Trust accounting and reporting are essential aspects of managing and overseeing trust funds and the financial activities associated with them. Trusts are legal arrangements in which a person, called a trustee, holds and manages assets on behalf of beneficiaries, who will eventually receive the assets or income generated by them. Trust accounting and reporting involve the accurate record-keeping, monitoring, and communication of the trust's financial transactions to ensure compliance with applicable laws, rules, and the terms of the trust agreement. Fiduciary responsibility is the ethical and legal obligation of a trustee to act in the best interests of the trust beneficiaries. This includes managing trust assets prudently, avoiding conflicts of interest, and maintaining the highest standards of care and professionalism. Accurate record-keeping is essential in trust accounting to ensure that all financial transactions are documented correctly. This helps maintain transparency, enables effective decision-making, and supports compliance with legal and regulatory requirements. Segregation of trust funds involves keeping trust assets separate from personal or business assets. This practice is vital to prevent the misuse or misappropriation of trust funds and to ensure the proper administration of the trust. Trust accounting must adhere to applicable laws, regulations, and professional standards to ensure proper administration, transparency, and accountability. Compliance protects the interests of trust beneficiaries, maintains professional integrity, and avoids potential legal issues. Opening a trust account involves selecting a financial institution, providing necessary documentation, and establishing appropriate account controls. It is essential to choose an institution with experience in handling trust accounts and to follow any specific requirements of the trust agreement. Trust account transactions include deposits, disbursements, and transfers of funds related to the trust. Deposits into trust accounts typically include income from trust assets, contributions from the trust grantor, or other sources of trust revenue. Proper documentation and record-keeping are necessary to ensure accurate tracking of deposits. Disbursements from trust accounts involve payments for trust expenses, distributions to beneficiaries, or other authorized expenditures. It is crucial to follow the trust agreement's guidelines and maintain accurate records of all disbursements. Transfers between trust accounts or between trust and non-trust accounts must be executed in accordance with the trust agreement and applicable regulations. Proper documentation and authorization are necessary to prevent the potential misuse of trust funds. Trust account reconciliation is the process of comparing trust account records with bank statements to identify discrepancies, errors, or potential fraud. Regular reconciliation is essential to maintain accurate records, ensure compliance, and safeguard trust assets. Periodic trust account statements provide a detailed overview of the trust's financial activities, including deposits, disbursements, and transfers. These statements are typically prepared monthly or quarterly and help maintain transparency, accountability, and compliance. Annual trust account summaries provide a comprehensive view of the trust's financial performance and activities during the year. They offer valuable insights for trustees, beneficiaries, and regulators, and support effective decision-making and planning. Trust account audits and reviews involve an independent examination of trust account records and procedures to ensure accuracy, compliance, and proper administration. Audits and reviews help identify potential issues, improve trust management, and maintain professional integrity. Trust accounting software offers various features to simplify and streamline the trust accounting and reporting process. These features may include automated transaction tracking, reconciliation tools, customizable reporting, and compliance management functions, which help ensure accuracy, efficiency, and compliance in trust management. Using trust reporting software can provide numerous benefits, such as improved accuracy, efficiency, and compliance. It helps automate complex processes, reduce manual errors, and save time. Additionally, it supports better decision-making and facilitates effective communication between trustees and beneficiaries. Popular trust accounting and reporting software solutions include Clio, TrustBooks, and QuickBooks. These software options cater to different needs and preferences, providing user-friendly interfaces, robust features, and customizable reporting capabilities to help trustees and other professionals manage trust accounts efficiently and effectively. Maintaining confidentiality and privacy in trust accounting and reporting is crucial to protect sensitive information related to trust beneficiaries, assets, and transactions. This involves implementing appropriate security measures, limiting access to authorized individuals, and adhering to data protection regulations. Trustees and trust account managers must avoid conflicts of interest that could compromise their fiduciary duties. This involves disclosing any potential conflicts, abstaining from self-dealing, and acting in the best interests of the trust beneficiaries at all times. Transparency and accountability are essential ethical considerations in trust accounting and reporting. They involve maintaining accurate records, providing timely and accurate reports to beneficiaries, and being responsive to inquiries or concerns from beneficiaries and other stakeholders. Mismanagement of trust funds can result from poor oversight, inadequate controls, or a lack of understanding of fiduciary duties. This can lead to the misuse or misappropriation of trust assets, undermining the trust's purpose and potentially causing legal issues. Inaccurate or incomplete records can impede effective trust management and create compliance risks. Proper record-keeping is essential for maintaining transparency, accountability, and legal compliance in trust accounting and reporting. Failure to comply with laws and regulations can result in fines, penalties, or legal actions against trustees and trust account managers. Compliance with legal and regulatory requirements is critical to safeguarding trust assets, protecting beneficiary interests, and maintaining professional integrity. Regular monitoring and review of trust accounts help ensure accuracy, compliance, and effective management. Trustees should schedule periodic reviews of account records, reconciliation processes, and reporting procedures to identify and address any issues or discrepancies. Implementing internal controls in trust accounting and reporting processes can help prevent fraud, errors, and mismanagement. These controls may include segregation of duties, authorization protocols, and reconciliation processes to ensure the integrity and security of trust accounts. Providing training and support for staff involved in trust accounting and reporting is essential for maintaining accurate records, ensuring compliance, and fostering a culture of professionalism and integrity. Ongoing training can help staff stay informed about regulatory changes and best practices in trust management. Trust accounting and reporting are crucial components of managing and overseeing trust funds and their associated financial activities. The principles of trust accounting include fiduciary responsibility, accurate record-keeping, segregation of trust funds, and compliance with legal and regulatory requirements. Trust reporting requirements involve periodic trust account statements, annual trust account summaries, and trust account audits and reviews. Trust accounting and reporting software can simplify and streamline the process, and there are ethical considerations to take into account, such as confidentiality and avoiding conflicts of interest. Common challenges in trust accounting and reporting include mismanagement of trust funds, inaccurate or incomplete records, and non-compliance with laws and regulations. Best practices for trust accounting and reporting involve regular monitoring and review, implementing internal controls, and providing training and support for staff. Following these best practices and principles can help ensure proper trust administration, transparency, accountability, and compliance, ultimately safeguarding the interests of trust beneficiaries and maintaining the trust's purpose. Individuals involved in trust management should consider seeking the assistance of an experienced estate planning lawyer to help navigate the complexities of trust accounting and reporting.What Is Trust Accounting and Reporting?
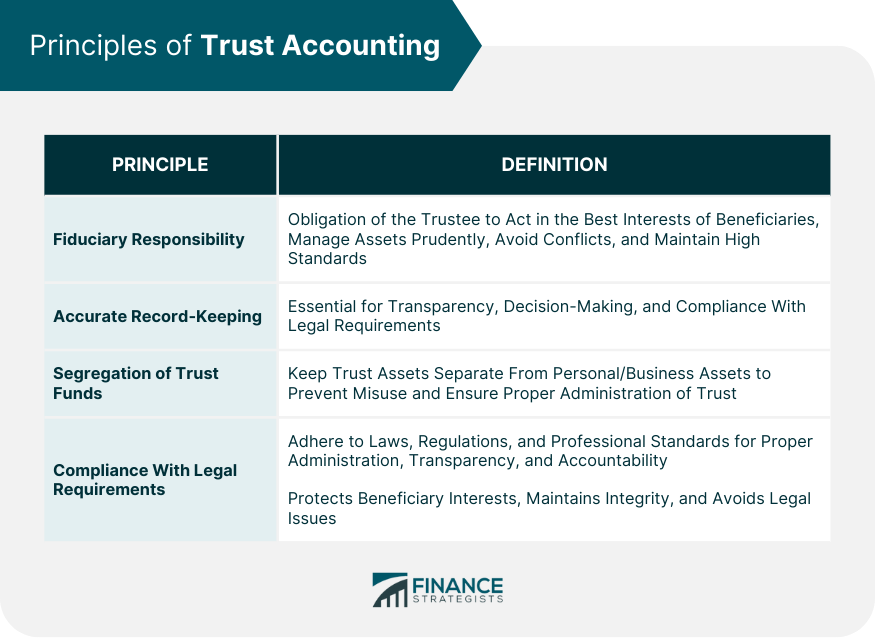
Principles of Trust Accounting
Fiduciary Responsibility
Accurate Record-Keeping
Segregation of Trust Funds
Compliance with Legal and Regulatory Requirements
Trust Accounting Process
Opening a Trust Account
Trust Account Transactions
Deposits
Disbursements
Transfers
Trust Account Reconciliation
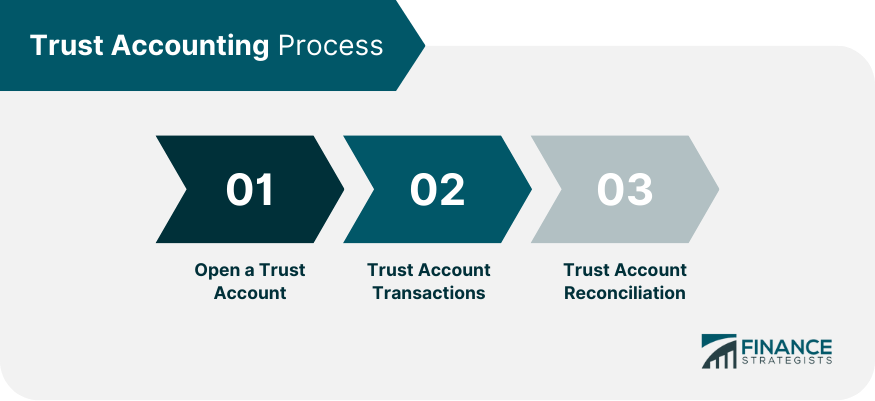
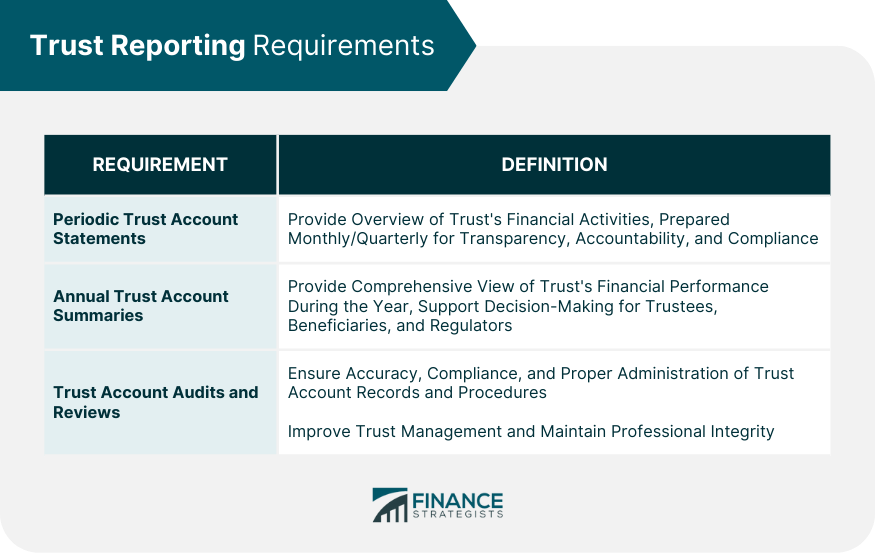
Trust Reporting Requirements
Periodic Trust Account Statements
Annual Trust Account Summaries
Trust Account Audits and Reviews
Trust Reporting Tools and Software
Features of Trust Accounting Software
Benefits of Using Trust Reporting Software
Popular Trust Accounting and Reporting Software
Ethical Considerations in Trust Accounting and Reporting

Confidentiality and Privacy
Avoiding Conflicts of Interest
Ensuring Transparency and Accountability
Common Trust Accounting and Reporting Challenges

Mismanagement of Trust Funds
Inaccurate or Incomplete Records
Non-compliance With Laws and Regulations
Best Practices in Trust Accounting and Reporting
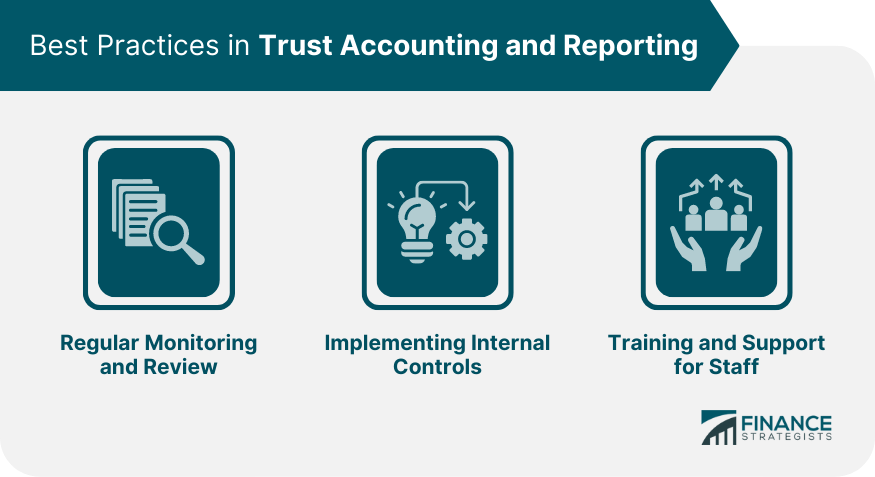
Regular Monitoring and Review
Implementing Internal Controls
Training and Support for Staff
Final Thoughts
Trust Accounting and Reporting FAQs
Trust accounting and reporting involve the management, record-keeping, and reporting of financial transactions related to trust funds, assets, or properties. It is essential for maintaining transparency, accountability, and compliance with legal and regulatory requirements while safeguarding the interests of beneficiaries.
The key principles of trust accounting and reporting include fiduciary responsibility, accurate record-keeping, segregation of trust funds, and compliance with legal and regulatory requirements. These principles ensure the proper administration of trusts and protect the interests of beneficiaries.
Trust reporting tools and software can streamline and automate the trust accounting and reporting process, improving accuracy, efficiency, and compliance. They offer features such as automated transaction tracking, reconciliation tools, customizable reporting, and compliance management functions, which simplify trust management for trustees and other professionals.
Common challenges in trust accounting and reporting include mismanagement of trust funds, inaccurate or incomplete records, and non-compliance with laws and regulations. These challenges can be addressed through regular monitoring and review, implementing internal controls, providing training and support for staff, and seeking the guidance of an experienced estate planning lawyer.
Best practices for ensuring transparency and accountability in trust accounting and reporting include maintaining accurate records, providing timely and accurate reports to beneficiaries, being responsive to inquiries or concerns, implementing internal controls, and adhering to ethical considerations such as confidentiality, avoiding conflicts of interest, and maintaining professional integrity.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.















