Foreign trusts are legal entities created under the trust laws of a foreign jurisdiction, typically designed for asset protection, estate planning, and tax benefits. They can provide a level of privacy, asset diversification, and legal protection not available through domestic trusts. In estate planning, foreign trusts can help individuals protect their assets and manage their wealth for future generations more effectively. A Grantor Trust is a foreign trust in which the grantor (the person establishing the trust) retains control over trust assets and is responsible for income tax payments on trust income. This type of trust is typically more straightforward and offers tax benefits to the grantor, including potential tax deferral opportunities. In a Non-Grantor Trust, the grantor relinquishes control over the trust assets, and the trust itself becomes responsible for income tax payments. This type of trust offers increased asset protection and greater privacy but may be subject to more complex tax regulations. An Asset Protection Trust is a foreign trust designed specifically to protect the grantor's assets from creditors and potential legal judgments. This type of trust offers increased asset protection compared to domestic trusts, due to the stricter trust laws and regulations in certain foreign jurisdictions. A Charitable Trust is a foreign trust established for charitable purposes. These trusts can offer significant tax benefits to the grantor, as they may qualify for charitable deductions under U.S. tax laws, while also allowing for the distribution of assets to charitable organizations. When establishing a foreign trust, it is essential to consider the trust laws and regulations in the chosen jurisdiction. Some jurisdictions have more favorable trust laws, offering increased asset protection and tax benefits. The political and economic stability of the chosen jurisdiction is another crucial factor to consider when establishing a foreign trust. Stable jurisdictions are more likely to provide long-term security and predictability for trust assets and beneficiaries. Choosing a reliable and competent trustee is essential for the successful management of a foreign trust. The trustee is responsible for administering the trust according to the trust agreement and ensuring compliance with relevant laws and regulations. It is crucial to select a trustee with experience in managing foreign trusts and a strong reputation for integrity and professionalism. The trust agreement is the legal document that outlines the terms and conditions governing the foreign trust. It is essential to work with an experienced attorney specializing in trust and estate law to draft a comprehensive and legally enforceable trust agreement. The trust agreement should clearly define the roles and responsibilities of the trustee, the rights of the beneficiaries, and the specific provisions for asset distribution and management. Foreign trusts can be funded with various types of assets, including cash, securities, real estate, and personal property. It is essential to consider the tax implications and potential risks associated with transferring these assets to a foreign trust. When funding a foreign trust, it is crucial to consider the tax implications and reporting requirements under U.S. tax laws. Failure to comply with these requirements may result in significant penalties and tax liabilities for the grantor. The FATCA imposes reporting requirements on U.S. taxpayers with foreign financial accounts, including foreign trusts. It is essential to ensure compliance with FATCA to avoid penalties and potential tax liabilities. U.S. taxpayers with foreign financial accounts exceeding certain thresholds may also be required to file a Report of FBAR. Proper reporting is crucial to maintain compliance with U.S. tax laws and avoid penalties. When establishing a foreign trust, it is essential to consider the legal and ethical implications of transferring assets to a foreign jurisdiction. It is crucial to work with legal and financial advisors to ensure compliance with applicable laws and regulations and maintain the highest ethical standards. Establishing and maintaining a foreign trust can be costly, with fees for legal, accounting, and trustee services. It is essential to weigh these costs against the potential benefits of a foreign trust to determine whether it is a suitable estate planning strategy. It is crucial to plan for the eventual termination of the foreign trust, either due to the death of the grantor or other circumstances. A well-drafted trust agreement should include provisions for trust termination and the distribution of assets to beneficiaries. A foreign trust can be integrated into a comprehensive domestic estate plan, offering additional asset protection and tax benefits. It is essential to work with an experienced estate planning attorney to ensure the seamless integration of a foreign trust with existing estate planning documents and strategies. Foreign trusts can be used in conjunction with other estate planning tools, such as wills, powers of attorney, and life insurance policies. This can create a more robust and comprehensive estate plan, addressing various financial, legal, and personal considerations. It is essential to designate beneficiaries for the foreign trust, ensuring that assets are distributed according to the grantor's wishes. Beneficiary designations should be periodically reviewed and updated to reflect changes in personal circumstances and relationships. Planning for trustee succession is crucial to ensure the continued management and administration of the foreign trust. A well-drafted trust agreement should include provisions for trustee succession, outlining the process for appointing a new trustee in the event of the current trustee's resignation, incapacity, or death. Foreign trusts can offer potential estate and gift tax savings, as they may be subject to lower tax rates in the foreign jurisdiction. Additionally, they may allow for tax deferral opportunities, enabling grantors to reduce their overall tax burden. Foreign trusts can offer tax deferral opportunities by allowing income and gains to accumulate within the trust without being subject to immediate taxation. This can result in significant long-term tax savings for the grantor and beneficiaries. Foreign trusts can provide a higher level of asset protection than domestic trusts by placing assets outside the reach of creditors and legal judgments. This is particularly valuable for individuals with substantial assets who want to protect their wealth from potential lawsuits or financial risks. Foreign trusts established in jurisdictions with strong asset protection laws can protect trust assets from legal judgments in the grantor's home country. This can offer peace of mind for individuals concerned about potential litigation or other legal challenges. Foreign trusts can offer greater privacy and confidentiality than domestic trusts, as they are often subject to less stringent public disclosure requirements. This can be an attractive feature for individuals who value their financial privacy. Foreign trusts can provide an opportunity to diversify investments internationally, reducing the risk associated with a concentrated domestic investment portfolio. This can result in a more balanced and resilient investment strategy for the grantor and beneficiaries. Foreign trusts offer a range of benefits in asset protection, tax efficiency, and estate planning strategies. They provide a level of privacy, legal protection, and asset diversification that may not be available through domestic trusts. By understanding the different types of foreign trusts, such as grantor trusts, non-grantor trusts, asset protection trusts, and charitable trusts, individuals can choose the structure that best suits their objectives. Establishing a foreign trust involves careful consideration of jurisdiction, trustee selection, drafting a comprehensive trust agreement, and funding the trust with appropriate assets. Compliance with U.S. tax laws, reporting requirements, and legal and ethical considerations is crucial throughout the process. Integrating a foreign trust with a domestic estate plan and utilizing other estate planning tools can enhance asset protection and tax benefits. Foreign trusts offer advantages such as reduced estate and gift taxes, tax deferral opportunities, asset protection from creditors and legal judgments, privacy and confidentiality, and international investment diversification. By leveraging these benefits and considering key considerations, individuals can effectively use foreign trusts to optimize their estate planning strategies.Definition and Purpose of Foreign Trusts
Types of Foreign Trusts
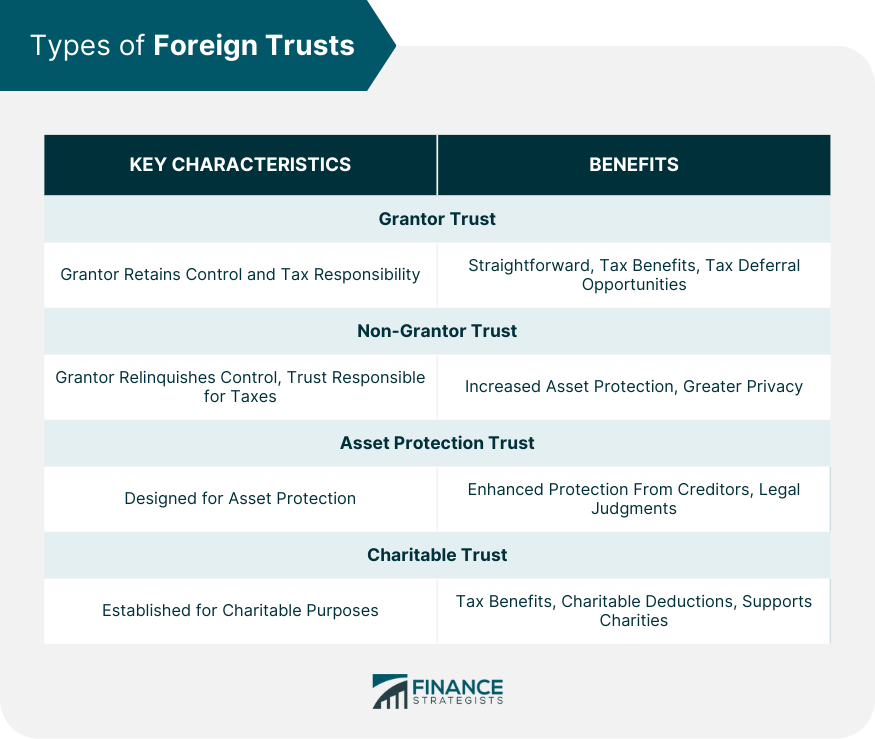
Grantor Trust
Non-Grantor Trust
Asset Protection Trust
Charitable Trust
Establishing a Foreign Trust
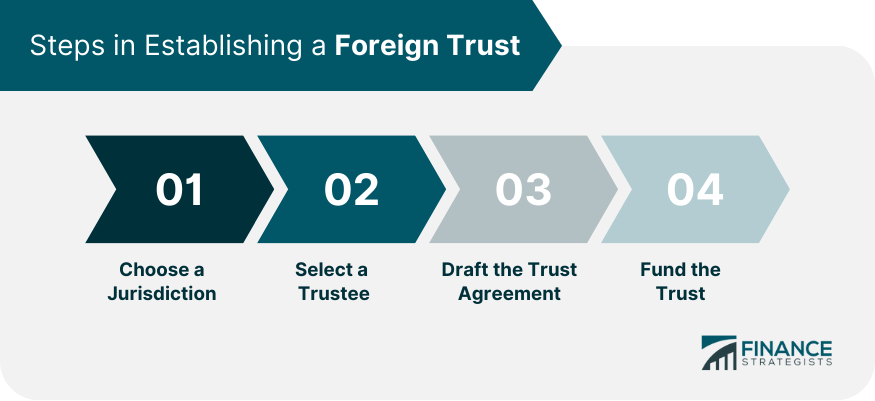
Choosing a Jurisdiction
Trust Laws and Regulations
Political and Economic Stability
Selecting a Trustee
Drafting the Trust Agreement
Funding the Trust
Types of Assets
Tax Implications
Key Considerations for Foreign Trusts
Compliance With U.S. Tax Laws and Reporting Requirements
Foreign Account Tax Compliance Act (FATCA)
Foreign Bank and Financial Accounts (FBAR)
Legal and Ethical Considerations
Potential Costs and Fees
Exit Strategies and Trust Termination

Foreign Trusts and Estate Planning Strategies
Integrating a Foreign Trust with a Domestic Estate Plan
Using Foreign Trusts in Conjunction With Other Estate Planning Tools
Succession Planning
Beneficiary Designations
Trustee Succession
Advantages of Foreign Trusts in Estate Planning
Tax Benefits
Reduced Estate and Gift Taxes
Tax Deferral Opportunities
Asset Protection
Shielding Assets From Creditors
Protection From Legal Judgments
Privacy and Confidentiality
International Investment Diversification

Conclusion
Foreign Trusts FAQs
Foreign trusts can provide several benefits in estate planning, including tax advantages, asset protection, privacy and confidentiality, and international investment diversification. These benefits can help protect and manage wealth more effectively for future generations.
Foreign trusts can offer potential tax benefits in estate planning by allowing for reduced estate and gift taxes and tax deferral opportunities. The foreign jurisdiction may have lower tax rates, and income and gains can accumulate within the trust without being subject to immediate taxation.
When selecting a jurisdiction for a foreign trust, it's essential to consider trust laws and regulations, as well as the political and economic stability of the jurisdiction. Choosing a stable jurisdiction with favorable trust laws can provide long-term security and predictability for the trust assets and beneficiaries.
U.S. taxpayers with foreign trusts must comply with several reporting requirements, including the Foreign Account Tax Compliance Act (FATCA) and the Report of Foreign Bank and Financial Accounts (FBAR). Ensuring compliance with these requirements can help avoid penalties and potential tax liabilities.
Yes, foreign trusts can be integrated with other estate planning tools, such as wills, powers of attorney, and life insurance policies. Working with experienced estate planning professionals can ensure the seamless integration of a foreign trust into a comprehensive estate plan, addressing various financial, legal, and personal considerations.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.















