Silent trusts are legal arrangements in which the beneficiaries of the trust are intentionally kept unaware of the trust's existence or its specific terms. The grantor, who creates the trust, instructs the trustee not to disclose information about the trust to the beneficiaries until a predetermined event or time, such as the beneficiary reaching a certain age or the grantor's death. The primary purpose of a silent trust is to prevent the beneficiaries from becoming aware of their future inheritance, which may help them develop a strong work ethic, avoid complacency, and maintain financial responsibility. Silent trusts can be useful estate planning tools, particularly for grantors who are concerned about the potential impact of wealth on their beneficiaries.
Silent trusts have their roots in English common law, where trusts were often created to protect the interests of wealthy families. Over time, the concept of silent trusts evolved and was adopted in various jurisdictions around the world, including the United States. In the U.S., the legal framework governing silent trusts varies from state to state. Some states explicitly allow silent trusts, while others have restrictions on the duration or conditions under which a silent trust can be maintained. It is essential to consult with an experienced estate planning attorney to ensure that a silent trust is established and administered in compliance with applicable laws and regulations. Silent trusts play a vital role in estate planning, providing utmost importance to privacy. Grantors can keep their assets, beneficiaries, and instructions confidential, shielding sensitive information from public scrutiny. This confidentiality is invaluable in preserving family dynamics, avoiding potential disputes, and protecting beneficiaries from undue attention. Silent trusts offer a discreet and effective solution for individuals seeking to safeguard their wealth while ensuring their loved ones' financial security. By maintaining control and privacy, these trusts empower grantors to shape their legacy and provide for their beneficiaries without compromising their personal affairs. The defining characteristic of a silent trust is the confidentiality maintained between the trustee and the beneficiaries. The trustee is legally bound to keep the trust's existence and terms hidden from the beneficiaries, as instructed by the grantor. This confidentiality can help preserve the beneficiaries' privacy and prevent them from making financial decisions based on their anticipated inheritance. In a silent trust, the trustee plays a crucial role, as they are responsible for managing the trust assets and carrying out the grantor's wishes without disclosing information about the trust to the beneficiaries. The trustee must act in the best interests of the beneficiaries and adhere to the trust agreement's terms, all while maintaining the confidentiality required by the grantor. In a silent trust, the beneficiary assumes a passive role, devoid of decision-making authority. They are unaware of the trust's existence, terms, or assets. Their primary responsibility is to wait patiently until the predetermined conditions are met for them to receive the trust's benefits. The duration of a silent trust can vary, depending on the grantor's wishes and the trust agreement's terms. Typically, a silent trust will remain in effect until a predetermined event or time, such as the beneficiary reaching a certain age or the grantor's death. At that point, the trustee will disclose the trust's existence and terms to the beneficiaries and proceed with the trust's administration and asset distribution. Silent trusts can offer a degree of flexibility, allowing the grantor to tailor the trust's terms to their specific estate planning goals and concerns. For example, the grantor can specify the conditions under which the trust's existence and terms will be disclosed to the beneficiaries, as well as any restrictions on the use or distribution of the trust assets. This flexibility enables the grantor to create a trust that meets their unique needs and objectives while still maintaining the desired level of confidentiality. An irrevocable silent trust is a trust that cannot be changed or revoked by the grantor once it is established. The assets transferred into an irrevocable silent trust are permanently removed from the grantor's control, which can provide potential tax benefits and asset protection. Irrevocable silent trusts maintain the confidentiality of the trust's existence and terms from the beneficiaries, as with any other silent trust. A revocable silent trust is a trust that can be altered or revoked by the grantor during their lifetime. This type of trust allows the grantor to maintain control over the trust assets and make changes to the trust's terms as needed. However, because the grantor retains control over the trust, revocable silent trusts generally do not provide the same level of tax benefits or asset protection as irrevocable silent trusts. The confidentiality of the trust's existence and terms is still maintained from the beneficiaries. A testamentary silent trust is a trust that is created by the grantor's will and becomes effective upon the grantor's death. Like other silent trusts, testamentary silent trusts keep the trust's existence and terms confidential from the beneficiaries. The primary difference between testamentary silent trusts and other types of silent trusts is the timing of their creation, with testamentary silent trusts only coming into effect after the grantor's death. One of the main advantages of silent trusts is the privacy they offer to both the grantor and the beneficiaries. By keeping the trust's existence and terms confidential, silent trusts can help protect the beneficiaries' privacy and prevent third parties from gaining information about the trust's assets or the beneficiaries' potential inheritance. Silent trusts can provide a level of asset protection for the trust's assets, as they are held and managed by the trustee on behalf of the beneficiaries. This separation of ownership can help shield the trust assets from the beneficiaries' creditors or legal judgments, ensuring that the assets are preserved for the beneficiaries' future benefit. Like other types of trusts, silent trusts can help avoid the probate process, which can be time-consuming, costly, and public. By transferring assets to a silent trust, the grantor can ensure that the assets are distributed to the beneficiaries according to the trust agreement's terms, without the need for probate court involvement. Depending on the structure and terms of the silent trust, there may be potential tax benefits for the grantor and the beneficiaries. For example, a properly structured irrevocable silent trust may help reduce the grantor's taxable estate, ultimately resulting in lower estate taxes for the beneficiaries. Additionally, silent trusts can provide tax-deferred growth of the trust assets, allowing the beneficiaries to benefit from compounding interest and potential tax savings. Silent trusts can be a valuable tool in a comprehensive estate plan, allowing the grantor to provide for their beneficiaries' future needs while maintaining privacy and encouraging personal growth. By tailoring the trust's terms to their specific goals and concerns, the grantor can create a customized estate plan that addresses their unique needs and objectives. The confidentiality inherent in silent trusts can lead to a lack of transparency, which may cause misunderstandings or disputes between the beneficiaries and the trustee. Without knowledge of the trust's existence or its terms, the beneficiaries may have difficulty understanding the trustee's actions or decisions and may feel left in the dark about their financial future. The lack of information available to the beneficiaries of a silent trust can make it challenging for them to monitor the trustee's performance and ensure that the trust assets are being managed appropriately. This lack of oversight could potentially lead to mismanagement or abuse of the trust assets by the trustee, with little recourse for the beneficiaries. Because the beneficiaries of a silent trust are unaware of the trust's existence and its terms, they have limited control over the trust assets and their future inheritance. This lack of control may be frustrating for the beneficiaries, who may feel powerless to influence the trustee's decisions or the distribution of the trust assets. Establishing and administering a silent trust can be more costly than other estate planning tools, such as a will or a traditional trust. The costs may include legal fees, trustee fees, and ongoing administrative expenses. While the potential benefits of a silent trust may outweigh these costs for some individuals, it is important to carefully consider the financial implications of establishing a silent trust. The legal framework governing silent trusts varies from state to state, and some states may have restrictions on the duration or conditions under which a silent trust can be maintained. Navigating these legal complexities can be challenging, and it is essential to consult with an experienced estate planning attorney to ensure that a silent trust is established and administered in compliance with applicable laws and regulations. Failure to properly establish or maintain a silent trust could result in unintended consequences, such as the trust being declared invalid or the assets being subject to probate. A silent trust is a type of trust in which the beneficiary has no legal title or rights to the trust assets until specific conditions or events, as outlined in the trust agreement, are fulfilled. Instead, the trustee manages the trust assets without the beneficiary's involvement or knowledge. Silent trusts are a unique and powerful estate planning tool that can provide privacy, asset protection, and other benefits for grantors and their beneficiaries. Understanding the characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages of silent trusts, as well as the various types of silent trusts, can help individuals make informed decisions about whether a silent trust is the right choice for their estate planning needs. However, due to the complexities and legal considerations involved in establishing and administering a silent trust, it is essential to consult with an experienced estate planning attorney. This will ensure that a silent trust is properly established and administered in accordance with the grantor's wishes and applicable laws, ultimately achieving the desired objectives while preserving the confidentiality and other benefits associated with silent trusts.What Are Silent Trusts?
Brief History of Silent Trusts
Importance of Silent Trusts
Characteristics of Silent Trusts
Confidentiality
Trustee's Role
Beneficiary's Role
Duration of the Trust
Flexibility

Types of Silent Trusts
Irrevocable Silent Trusts
Revocable Silent Trusts
Testamentary Silent Trusts
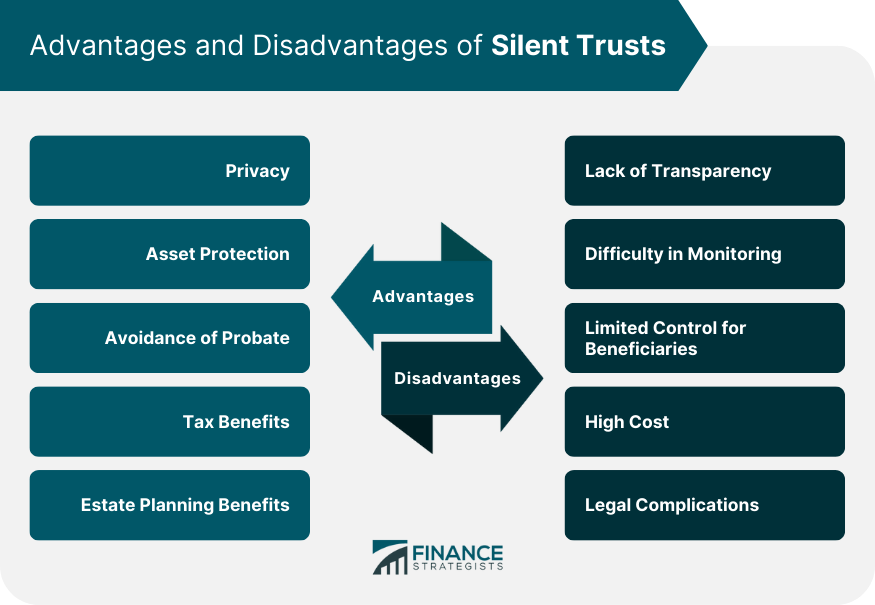
Advantages of Silent Trusts
Privacy
Asset Protection
Avoidance of Probate
Tax Benefits
Estate Planning Benefits
Disadvantages of Silent Trusts
Lack of Transparency
Difficulty in Monitoring
Limited Control for Beneficiaries
High Cost
Legal Complications
Final Thoughts
Silent Trusts FAQs
Silent trusts are trusts where beneficiaries lack knowledge of their existence, terms, or assets until predetermined conditions are met for them to receive the trust's benefits.
Anyone can create a silent trust, but it is typically used by wealthy individuals who desire privacy in their estate planning.
Advantages include privacy, asset protection, avoidance of probate, tax benefits, and estate planning benefits.
Disadvantages include lack of transparency, difficulty in monitoring, limited control for beneficiaries, high cost, and legal complications.
The types of silent trusts include irrevocable, revocable, and testamentary silent trusts.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











