Risk preference refers to an individual's attitude towards financial risk, which affects their willingness to invest in assets with uncertain outcomes. It is a key factor that influences investment behavior and financial decision-making. Risk preference plays a crucial role in the world of finance, as it significantly impacts an individual's investment decisions and financial planning. Understanding risk preferences is essential for both individuals and financial advisors, as it helps in determining appropriate investment strategies and creating a well-balanced portfolio that aligns with an investor's financial goals and risk tolerance. Risk preferences can be broadly categorized into three types: risk-averse, risk-neutral, and risk-seeking. Risk-averse individuals prefer to avoid risk and are more likely to choose investments with lower returns but higher certainty. Risk-neutral individuals are indifferent to risk and make decisions based solely on expected returns. Risk-seeking individuals, on the other hand, are willing to take on higher levels of risk in pursuit of higher potential returns. Risk preferences are influenced by various factors, including personality traits, past experiences, financial knowledge, and current financial circumstances. They can also change over time due to changes in personal circumstances, such as age, income, and family responsibilities. Investors with a clear understanding of their risk preferences can make more informed financial decisions and build a portfolio that is tailored to their unique needs and circumstances. By taking into account an individual's risk tolerance, financial advisors can recommend investment strategies that balance the potential for returns with the risk of financial loss. Furthermore, understanding risk preferences can help investors to avoid emotional decision-making, which can lead to poor investment choices and undermine long-term financial goals. Instead, investors can focus on making rational, data-driven decisions that are aligned with their risk preferences and long-term financial objectives. Ultimately, the importance of understanding risk preferences in financial decision-making cannot be overstated. By developing a clear understanding of their risk tolerance and appetite, investors can make informed decisions that maximize the potential for returns while minimizing the risk of financial loss. Whether you are a seasoned investor or just getting started, taking the time to understand your risk preferences can help you achieve your financial goals and build a secure financial future. Risk preferences are shaped by a combination of demographic, psychological, and social factors. Understanding these factors can help investors and financial professionals to better assess and manage risk preferences. Age: Risk tolerance generally decreases with age, as older investors tend to prioritize preserving their wealth over seeking high returns. Gender: Studies suggest that men tend to be more risk-tolerant than women, although the gap has been narrowing. Education: Higher education levels are associated with increased financial literacy and a greater willingness to take risks. Income: Higher-income individuals typically have a greater capacity to take on risk, as they possess more financial resources to absorb potential losses. Personality Traits: Certain personality traits, such as openness to experience and extroversion, are positively correlated with risk-taking behavior. Cognitive Biases: Biases, such as overconfidence and loss aversion, can influence risk preferences and investment decisions. Heuristics: Mental shortcuts, or heuristics, can also impact risk preferences by simplifying complex financial decisions. Influence of Family and Peers: The attitudes and behaviors of family members and peers can shape an individual's risk preferences. Societal Norms and Cultural Values: Cultural factors, such as societal norms and values, can impact risk preferences by promoting or discouraging risk-taking behavior. Media Influence: The portrayal of financial risk in the media can shape public perceptions and influence risk preferences. Risk-averse investors prefer investments with lower levels of risk and are willing to accept lower returns in exchange for more predictable outcomes. Focus on wealth preservation Preference for low-risk investments Emphasis on capital protection Blue-chip stocks Diversified portfolios Lower potential for significant losses Limited growth potential Risk-neutral investors do not have a preference for either high-risk or low-risk investments. They primarily focus on the expected return of an investment, regardless of the associated risk. Equally consider high-risk and low-risk investments Focus on maximizing expected returns Balanced portfolios Potential for moderate growth Limited impact of market fluctuations Risk-seeking investors are willing to take on higher levels of risk in pursuit of potentially greater returns. They are more comfortable with the possibility of significant losses in exchange for higher potential gains. Focus on wealth accumulation Preference for high-risk investments Emphasis on capital growth Growth stocks Small-cap stocks High-yield bonds and alternative investments Higher potential for significant gains Greater likelihood of substantial losses To create investment strategies that align with an individual's risk preference, accurate assessment and measurement of risk tolerance are essential. Standardized questionnaires and surveys can help individuals assess their risk preferences by gauging their attitudes, investment experience, and financial goals. In-depth interviews with financial professionals can help in assessing an individual's risk preferences and understanding their unique financial situation. Economic Games - Economic games and simulations can be employed to measure risk preferences by observing participants' decision-making behavior in controlled settings. Behavioral Experiments - Behavioral experiments can provide insights into individuals' risk preferences by examining their reactions to different financial scenarios and investment choices. Risk tolerance questionnaires are designed to help financial advisors assess clients' risk preferences and recommend suitable investment strategies. Metrics such as the Sharpe ratio and Sortino ratio can be used to evaluate an investment's risk-adjusted performance, which can help investors make informed decisions based on their risk preferences. Financial planning software can help in assessing risk preferences by simulating various investment scenarios and analyzing the potential impact on an investor's portfolio. A well-diversified portfolio that aligns with an investor's risk preference can help balance risk and return, providing greater financial stability. Understanding risk preferences is essential for constructing a portfolio that meets an investor's unique needs and financial goals. Investors must weigh the potential returns against the associated risks when selecting investments that match their risk preferences. Aligning risk preferences with investment strategies can help investors achieve their short-term and long-term financial goals. Different financial goals may require different levels of risk tolerance, and understanding one's risk preferences can help in making appropriate investment decisions. Investors must balance their desire for returns with their risk tolerance to create a sustainable investment strategy that meets their financial objectives. A well-balanced investment strategy that aligns with an individual's risk preference can contribute to their overall financial wellbeing. Understanding and managing risk preferences can help reduce financial stress and promote emotional and psychological wellbeing. Aligning risk preferences with investment strategies can contribute to long-term financial security and stability. Financial advisors play a critical role in helping clients understand and manage their risk preferences to achieve their financial goals. Financial advisors must act in their clients' best interests, which includes understanding and respecting their risk preferences. Financial advisors are subject to regulatory requirements that mandate the accurate assessment of clients' risk preferences and the recommendation of suitable investment strategies. Financial advisors must collect comprehensive information about clients' financial situations, goals, and risk preferences to provide personalized advice. Advisors must evaluate clients' risk tolerance, which is their willingness to take on risk, and risk capacity, which is their ability to absorb financial losses. Financial advisors must recommend investment strategies that align with clients' risk preferences, ensuring their financial goals are met while minimizing unnecessary risk exposure. Advisors should continuously monitor and adjust clients' portfolios to ensure they remain aligned with their risk preferences and evolving financial goals. Understanding and managing risk preferences is crucial for both individuals and financial advisors in the world of finance. Aligning risk preferences with investment strategies can help investors achieve their financial goals while minimizing potential losses. Financial advisors play a critical role in assessing clients' risk preferences, constructing portfolios that match their unique needs, and providing ongoing support to help them navigate the complexities of the financial landscape. Continuing to explore the complexities of risk preferences, it becomes increasingly clear that this aspect of financial decision-making is dynamic and multifaceted. The ability to identify, assess, and manage risk preferences effectively is a key skill for both investors and financial professionals, as it can significantly impact the success of investment strategies and overall financial well-being. It is important to recognize that risk preferences are not static and can change over time due to various life events, personal circumstances, and external factors. Regular reviews of investment strategies and risk preferences are essential to ensure that an individual's financial plan remains aligned with their evolving needs and goals. Enhancing financial literacy can help individuals better understand the implications of their risk preferences and make more informed decisions about their investments. Education and awareness programs, as well as access to reliable financial information and resources, can play a crucial role in promoting better risk management and financial decision-making.What Is Risk Preference?
Importance of Understanding Risk Preferences in Financial Decision-Making
Factors Influencing Risk Preference
Demographic Factors
Psychological Factors
Social and Cultural Factors
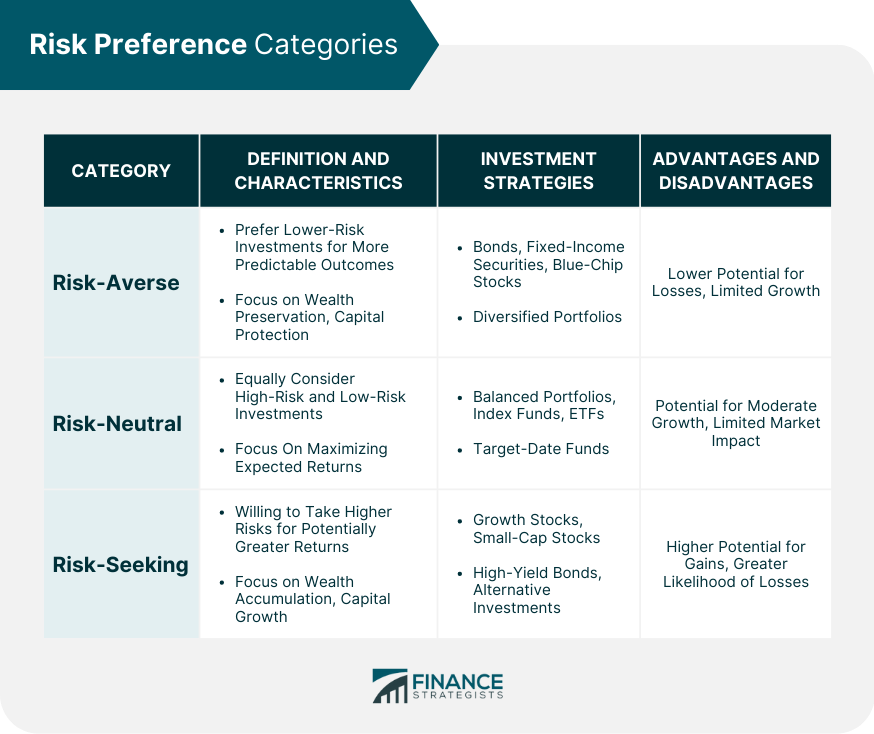
Risk Preference Categories
Risk-Averse
Definition
Characteristics
Investment Strategies
Advantages and Disadvantages
Risk-Neutral
Definition
Characteristics
Investment Strategies
Advantages and Disadvantages
Risk-Seeking
Definition
Characteristics
Investment Strategies
Advantages and Disadvantages
Assessing and Measuring Risk Preference
Self-Assessment Methods
Questionnaires and Surveys
Interviews
Experimental Methods
Financial Tools and Metrics
Risk Tolerance Questionnaires
Risk-Adjusted Performance Measures
Financial Planning Software
Importance of Aligning Risk Preferences With Investment Strategies
Diversification and Asset Allocation
Role of Risk Preferences in Portfolio Construction
Risk-Return Tradeoff
Personal Financial Goals
Short-Term vs Long-Term Goals
Balancing Risk and Return
Impact on Financial Wellbeing
Emotional and Psychological Wellbeing
Financial Security
Role of Financial Advisors in Assessing Risk Preferences
Fiduciary Responsibility
Ethical Considerations
Regulatory Requirements
Client Profiling and Risk Assessment
Gathering Client Information
Assessing Risk Tolerance and Capacity
Tailoring Investment Strategies
Recommendations Based on Risk Preferences
Ongoing Portfolio Management and Adjustments
Conclusion
Adapting to Changing Risk Preferences
Improving Financial Literacy
Risk Preference FAQs
Risk preference refers to an individual's or organization's willingness and inclination to take on risk in pursuit of financial gain.
Risk preference is determined by a variety of factors, including an individual's or organization's financial goals, investment experience, and overall financial situation. It is often expressed as a risk preference profile, such as risk-averse, risk-neutral, or risk-seeking.
Understanding risk preference is important because it helps individuals and organizations make informed investment decisions that are aligned with their financial goals and risk preferences. It also helps manage risk by avoiding investments that are outside of the acceptable risk range.
Yes, risk preference can change over time as an individual's or organization's financial situation, investment experience, and risk preferences change. It is important for individuals and organizations to periodically review and adjust their risk preference to ensure that it remains appropriate for their financial goals and circumstances.
Risk preference refers to an individual's or organization's willingness to take on risk, while risk tolerance refers to an individual's or organization's ability to handle and cope with risk. Risk tolerance is often influenced by an individual's or organization's financial situation and psychological factors.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.















