A listed security is a financial instrument, such as a stock, bond, or option, that is traded on a specific exchange. These securities meet the exchange's requirements and pay listing fees, allowing them to be bought and sold on that platform. This listing provides a venue for trading and offers investors transparency, increased liquidity, and regulatory oversight. Listed securities play a crucial role in the global financial landscape. They serve as a key component of the capital market, helping companies raise funds for growth and expansion. Investors, on the other hand, can participate in the financial performance of these companies, potentially earning returns on their investments. In essence, the trading of listed securities forms the bedrock of modern capitalism and economic growth. Listed securities are traded on organized exchanges, while unlisted securities are traded over-the-counter (OTC) or through private transactions. Listed securities offer higher liquidity due to the large trading volumes on exchanges, while unlisted securities typically have lower liquidity. Listed securities are subject to stringent regulatory requirements, providing investors with more protection. In contrast, unlisted securities have less regulatory oversight, leading to higher risks. Unlisted securities may offer the potential for higher returns but come with increased risk due to lower liquidity and less regulatory oversight. To list a security, a company must first meet the specific requirements of the exchange, such as minimum amounts of publicly held shares, market capitalization, and pre-tax income. Once the requirements are met, the company pays a listing fee and submits an application for review by the exchange. Upon approval, the company's securities are admitted to the exchange, allowing them to be traded by the public. Common shares represent ownership in a company and come with voting rights, allowing shareholders to have a say in corporate decisions. Shareholders may also receive dividends, which are a portion of the company's profits distributed to its owners. Preferred shares, similar to common shares, represent ownership in a company. However, they have a higher claim on the company's assets and earnings. This means preferred shareholders receive dividends before common shareholders. These shares typically don't come with voting rights. A bond is a debt instrument issued by corporations or governments to raise capital. Bondholders are essentially lending money to the issuer in exchange for regular interest payments and the return of the principal amount at maturity. An Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) is a type of listed security that tracks an index, sector, commodity, or basket of assets. ETFs offer diversification as they hold various securities, and they can be bought or sold on an exchange just like a single stock. Options and futures are derivatives, meaning their value is derived from an underlying asset. They provide investors with the right or obligation to buy or sell the underlying asset at a predetermined price within a specific timeframe. One of the key benefits of listed securities is liquidity, which refers to the ease with which securities can be bought or sold without significantly impacting their price. The presence of a large number of buyers and sellers on exchanges ensures that transactions can be executed swiftly. Listed securities are subject to regulatory oversight from various bodies, ensuring fairness and transparency in transactions. Companies with listed securities are required to disclose pertinent information, such as financial statements and significant corporate events, ensuring investors can make informed decisions. Listing securities on an exchange enables companies to raise capital from a broad pool of investors. This capital can be used for various purposes, such as expanding operations, funding research and development, or reducing debt. For individual investors, listed securities provide an opportunity to invest in a wide array of companies and sectors. They can diversify their portfolios, manage risk, and potentially earn returns through capital gains and dividends. While listed securities offer many advantages, they are not immune to market volatility. Economic events, corporate news, and changes in investor sentiment can trigger drastic price swings. Investors must be prepared to manage the inherent risk associated with these price fluctuations. For companies, listing securities involves significant costs. Apart from the listing fees, there are costs associated with maintaining regulatory compliance, including audit fees, legal fees, and the cost of preparing and distributing periodic financial disclosures. Despite the potential for returns, investing in listed securities carries the risk of financial loss. The value of an investment can decrease due to a variety of factors, including poor company performance, economic downturns, or market volatility. Listed securities serve as vital conduits for capital flow in the global economy. They allow companies to raise capital for expansion, fueling economic growth. They also provide a measure of economic health, with robust securities markets often indicating a thriving economy. The performance of listed securities can influence various economic indicators. For instance, a rising stock market can boost consumer and business confidence, potentially leading to increased spending and investment. During global economic crises, the value of listed securities can plummet, reflecting economic uncertainty. However, they can also serve as a barometer for recovery, as rising security prices often signal improving economic conditions. The SEC oversees securities exchanges, securities brokers and dealers, investment advisors, and mutual funds in the U.S. It aims to protect investors, maintain fair, orderly, and efficient markets, and facilitate capital formation. The FCA is responsible for regulating financial firms providing services to consumers and maintaining the integrity of the UK’s financial markets. It focuses on the regulation of conduct by both retail and wholesale financial services firms. Other major regulatory bodies include the European Securities and Markets Authority (ESMA) in the European Union, the Securities and Futures Commission (SFC) in Hong Kong, and the Australian Securities and Investments Commission (ASIC) in Australia. Each of these bodies oversees the operation of securities markets and protects investors in their respective jurisdictions. A listed security is a financial instrument that is approved for trading on a specific exchange. They come in various types, such as common shares, preferred shares, bonds, ETFs, options, and futures. These securities serve as the cornerstone of the global economy, facilitating the transfer of capital from investors to companies. The benefits of investing in listed securities are numerous. They offer liquidity, which means they can be easily bought or sold. They also come with a high degree of transparency and regulatory oversight, which can provide investors with a certain level of protection. However, investing in listed securities is not without risk. Market volatility can lead to fluctuations in the value of these securities, and there's always a risk of financial loss. For companies, the cost of regulatory compliance can be high. Understanding the dynamics of listed securities is critical to making informed decisions as an investor. Therefore, seeking the services of a professional wealth management advisor could be beneficial. What Is Listed Security?
Difference Between Listed and Unlisted Securities
Trading Platform
Liquidity
Regulatory Protection
Potential Returns and Risks

Process of Listing a Security
Meeting Exchange Requirements
Paying Listing Fees and Submitting Application
Approval and Admission to the Exchange

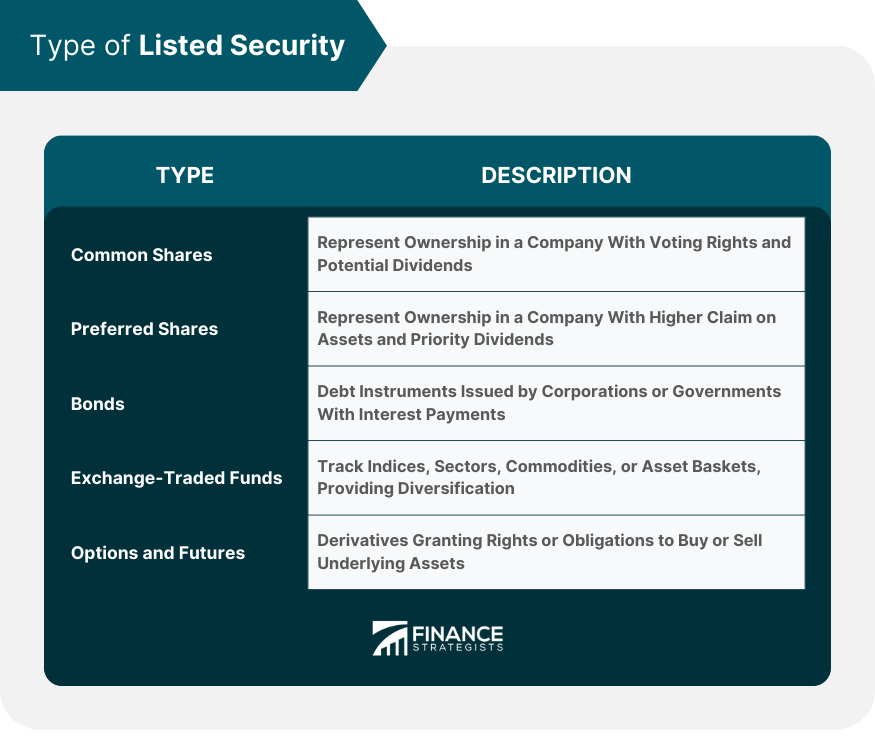
Types of Listed Security
Common Shares
Preferred Shares
Bonds
Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs)
Options and Futures
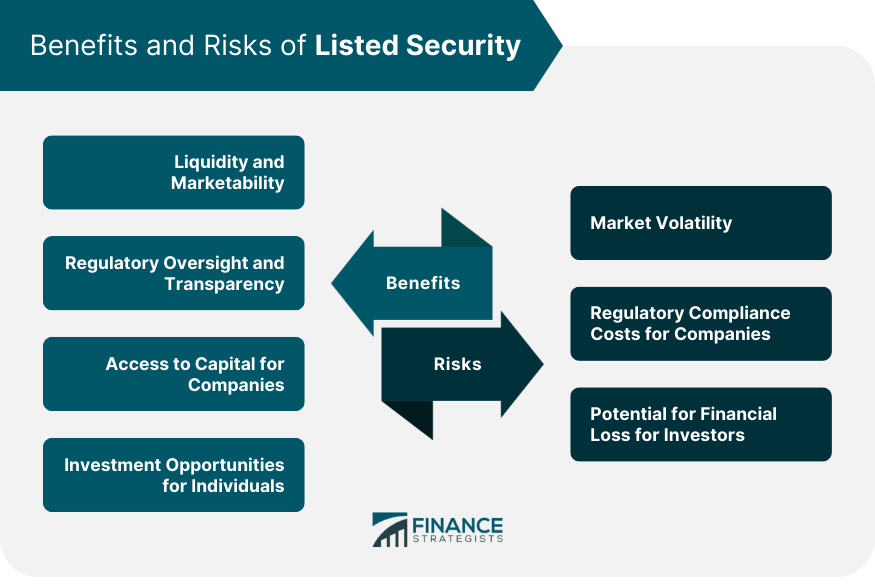
Benefits of Listed Security
Liquidity and Marketability
Regulatory Oversight and Transparency
Access to Capital for Companies
Investment Opportunities for Individuals
Limitations and Risks of Listed Security
Market Volatility
Regulatory Compliance Costs for Companies
Potential for Financial Loss for Investors
Listed Security and the Global Economy
Regulatory Bodies Overseeing Listed Security
Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) in the United States
Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) in the United Kingdom
Other Significant Global Regulatory Bodies
Final Thoughts
Listed Security FAQs
A listed security is a financial instrument, such as a stock, bond, or option, that is approved for trading on a specific exchange.
A company must meet specific requirements, pay listing fees, and submit an application for review to list a security.
Listed securities offer benefits like liquidity, regulatory oversight, transparency, and a wide array of investment opportunities.
The risks include market volatility, which can lead to financial loss, and the costs associated with regulatory compliance for companies.
Listed securities allow companies to raise capital, fueling economic growth. They also serve as indicators of economic health and can influence other economic factors.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.















