A global bond is a debt security issued by a government, corporation, or international organization that can be bought and sold in multiple countries and currencies. These bonds provide investors with a way to diversify their portfolios and gain exposure to various markets around the world. Global bonds serve to raise capital for issuers and offer several benefits for investors, such as portfolio diversification, potential higher yields, and access to a broader range of investment opportunities. They can also help mitigate risks associated with investing in a single market or currency. There are different types of global bonds, such as Eurobonds, foreign bonds, and supranational bonds. Each type varies based on the issuer, the currency in which it is denominated, and the market in which it is primarily traded. Eurobonds are bonds issued by governments or corporations in a currency other than the issuer's domestic currency. These bonds are typically traded in international markets and can offer investors exposure to foreign currencies and interest rate environments. Foreign bonds are bonds issued by a foreign entity in the domestic market and currency of another country. These bonds are subject to the regulatory framework and market practices of the country in which they are issued, providing investors with an opportunity to invest in foreign issuers while mitigating currency risks. Supranational bonds are issued by international organizations such as the World Bank or the European Investment Bank. These bonds are typically backed by the member countries of the issuing organization, resulting in high credit ratings and lower risks for investors. Governments issue global bonds to finance budget deficits, infrastructure projects, and other public expenditures. These bonds are typically considered lower-risk investments due to the backing of the issuing government and are particularly attractive to risk-averse investors. International organizations, such as the World Bank and the International Monetary Fund (IMF), issue global bonds to fund development projects and provide financial assistance to member countries. These bonds generally have a high credit rating, reflecting the financial stability of these institutions. Corporations issue global bonds to raise capital for various purposes, such as funding business expansions, acquisitions, or debt refinancing. Corporate global bonds typically offer higher yields compared to government bonds, but they also carry higher risks due to the potential for default. The primary market is where global bonds are initially issued and sold to investors. Issuers work with underwriters to determine the bond's structure, pricing, and distribution, allowing them to raise capital directly from investors. The secondary market is where investors buy and sell previously issued global bonds. Trading on the secondary market allows bondholders to liquidate their investments and provides a mechanism for determining the bond's market value. Market participants in global bond markets include issuers, underwriters, investors, and intermediaries such as brokers and dealers. These participants contribute to the efficient functioning of the market by facilitating the issuance, trading, and valuation of global bonds. Global bonds offer investors the opportunity to diversify their portfolios across different markets and currencies. This is particularly advantageous for investors looking to reduce the risk associated with investing in a single market or currency. By spreading investments across a broader range of geographic locations and economies, investors can mitigate potential losses that might occur if one particular market performs poorly. Depending on the countries and specific bonds chosen, investing in global bonds can potentially offer higher yields compared to domestic bonds. This is largely due to the fact that global bonds often carry higher risk, leading to higher interest rates. In emerging markets, for example, the potential for economic growth can lead to higher yields on bonds issued by those countries. Investing in global bonds also gives investors exposure to economic growth in various regions around the world. This can be especially beneficial for investors looking to tap into the growth potential of emerging markets. As these economies grow, the value of their bonds can increase, providing potential capital gains for investors. Global bond investing can serve as a hedge against risks associated with domestic market fluctuations. For instance, if an investor's home country experiences economic instability or a downturn, having investments in international bonds could potentially offset some of these losses. This is particularly beneficial in creating a well-rounded, resilient portfolio that can withstand various market conditions. One of the main risks associated with investing in global bonds is currency fluctuation. This occurs when the value of the foreign currency that a bond is denominated in changes relative to the investor's home currency. A depreciation of the foreign currency can lead to a decrease in the value of the bond investment when converted back into the home currency, impacting the investor's overall return. Political and economic instability in certain regions can also pose a significant risk for global bond investors. These factors can affect the issuer's ability to meet their financial obligations, potentially leading to default. For instance, a country experiencing political unrest may see its economy suffer, reducing its ability to repay its debts. Similarly, an economic crisis can increase the risk of default, leading to potential losses for bondholders. Credit risk is another concern for global bond investors. This refers to the risk that the issuer of the bond may default on their obligation to repay the bond. While all bonds carry some level of credit risk, this risk can be higher for bonds issued in emerging markets or by issuers with lower credit ratings. Interest rates play a crucial role in determining global bond performance, as they influence bond prices and yields. When interest rates rise, bond prices typically fall, and vice versa. Investors should monitor interest rate trends in different countries to gauge the potential impact on their global bond investments. Exchange rate fluctuations can significantly affect the value of global bond investments, particularly for bonds denominated in foreign currencies. Changes in exchange rates can either enhance or erode the returns on global bonds, making it essential for investors to monitor currency movements and manage the associated risks. Economic and political factors in various countries can influence global bond performance. Factors such as economic growth, inflation, and political stability can impact bond yields and credit ratings, affecting the overall attractiveness of global bonds to investors. Credit ratings assigned by rating agencies reflect the creditworthiness of the bond issuer and the likelihood of default. Higher-rated bonds are generally considered safer investments, while lower-rated bonds carry higher risks but may offer higher yields. Investors should consider credit ratings when evaluating global bond investment opportunities. Global bond indices serve as benchmarks for measuring the performance of global bond markets and individual bond investments. These indices provide investors with a comprehensive view of the global bond market, enabling them to evaluate and compare the performance of their investments against a representative market standard. Some popular global bond indices include the Bloomberg Barclays Global Aggregate Bond Index, the J.P. Morgan Global Government Bond Index, and the FTSE World Government Bond Index. These indices track the performance of various segments of the global bond market, providing investors with valuable insights into market trends and potential investment opportunities. Investors can use global bond indices as benchmarks to evaluate the performance of their bond investments and make informed decisions about portfolio allocation and risk management. By comparing their investments to a relevant index, investors can assess whether they are achieving their desired level of return and diversification. Active management involves the selection of individual global bonds or sectors with the aim of outperforming the market or a specified benchmark. This approach requires extensive research, analysis, and market knowledge, as well as the ability to effectively manage currency and interest rate risks. Passive management involves investing in a diversified portfolio of global bonds that closely tracks a specific global bond index. This approach typically results in lower management fees and reduced trading costs compared to active management, making it a more cost-effective option for many investors. Currency hedging is a strategy used by investors to mitigate the impact of currency fluctuations on their global bond investments. By employing various financial instruments, such as currency forwards or options, investors can protect themselves against potential losses resulting from adverse currency movements. Investing in global bonds may have tax implications for investors, depending on their residency and the jurisdiction of the bond issuer. Investors should consult with a tax advisor to understand the potential tax implications of their global bond investments and ensure compliance with relevant tax laws. Global bond markets are subject to various legal and regulatory frameworks, which may differ between countries and jurisdictions. Investors must familiarize themselves with the applicable regulations and disclosure requirements for their global bond investments to ensure compliance and avoid potential legal issues. Issuers of global bonds are typically subject to disclosure requirements, which may vary depending on the jurisdiction in which the bond is issued. Investors should review the available disclosure documents, such as prospectuses and financial statements, to gain a better understanding of the issuer's creditworthiness and the associated risks. Global bonds play a crucial role in the financial landscape, providing issuers with access to capital and offering investors a diverse range of investment opportunities. They allow for risk diversification, exposure to various markets and currencies, and potential for higher returns compared to domestic bonds. As the global economy becomes increasingly interconnected, the importance of global bonds in the financial landscape is likely to grow. The global bond market continues to evolve, presenting both opportunities and challenges for investors. Emerging markets offer potential for higher yields and economic growth, while technological advancements may revolutionize the way bonds are issued and traded. However, investors must also navigate risks associated with currency fluctuations, geopolitical instability, and regulatory complexity. Successful global bond investing requires a well-considered approach that balances risk and return. Investors must carefully evaluate the potential benefits and risks associated with global bonds, diversify their portfolios to mitigate potential market downturns, and stay informed about economic, political, and regulatory developments that may impact the performance of their investments. As the global bond market continues to evolve, investors must be prepared to adapt their strategies and embrace new opportunities and challenges. By staying informed, diversifying their portfolios, and employing effective risk management techniques, investors can successfully navigate the dynamic world of global bond investing and capitalize on its potential rewards.What Is a Global Bond?
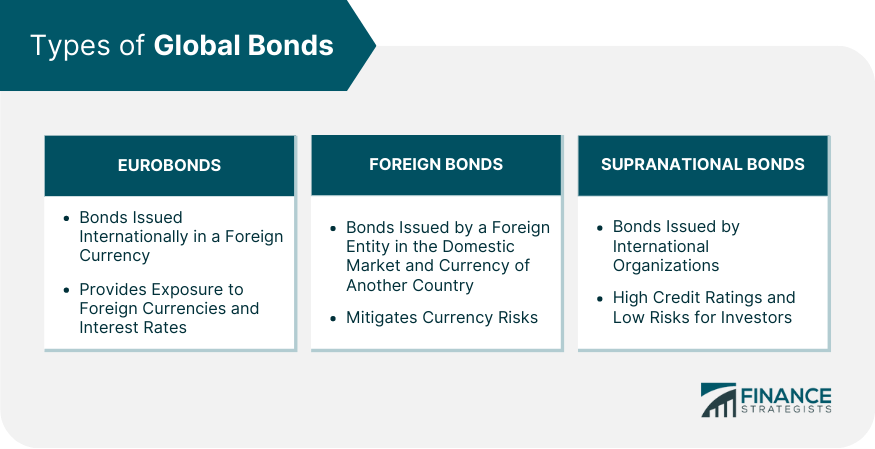
Types of Global Bonds
Eurobonds
Foreign Bonds
Supranational Bonds
Issuers of Global Bonds
Governments
International Organizations
Corporations
Global Bond Markets
Primary Market
Secondary Market
Market Participants
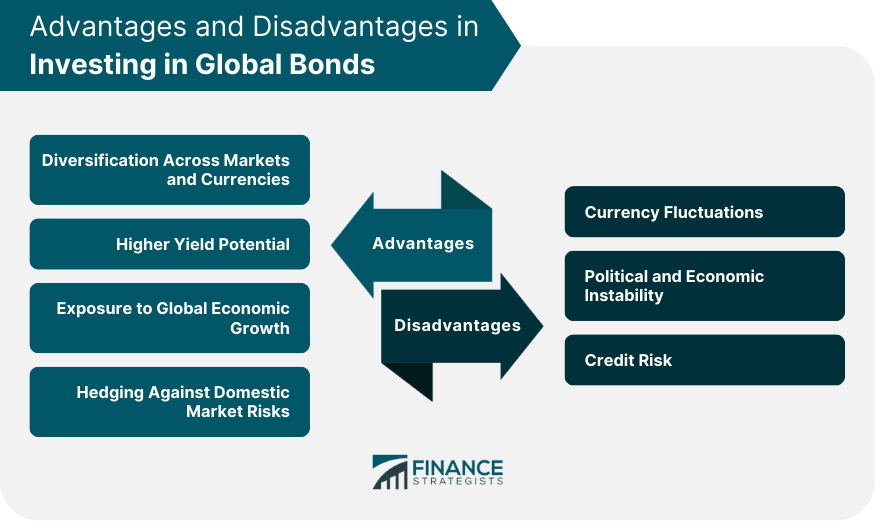
Advantages in Investing in Global Bonds
Diversification Across Markets and Currencies
Higher Yield Potential
Exposure to Global Economic Growth
Hedging Against Domestic Market Risks
Disadvantages in Investing in Global Bonds
Currency Fluctuations
Political and Economic Instability
Credit Risk
Factors Affecting Global Bond Performance

Interest Rates
Exchange Rates
Economic and Political Factors
Credit Ratings
Global Bond Indices
Purpose of Global Bond Indices
Popular Global Bond Indices
Benchmarking and Performance Evaluation
Strategies for Investing in Global Bonds
Active Management
Passive Management
Currency Hedging
Global Bond Regulations and Compliance
Taxation Issues
Legal and Regulatory Frameworks
Disclosure Requirements
Final Thoughts
Global Bond FAQs
Global bonds are debt securities issued by governments, corporations, or international organizations in various countries and currencies. They offer investors diversification, exposure to different markets and currencies, and potentially higher returns compared to domestic bonds.
The main risks associated with global bonds include currency fluctuations, political and economic instability in certain regions, and credit risk linked to the issuer's ability to repay the bond. Investors should carefully evaluate these risks when considering global bond investments.
Global bonds can provide diversification by allowing investors to gain exposure to different markets, currencies, and interest rate environments. This diversification can help reduce overall portfolio risk and volatility, minimizing the impact of any single market downturn.
Some popular global bond indices include the Bloomberg Barclays Global Aggregate Bond Index, the J.P. Morgan Global Government Bond Index, and the FTSE World Government Bond Index. These indices track the performance of various segments of the global bond market, providing valuable insights into market trends and investment opportunities.
Investors can use various strategies, such as active or passive management, currency hedging, and portfolio diversification, to manage risks and maximize potential returns from global bond investments. Staying informed about economic, political, and regulatory developments is also crucial for successful global bond investing.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.















