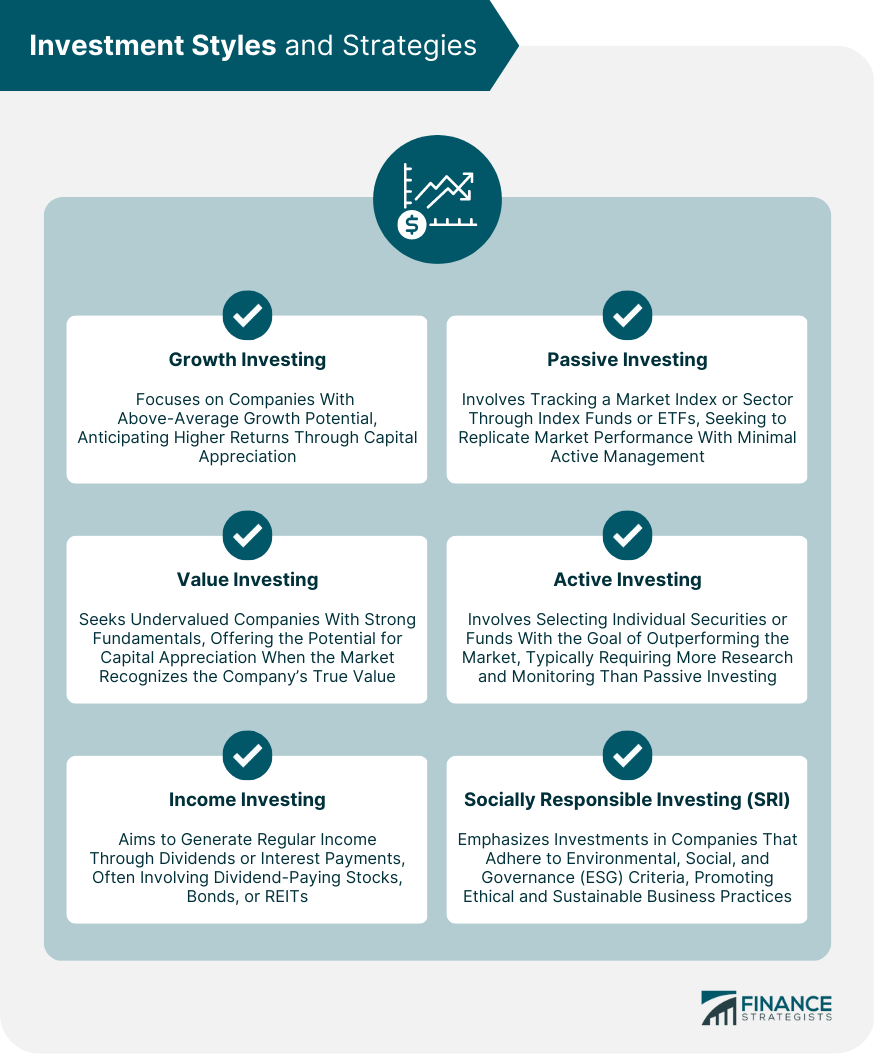
Investment Styles and Strategies
Growth Investing
Value Investing
Income Investing
Passive Investing
Active Investing
Socially Responsible Investing (SRI)
Investment Risk Management
Understanding Different Types of Risks
Strategies to Manage and Mitigate Risks
Tax Implications and Strategies
Understanding Tax Implications of Investments
Tax-Efficient Investing Strategies
Tax-Advantaged Investment Accounts
Monitoring and Reviewing Investment Performance
Establishing Benchmarks and Performance Metrics
Regularly Reviewing and Rebalancing the Portfolio
Adjusting Investment Strategies as Needed

Seeking Professional Investment Advice
Evaluating the Need for Professional Advice
Types of Financial Advisors
Choosing the Right Financial Advisor
Conclusion
Investment Advice FAQs
Investment advice is guidance provided by financial professionals on how to invest your money in a way that helps you achieve your financial goals, such as saving for retirement, funding education, or generating additional income.
Investment advice can help you make informed decisions about how to invest your money, taking into account your risk tolerance, financial goals, and other factors. Good investment advice can help you maximize returns while minimizing risks.
Investment advice can be provided by a variety of financial professionals, including financial planners, investment advisors, and stockbrokers. However, it's important to choose an advisor who is qualified, experienced, and has your best interests at heart.
When choosing an investment advisor, look for someone who is registered with the Securities and Exchange Commission or a state regulatory agency. You should also look for an advisor who has experience working with clients like you and who has a track record of providing solid investment advice.
To get started with investment advice, consider working with a financial planner or investment advisor. They can help you assess your financial situation, develop a plan for investing your money, and monitor your progress over time. You can also do your own research by reading books, articles, and online resources about investing.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.















