A Kangaroo bond is a type of foreign bond that is issued by a non-Australian entity in the Australian financial market and is denominated in Australian dollars (AUD). Kangaroo bonds are similar to other types of foreign bonds, such as Yankee bonds (issued in the US market) and Samurai bonds (issued in the Japanese market), in that they allow foreign entities to access local markets and raise capital in local currency. Kangaroo bonds first emerged in the late 20th century as a means for foreign entities to access the Australian capital market and diversify their funding sources. Over the years, the market for Kangaroo bonds has grown significantly, with a wide range of issuers, including multinational corporations, financial institutions, and sovereign governments, tapping into the Australian market to raise funds. Kangaroo bonds play an essential role in the global financial market, as they offer issuers and investors a range of benefits, such as diversification, access to the Australian market, and potential for higher yields. By providing an additional funding source for foreign entities and investment opportunities for Australian investors, Kangaroo bonds help to promote cross-border capital flows, strengthen financial market integration, and support global economic growth. Kangaroo bonds are denominated in Australian dollars (AUD), which enables foreign issuers to raise funds in the local currency and manage their currency exposure more effectively. By issuing bonds in AUD, issuers can access a broader investor base in the Australian market, while investors gain exposure to foreign entities without the need for currency conversion. A wide range of entities can issue Kangaroo bonds, including multinational corporations, financial institutions, and sovereign governments. Issuers typically use the proceeds from Kangaroo bonds to fund operations, investments, or capital projects, either within Australia or in other markets where they have exposure to AUD-denominated assets or liabilities. Kangaroo bonds typically pay a fixed or floating interest rate, which is determined at the time of issuance. The interest rate on a Kangaroo bond is generally influenced by factors such as the issuer's credit rating, prevailing market interest rates, and the bond's term to maturity. Kangaroo bonds can have various maturity dates, ranging from short-term notes with maturities of one year or less to long-term bonds with maturities of 10 years or more. The maturity date of a Kangaroo bond depends on the issuer's funding needs and the preferences of the Australian investor base. One of the main advantages of Kangaroo bonds for both issuers and investors is diversification. Issuers can diversify their funding sources and reduce their reliance on their home markets, while investors can gain exposure to foreign entities and potentially benefit from a broader range of investment opportunities. Kangaroo bonds provide foreign issuers with access to the Australian capital market, enabling them to tap into a large and diverse investor base. By issuing bonds in AUD, issuers can attract Australian investors who may be more familiar with the local market and more comfortable investing in AUD-denominated securities. Kangaroo bonds may offer higher yields compared to domestic bonds, particularly for investors in low-interest-rate environments. This can make Kangaroo bonds an attractive investment option for yield-seeking investors looking to diversify their portfolios and enhance their overall returns. Since Kangaroo bonds are denominated in AUD, they can help issuers and investors manage their currency risk more effectively. Issuers can raise funds in the local currency to finance their AUD-denominated assets or liabilities, while investors can gain exposure to foreign entities without the need to convert their investments into another currency, reducing their exposure to currency fluctuations. Investing in Kangaroo bonds exposes investors to the credit risk of the issuer, which is the risk that the issuer may default on its interest payments or principal repayment. The credit risk associated with a Kangaroo bond is influenced by factors such as the issuer's financial stability, credit rating, and the economic environment in which it operates. Kangaroo bonds are subject to interest rate risk, which arises from fluctuations in market interest rates. When market interest rates rise, the prices of existing bonds tend to fall, as new bonds offer higher yields. Conversely, when market interest rates fall, bond prices generally rise. Investors should be aware of the potential impact of interest rate movements on the value of their Kangaroo bond investments. While Kangaroo bonds are denominated in AUD and can help issuers and investors manage their currency risk, they still expose investors to potential currency fluctuations between their home currency and the AUD. If the AUD depreciates relative to the investor's home currency, the value of the investor's Kangaroo bond holdings may decline when converted back into their home currency, leading to potential losses. US Treasury bonds are debt securities issued by the US government and are considered among the safest investments globally due to the creditworthiness of the US government. In comparison, Kangaroo bonds are issued by foreign entities and carry higher credit risk than US Treasury bonds. However, Kangaroo bonds may offer higher yields to compensate for the increased risk. Eurobonds are debt securities issued by international entities in a currency other than that of the issuer's home country. Both Eurobonds and Kangaroo bonds provide issuers with access to foreign capital markets and allow them to diversify their funding sources. However, Kangaroo bonds are specifically denominated in AUD and are issued in the Australian market, while Eurobonds can be denominated in various currencies and are issued in international markets. Samurai bonds are debt securities issued by foreign entities in the Japanese market and are denominated in Japanese yen (JPY). Like Kangaroo bonds, Samurai bonds allow issuers to access foreign capital markets, diversify their funding sources, and manage their currency exposure. The main difference between the two is the currency denomination and the market in which they are issued. Foreign entities looking to issue Kangaroo bonds must meet certain requirements, such as obtaining approval from the Australian Securities and Investments Commission (ASIC) and obtaining a credit rating from a recognized rating agency. Additionally, issuers must comply with Australian disclosure and reporting requirements, as well as any applicable tax and regulatory obligations. Investors interested in purchasing Kangaroo bonds must meet certain eligibility criteria, which may include being a qualified institutional investor or meeting minimum investment thresholds. Investors should also conduct thorough due diligence on the issuer and the bond's terms and conditions to ensure they understand the associated risks and potential returns. The timeline for issuing a Kangaroo bond can vary depending on factors such as the issuer's credit rating, the regulatory approval process, and market conditions. Typically, the process involves obtaining approvals, preparing offering documents, engaging with potential investors, and finalizing the bond's terms and conditions. Once the issuance is complete, the Kangaroo bond is listed on a securities exchange or traded over-the-counter, depending on the specific bond structure and the issuer's preferences. A Kangaroo bond is a foreign bond issued by a non-Australian entity in the Australian financial market and denominated in Australian dollars (AUD). These bonds provide issuers with access to the Australian capital market and offer investors an opportunity to diversify their portfolios and potentially benefit from higher yields. Kangaroo bonds have several key characteristics, including their currency denomination in AUD, the diverse range of issuers, the interest rate, and the maturity date. These characteristics influence the bond's risk and return profile and should be considered by both issuers and investors when evaluating the suitability of Kangaroo bonds for their financing or investment needs. Kangaroo bonds offer various advantages, such as diversification, access to the Australian market, higher yields, and lower currency risk. However, they also come with potential risks, including credit risk, interest rate risk, and currency risk. Investors should carefully weigh the advantages and disadvantages of Kangaroo bonds to determine their appropriateness for their financial goals and risk tolerance. Kangaroo bonds play an important role in the global financial market by providing foreign entities with access to the Australian capital market and offering investment opportunities for Australian investors. By understanding the characteristics, advantages, and risks associated with Kangaroo bonds, issuers and investors can make informed decisions and tailor their financing or investment strategies to achieve their objectives.Definition of Kangaroo Bond
Brief History of Kangaroo Bonds
Importance of Kangaroo Bonds in the Financial Market
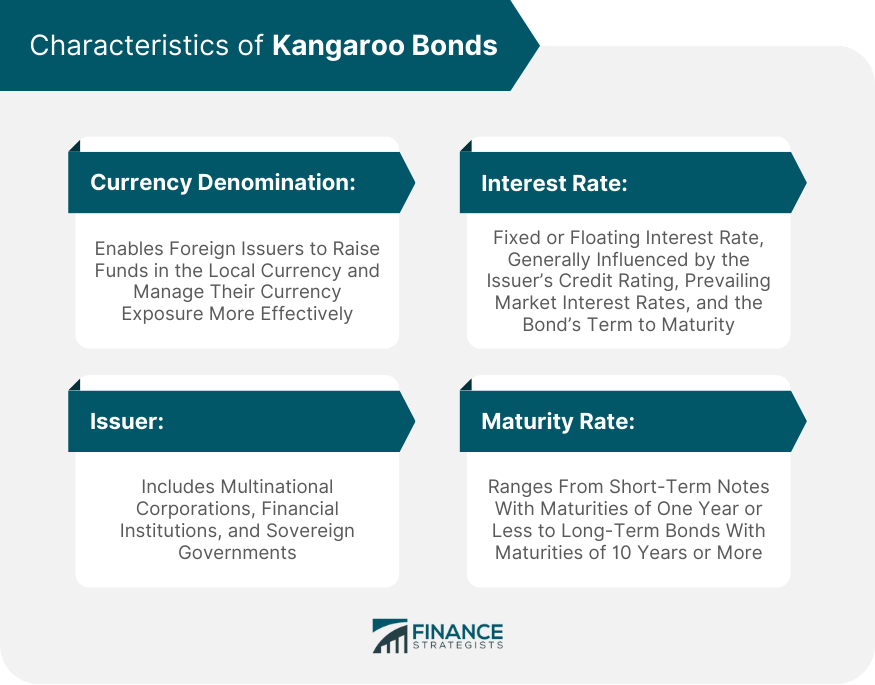
Characteristics of Kangaroo Bonds
Currency Denomination
Issuer
Interest Rate
Maturity Date
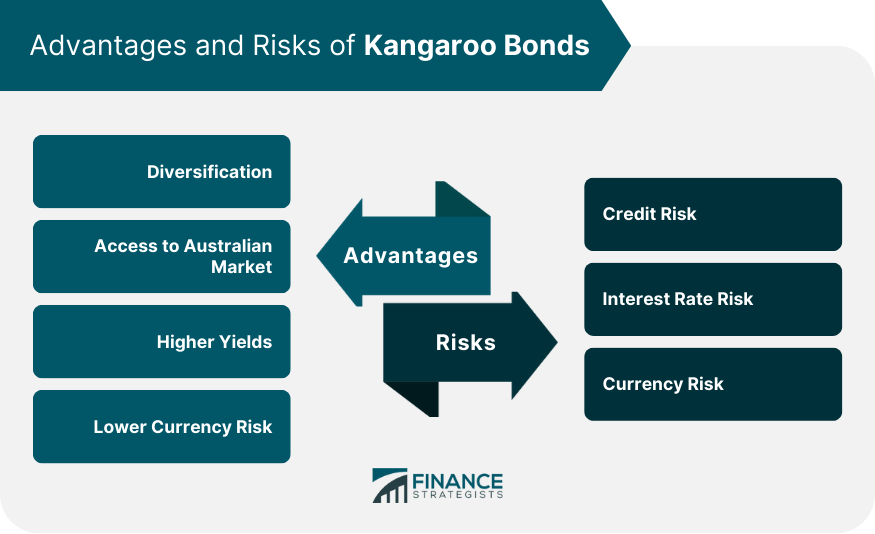
Advantages of Kangaroo Bonds
Diversification
Access to the Australian Market
Higher Yields
Lower Currency Risk
Risks of Kangaroo Bonds
Credit Risk
Interest Rate Risk
Currency Risk
Comparison With Other Bonds
US Treasury Bonds
Eurobonds
Samurai Bonds
Kangaroo Bond Issuance Process
Requirements for Issuers
Requirements for Investors
Kangaroo Bond Issuance Timeline
Final Thoughts
Kangaroo Bond FAQs
A Kangaroo bond is a type of bond issued in the Australian market but denominated in a foreign currency.
Kangaroo bonds are typically issued by foreign entities, such as corporations or government agencies, seeking to raise funds in the Australian market.
Investing in Kangaroo bonds can offer benefits such as diversification, access to the Australian market, higher yields, and lower currency risk.
The risks associated with Kangaroo bonds include credit risk, interest rate risk, and currency risk.
Investors can invest in Kangaroo bonds through a broker or financial advisor who can help them navigate the process of purchasing these bonds.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











