Group health insurance is a type of insurance coverage that provides medical benefits to employees and their dependents as part of an employer-sponsored benefit package. It is typically more affordable and offers broader coverage compared to individual health insurance plans due to the larger pool of insured individuals. The main purpose of group health insurance is to protect employees and their families from the financial burden of medical expenses. The benefits of group health insurance include lower premiums, better coverage options, and increased access to healthcare providers, which contribute to overall employee satisfaction and retention. HMOs are managed care plans that require members to choose a primary care physician (PCP) within a limited network of healthcare providers. The PCP is responsible for coordinating all medical care and making referrals to specialists as needed. HMOs generally have lower out-of-pocket costs but offer limited provider choice. PPOs offer more flexibility in provider choice compared to HMOs, allowing members to see any healthcare provider within a preferred network without requiring a referral. PPOs usually have higher out-of-pocket costs but provide greater freedom in accessing medical care, making them a popular choice for employees seeking a balance between cost and flexibility. EPOs combine aspects of both HMOs and PPOs, offering a limited network of healthcare providers without requiring a PCP or referrals for specialist care. Members must stay within the EPO network to receive coverage, resulting in lower costs than PPOs but less flexibility than HMOs. POS plans offer a hybrid approach to healthcare coverage by combining features of HMOs and PPOs. Members choose a PCP within a network but can also access out-of-network providers at a higher cost. This provides a balance between the lower costs of HMOs and the flexibility of PPOs. High-Deductible Health Plans (HDHPs) are characterized by their higher annual deductibles and lower monthly premiums compared to other types of group health insurance plans. These plans are designed to encourage members to make cost-conscious healthcare decisions and are often paired with Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) to help offset out-of-pocket expenses. Group health insurance plans typically cover employees and their eligible dependents, including spouses and children. This comprehensive coverage helps ensure that employees and their families have access to necessary healthcare services, providing financial protection and peace of mind. Employers usually share the cost of group health insurance premiums with their employees, with employers paying a portion of the premium and employees contributing the remainder. This cost-sharing arrangement helps make group health insurance more affordable for employees and can be a valuable incentive for attracting and retaining talent. Both employers and employees benefit from tax advantages associated with group health insurance. Employers can deduct their portion of premium costs as a business expense, while employees' contributions are typically made on a pre-tax basis, lowering their taxable income and reducing their overall tax liability. Group health insurance plans are subject to guaranteed issue and renewability requirements, meaning that insurers cannot deny coverage based on pre-existing conditions or other health factors. Additionally, as long as the employer continues to offer the plan, employees cannot be denied renewal of their coverage, providing stability and continuity in their healthcare coverage. The size of the employee group can impact the cost of group health insurance, with larger groups often benefiting from lower premiums due to the risk being spread across a greater number of individuals. Insurers are more likely to offer competitive rates for larger groups, as the potential for high-cost claims is offset by the increased number of premium-paying members. The age and overall health status of employees within a group can also affect group health insurance costs. Older and less healthy employees are generally associated with higher healthcare expenses, leading to increased premiums for the entire group. Some insurers may offer wellness programs to encourage healthier lifestyles, which can help control costs over time. The geographic location of a company and its employees can impact group health insurance costs, as healthcare expenses vary across regions due to differences in the cost of living and the availability of medical services. Companies located in areas with higher healthcare costs may face higher insurance premiums as a result. The scope of coverage and benefits offered by a group health insurance plan directly affects its cost. Plans with more comprehensive coverage, including lower deductibles and out-of-pocket maximums, and a broader range of covered services, will generally have higher premiums. Employers must balance the desire for extensive coverage with the need to manage costs. The industry and occupation of employees within a group can also influence group health insurance costs. Some industries and occupations are associated with higher risks of illness or injury, leading to increased healthcare expenses and higher insurance premiums. Employers in high-risk industries may need to consider additional strategies for managing healthcare costs, such as implementing workplace safety programs or offering supplemental insurance options. Employers are responsible for selecting a suitable group health insurance plan and negotiating terms with insurance providers. This involves assessing the needs and preferences of the workforce, comparing different plan options, and negotiating rates and coverage levels to ensure a cost-effective solution that meets employee needs. Employers must provide information to employees about the available group health insurance options, including the scope of coverage, costs, and enrollment procedures. This may involve distributing plan materials, hosting informational sessions, and answering employee questions to help them make informed decisions about their health coverage. Employers are responsible for administering the group health insurance plan, including collecting and remitting employee premium contributions, managing enrollment and changes in coverage, and coordinating with the insurance provider on claims and other issues. This requires ongoing communication with both employees and the insurance provider to ensure the smooth operation of the plan. Offering group health insurance requires employers to comply with various federal and state regulations, such as the Affordable Care Act, COBRA, HIPAA, and ERISA. This involves maintaining appropriate records, providing required notices, and ensuring the plan meets all legal requirements and protections for employees. Employees should carefully review the available group health insurance options offered by their employer and compare the coverage, costs, and provider networks to determine the best fit for their needs. This may involve assessing their personal health situation, budget, and preferences for specific healthcare providers or services. When considering group health insurance options, employees should evaluate the costs and coverage of each plan, including premiums, deductibles, copayments, and out-of-pocket maximums. It's essential to understand how these factors will affect their overall healthcare expenses and weigh the trade-offs between lower costs and more comprehensive coverage. Employees should be aware of any network restrictions or limitations on provider choices within their group health insurance plan. Some plans may require the use of in-network providers or impose higher costs for out-of-network care, which could impact access to preferred healthcare providers and services. Employees with high-deductible health plans may have the option to utilize Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) or Flexible Spending Accounts (FSAs) to set aside pre-tax funds for healthcare expenses. These accounts can help employees manage out-of-pocket costs and provide additional tax advantages related to their healthcare spending. The Affordable Care Act (ACA) imposes certain requirements on group health insurance plans, such as covering essential health benefits, providing free preventive services, and prohibiting discrimination based on pre-existing conditions. Employers must ensure that their plans comply with these requirements to protect employees and avoid potential penalties. The Consolidated Omnibus Budget Reconciliation Act (COBRA) requires employers to offer continuation of group health insurance coverage to eligible employees and their dependents who lose coverage due to a qualifying event, such as job loss or a reduction in work hours. Employers must provide timely notification of COBRA rights and facilitate the continuation of coverage for those who elect it. The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) establishes privacy and security standards for protected health information and provides certain rights for individuals regarding their health information. Employers offering group health insurance must ensure that their plans comply with HIPAA requirements, including safeguarding employee health data and providing required notices and disclosures. The Employee Retirement Income Security Act (ERISA) sets minimum standards for private-sector group health insurance plans, including reporting and disclosure requirements, fiduciary responsibilities, and grievance and appeals procedures. Employers must comply with ERISA requirements to ensure their group health insurance plans meet these standards and protect the interests of employees. Group health insurance is a vital component of employee benefits packages, offering affordable healthcare coverage to employees and their dependents. With various plan types, features, and regulatory requirements, employers must carefully consider their responsibilities and options when providing group health insurance. As the healthcare landscape evolves, trends such as telehealth, value-based care, and personalized plans will continue to shape the future of group health insurance. Both employers and employees must stay informed and adapt to these changes to ensure they can continue to provide and access high-quality, cost-effective healthcare coverage.What Is Group Health Insurance?
Types of Group Health Insurance Plans
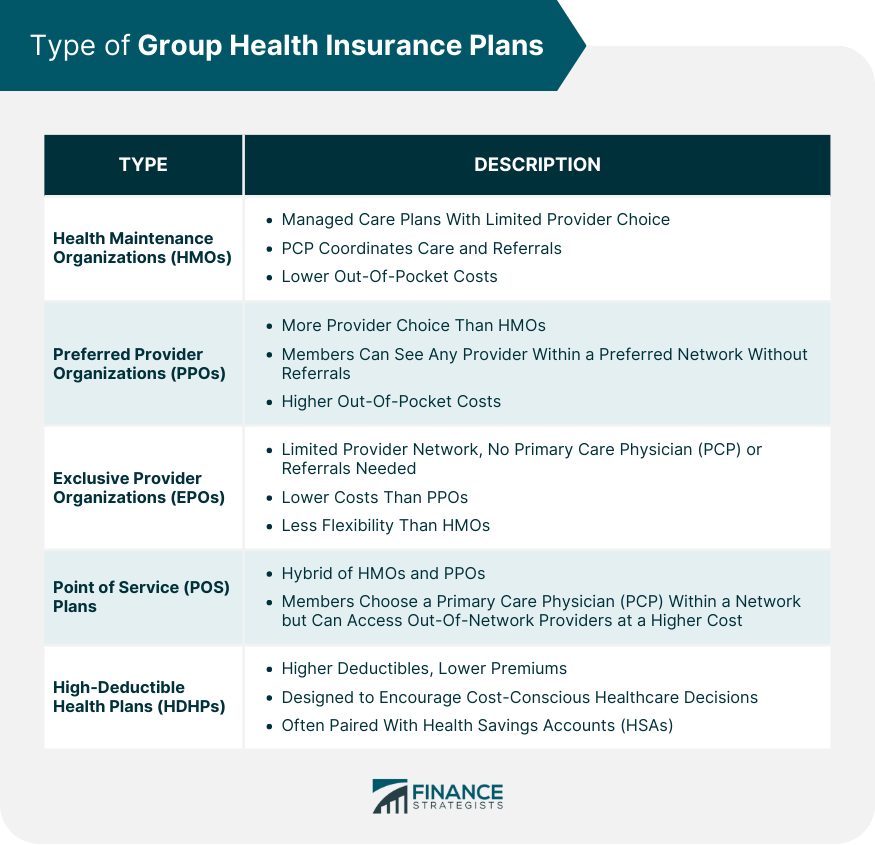
Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs)
Preferred Provider Organizations (PPOs)
Exclusive Provider Organizations (EPOs)
Point of Service (POS) Plans
High-Deductible Health Plans (HDHPs)
Features of Group Health Insurance
Coverage for Employees and Dependents
Premium Sharing Between Employers and Employees
Tax Advantages for Employers and Employees
Guaranteed Issue and Renewability
Factors Affecting Group Health Insurance Costs
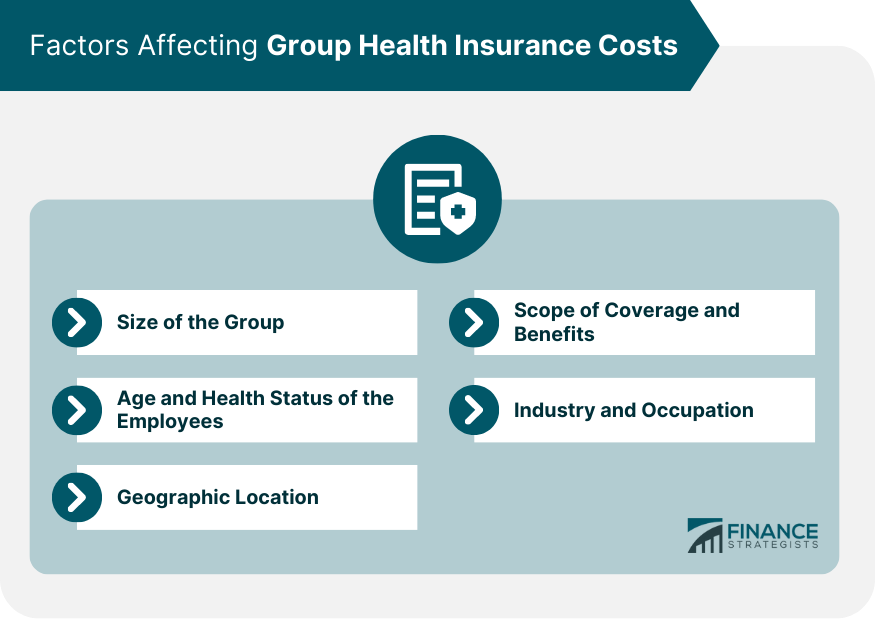
Size of the Group
Age and Health Status of the Employees
Geographic Location
Scope of Coverage and Benefits
Industry and Occupation
Employer Responsibilities in Offering Group Health Insurance

Choosing a Plan and Negotiating With Insurance Providers
Educating Employees About Plan Options and Enrollment
Administering the Plan and Managing Employee Contributions
Compliance With Federal and State Regulations
Employee Considerations for Group Health Insurance
Comparing Available Plan Options
Evaluating Costs and Coverage
Understanding Network Restrictions and Provider Choices
Utilizing Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) and Flexible Spending Accounts (FSAs)
Legal and Regulatory Framework for Group Health Insurance
Affordable Care Act (ACA) Requirements and Protections
Consolidated Omnibus Budget Reconciliation Act (COBRA)
Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA)
Employee Retirement Income Security Act (ERISA)
Final Thoughts
Group Health Insurance FAQs
Group health insurance provides affordable healthcare coverage to employees and their dependents. It offers a range of benefits, including lower premiums, tax advantages, and guaranteed issue and renewability.
Some common types of group health insurance plans include Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs), Preferred Provider Organizations (PPOs), Exclusive Provider Organizations (EPOs), Point of Service (POS) plans, and High-Deductible Health Plans (HDHPs).
Employers must consider factors such as cost, coverage, network restrictions, and employee preferences when choosing a group health insurance plan. They may also negotiate with insurance providers to obtain the best possible terms and rates.
Employees should compare available plan options, evaluate costs and coverage, understand network restrictions and provider choices, and consider the potential benefits of Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) and Flexible Spending Accounts (FSAs) when choosing a group health insurance plan.
Employers must comply with various legal and regulatory requirements, including the Affordable Care Act (ACA), the Consolidated Omnibus Budget Reconciliation Act (COBRA), the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), and the Employee Retirement Income Security Act (ERISA) when offering group health insurance.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











