Economic outlook refers to the expected future state of an economy, encompassing factors such as growth rates, employment levels, and inflation rates. It serves as a projection of the overall health and performance of an economy over a specified period. A clear understanding of the economic outlook is vital for businesses, governments, and individuals, as it helps guide decision-making processes, risk management, and strategic planning. Accurate economic forecasts enable organizations and individuals to make well-informed decisions regarding investments, hiring, and financial planning. International trade plays a crucial role in shaping the economic outlook, as it affects the supply and demand of goods and services across borders. Changes in trade policies, tariffs, and trade agreements can significantly impact global trade and, consequently, a country's economic prospects. Currency exchange rates influence the cost of imports and exports, affecting trade balances and competitiveness. Fluctuations in exchange rates can have wide-ranging effects on the economic outlook by influencing inflation, interest rates, and consumer spending. Geopolitical events, such as conflicts, political changes, and natural disasters, can create uncertainty and impact global economic stability. These events can disrupt trade, affect investor confidence, and alter the economic outlook for affected regions and the global economy. Fiscal and monetary policies, implemented by governments and central banks, are essential tools for managing economic growth, inflation, and employment. These policies can influence the economic outlook through tax rates, government spending, interest rates, and the money supply. Consumer spending drives economic growth by fueling demand for goods and services. Changes in consumer confidence, income levels, and access to credit can impact spending patterns and shape the overall economic outlook. Business investment in infrastructure, equipment, and research and development is a critical driver of economic growth and productivity. Economic outlook influences investment decisions, as businesses consider factors such as market demand, access to capital, and the competitive landscape. Labor market conditions, including employment levels, wage growth, and workforce participation, directly affect the economic outlook. A strong labor market can boost consumer spending and drive economic growth, while high unemployment rates can lead to decreased demand and slower growth. Inflation and interest rates play a significant role in determining the economic outlook. Central banks often target specific inflation rates to maintain price stability and economic growth. Interest rates can influence consumer spending, business investment, and overall economic activity. Stock market performance is often considered a leading indicator of the economic outlook, as it reflects investor expectations for future growth and profitability. Strong stock market performance can signal investor confidence in the economy, while declines may suggest concerns about future economic conditions. Business confidence indices measure the optimism or pessimism of business leaders regarding future economic conditions. High levels of business confidence can lead to increased investment and hiring, while low levels may indicate concerns about future growth and a potential economic downturn. Consumer sentiment indices gauge the overall confidence of consumers in the economy. These indices can provide insights into future consumer spending patterns, which are critical for economic growth. Positive consumer sentiment can signal strong economic prospects, while negative sentiment may suggest a potential slowdown. GDP growth is a key measure of a country's economic performance and a lagging indicator of the economic outlook. It represents the total value of goods and services produced within a specific period and can help assess the overall health of an economy. Consistent GDP growth typically signals a strong economic outlook, while stagnating or declining GDP may indicate economic weakness or recession. The unemployment rate is a lagging indicator of the economic outlook, reflecting the percentage of the labor force without employment. High unemployment rates can suggest economic weakness or recession, while low unemployment rates often indicate a strong labor market and a healthy economy. The inflation rate measures the rate at which the general price level of goods and services is rising over time. As a lagging indicator, the inflation rate can help assess the overall health of an economy and the effectiveness of monetary policies. High inflation rates may signal economic instability, while low or moderate inflation rates often suggest a stable economic outlook. Short-term economic outlook forecasts typically focus on quarterly and annual projections, offering insights into economic growth, inflation, and employment trends. These forecasts can help businesses, governments, and individuals make informed decisions about budgeting, investments, and other financial planning matters. Short-term economic forecasts also address potential risks and opportunities that can impact the economy, such as policy changes, geopolitical events, or natural disasters. Identifying these factors can help stakeholders prepare for and mitigate potential negative effects on their financial well-being. Demographic trends, such as population growth, aging, and migration patterns, play a significant role in shaping the long-term economic outlook. These trends can impact labor markets, consumer spending, and government policies, all of which can influence economic growth and stability. Technological advancements can drive economic growth by increasing productivity, improving living standards, and creating new industries. Understanding the potential long-term impacts of emerging technologies is essential for anticipating economic trends and identifying potential growth opportunities. Environmental and sustainability concerns, such as climate change and resource depletion, can have far-reaching implications for the long-term economic outlook. Addressing these challenges is crucial for ensuring sustainable economic growth and preserving the well-being of future generations. The economic outlook influences financial markets by affecting investor confidence, interest rates, and the availability of credit. A positive outlook can boost stock prices and encourage investment, while a negative outlook may lead to market declines and reduced investment activity. The real estate market is sensitive to changes in the economic outlook, as factors such as employment, income, and interest rates can impact housing demand and prices. A strong economy can drive demand for real estate, while economic downturns can lead to decreased demand and falling property values. The manufacturing and industrial sector is heavily influenced by the economic outlook, as demand for goods and services, access to capital, and global trade conditions can impact production and investment decisions. A favorable outlook can stimulate growth in the sector, while an unfavorable outlook may result in reduced production and investment. The services sector, which includes industries such as healthcare, education, and retail, is also impacted by the economic outlook. Consumer spending, employment levels, and overall economic conditions can affect demand for services and the sector's growth prospects. The agricultural sector can be affected by the economic outlook through factors such as consumer demand, commodity prices, and government policies. Economic conditions can impact agricultural production, exports, and investment in new technologies and infrastructure. Diversification of investments is a strategy for managing risk in response to changes in the economic outlook. By spreading investments across various asset classes, industries, and geographic regions, businesses and individuals can mitigate potential losses and take advantage of growth opportunities. Cost management and efficiency improvements can help businesses and individuals navigate economic fluctuations by reducing expenses and optimizing resource utilization. Implementing cost-saving measures and improving operational efficiency can contribute to financial stability during periods of economic uncertainty. Focusing on innovation and adaptability can help businesses and individuals stay competitive in a dynamic economic environment. By embracing new technologies, developing innovative products and services, and adapting to changing market conditions, organizations can capitalize on emerging opportunities and mitigate potential risks. Workforce planning and skills development can help businesses and individuals prepare for changes in the economic outlook by ensuring they have the necessary human resources and capabilities to adapt. Investing in employee training, upskilling, and talent acquisition can promote organizational resilience and support long-term success. Understanding the economic outlook is crucial for informed decision-making by businesses, governments, and individuals. By anticipating trends and potential risks, stakeholders can make strategic choices that maximize growth opportunities and mitigate potential losses. The economic outlook is inherently dynamic, and subject to constant change due to a wide range of factors. Continuous monitoring and adaptation are necessary for businesses and individuals to respond effectively to shifts in the economic landscape and maintain financial stability. A knowledgeable professional can provide tailored advice and strategies to help businesses and individuals navigate the ever-changing economic environment and achieve their financial goals.What Is an Economic Outlook?
Factors Influencing Economic Outlook
Global Economic Factors
International Trade
Currency Exchange Rates
Geopolitical Events
Domestic Economic Factors
Fiscal and Monetary Policies
Consumer Spending
Business Investment
Labor Market Conditions
Inflation and Interest Rates

Economic Outlook Indicators
Leading Indicators
Stock Market Performance
Business Confidence Indices
Consumer Sentiment Indices
Lagging Indicators
Gross Domestic Product (GDP) Growth
Unemployment Rate
Inflation Rate

Economic Outlook Forecasts
Short-Term Outlook
Quarterly and Annual Forecasts
Potential Risks and Opportunities
Long-Term Outlook
Demographic Trends
Technological Advancements
Environmental and Sustainability Concerns
Impact of Economic Outlook on Various Sectors
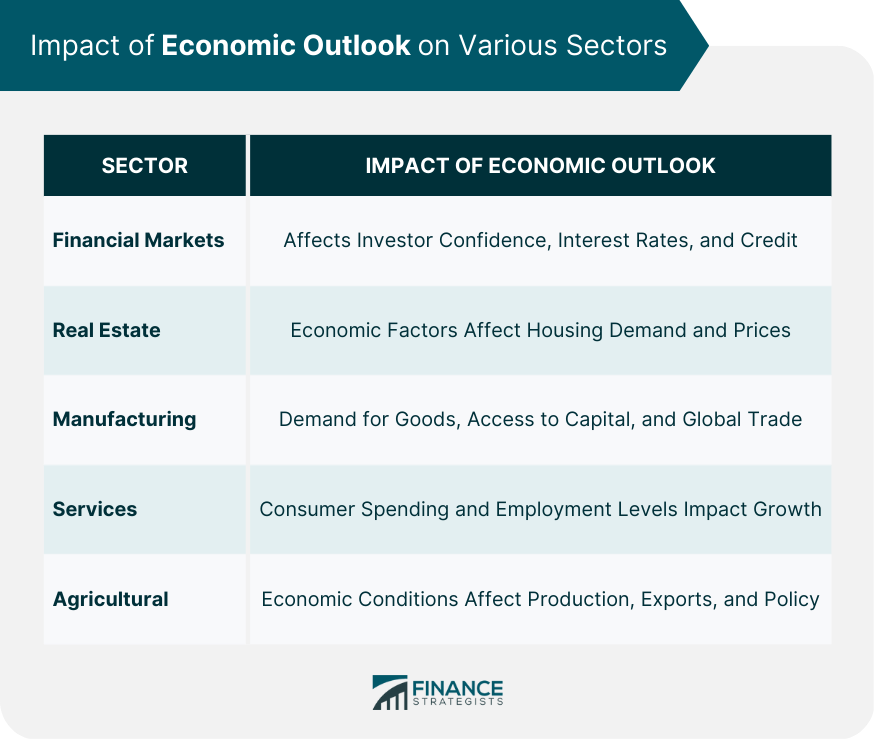
Financial Markets
Real Estate Market
Manufacturing and Industrial Sector
Services Sector
Agricultural Sector
Strategies for Businesses and Individuals in Response to Economic Outlook
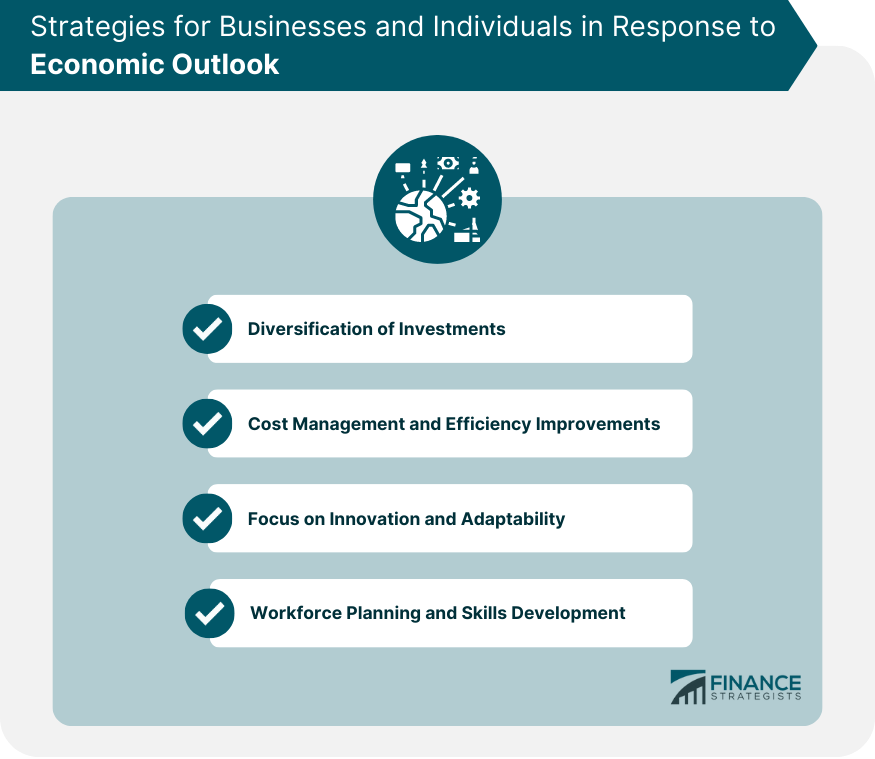
Diversification of Investments
Cost Management and Efficiency Improvements
Focus on Innovation and Adaptability
Workforce Planning and Skills Development
Final Thoughts
Economic Outlook FAQs
The economic outlook influences financial markets by affecting investor confidence, interest rates, and the availability of credit. A positive outlook can boost stock prices and encourage investment, while a negative outlook may lead to market declines and reduced investment activity.
The economic outlook is shaped by a variety of factors, including global economic factors (international trade, currency exchange rates, and geopolitical events) and domestic economic factors (fiscal and monetary policies, consumer spending, business investment, labor market conditions, and inflation and interest rates).
Strategies for responding to changes in the economic outlook include diversification of investments, cost management and efficiency improvements, focusing on innovation and adaptability, and workforce planning and skills development.
A clear understanding of the economic outlook is vital for informed decision-making, risk management, and strategic planning. Accurate economic forecasts enable organizations and individuals to make well-informed decisions regarding investments, hiring, and financial planning.
Continuous monitoring of leading and lagging economic indicators, such as stock market performance, business confidence indices, consumer sentiment indices, GDP growth, unemployment rate, and inflation rate, can help businesses and individuals anticipate changes in the economic outlook. Adapting to these changes may involve seeking the guidance of a financial advisor for tailored advice and strategies.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











