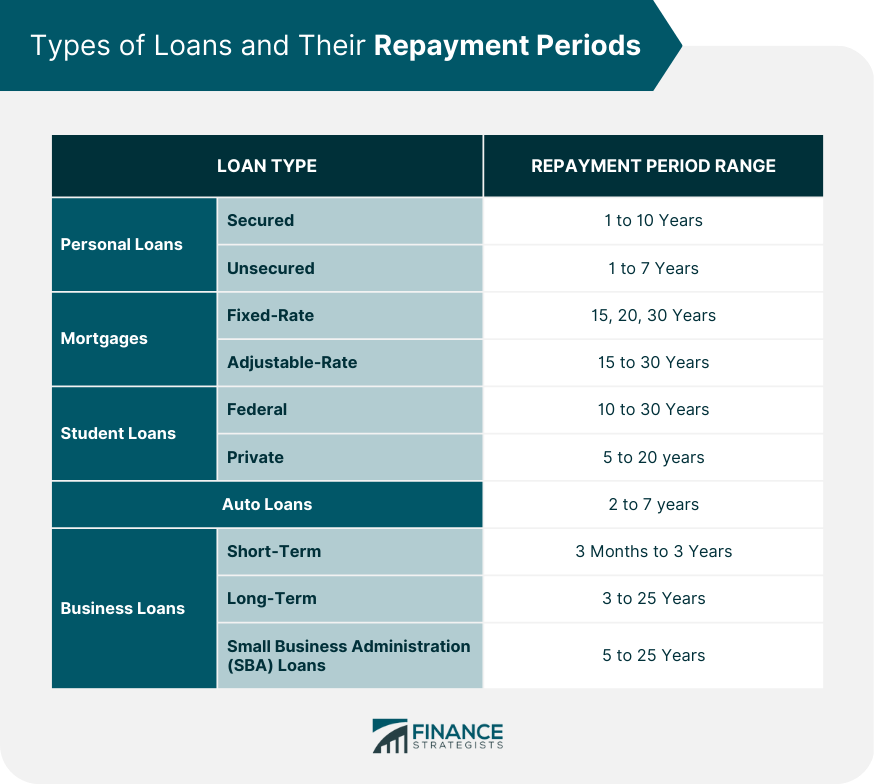
A loan repayment period is the duration of time over which a borrower is required to repay a loan, including the principal amount and interest. It is crucial for borrowers to understand loan repayment periods, as they have a direct impact on the monthly payments, total interest paid, and overall financial planning. Secured personal loans are backed by collateral, such as a home or a car. These loans typically have repayment periods ranging from 1 to 10 years, depending on the lender and the amount borrowed. Unsecured personal loans do not require collateral and are often used for various purposes, such as debt consolidation or home improvement. Repayment periods for unsecured loans generally vary between 1 and 7 years. Fixed-rate mortgages have a set interest rate that does not change over the life of the loan. The most common repayment periods for fixed-rate mortgages are 15, 20, and 30 years. Adjustable-rate mortgages (ARMs) have interest rates that change periodically, based on a financial index. ARMs generally have initial fixed-rate periods, followed by adjustable-rate periods. The total repayment period usually ranges from 15 to 30 years. Federal student loans, offered by the U.S. government, have various repayment plans with terms ranging from 10 to 30 years, depending on the specific plan chosen. Private student loans are offered by banks, credit unions, and other financial institutions. Repayment periods for private student loans typically range from 5 to 20 years. Auto loans are used to finance vehicle purchases and typically have repayment periods ranging from 2 to 7 years. Short-term business loans generally have repayment periods of 3 months to 3 years and are often used for working capital or to finance specific projects. Long-term business loans usually have repayment periods of 3 to 25 years and are used for large investments, such as purchasing real estate or equipment. Small Business Administration (SBA) loans are government-backed loans for small businesses. Repayment periods for SBA loans range from 5 to 25 years, depending on the loan type. Interest rates play a critical role in determining loan repayment periods. Generally, loans with lower interest rates have longer repayment periods, while loans with higher interest rates have shorter repayment periods. The loan amount directly affects the repayment period, as larger loans typically require longer repayment periods to ensure affordability for the borrower. A borrower's credit history can influence the repayment period, as lenders may offer shorter repayment periods to borrowers with lower credit scores, due to the higher risk involved. Lenders have varying policies regarding loan repayment periods, which can be influenced by factors such as the type of loan, the borrower's financial situation, and the lender's risk tolerance. Economic conditions, such as the prevailing interest rate environment and the overall health of the economy, can influence loan repayment periods. The repayment period has a direct impact on the monthly payment amount, with shorter repayment periods resulting in higher monthly payments and longer repayment periods leading to lower monthly payments. A longer repayment period generally results in higher total interest paid over the life of the loan, while a shorter repayment period reduces the total interest paid. Loan repayment periods can affect a borrower's credit score. Timely repayment of loans with longer terms can have a positive impact on credit scores while defaulting or late payments on loans with shorter terms can negatively affect credit scores. Understanding loan repayment periods is essential for effective financial planning and budgeting. Borrowers need to consider the implications of their chosen repayment period on their monthly payments and overall financial situation. Selecting the appropriate loan term is crucial for managing loan repayment effectively. Borrowers should consider their financial goals, monthly budget, and long-term plans when determining the optimal repayment period. Prepayment and refinancing options can help borrowers manage their loan repayment periods. Prepayment allows borrowers to pay off their loans early, reducing the total interest paid. Refinancing can provide borrowers with better interest rates or longer repayment periods, depending on their financial situation. Loan consolidation involves combining multiple loans into a single loan with a new repayment period and interest rate. This strategy can simplify loan management and may result in lower monthly payments or reduced interest rates. Income-driven repayment plans, available for federal student loans, base monthly payments on the borrower's income and family size. These plans can provide borrowers with more manageable monthly payments and extend repayment periods. Loan forgiveness programs, such as Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF) for federal student loans, can help eligible borrowers reduce or eliminate their loan balances, effectively shortening their repayment periods. Government policies, such as regulations on maximum loan terms or caps on interest rates, can influence loan repayment periods. Consumer protection laws and regulations, such as the Truth in Lending Act (TILA), ensure that borrowers have access to clear and accurate information about loan terms and repayment periods. Some loans may include prepayment penalties, which are fees for paying off a loan early. Additionally, defaulting on a loan can result in severe consequences, such as damaged credit, wage garnishment, or legal action. Loan repayment periods have a significant impact on borrowers and their financial planning. Understanding the types of loans and their repayment periods is essential for choosing the right loan term and effectively managing loan repayments. Factors such as interest rates, loan amount, borrower's credit history, lender's policies, and economic conditions can influence loan repayment periods. Borrowers need to consider the impact of the repayment period on their monthly payments, total interest paid, credit score, and financial planning. Effective strategies for managing loan repayment periods include selecting the appropriate loan term, prepayment and refinancing options, loan consolidation, income-driven repayment plans, and loan forgiveness programs. It is also essential for borrowers to be aware of the regulatory environment and legal considerations, such as government policies, consumer protection laws, and penalties for early repayment or default. By carefully considering loan repayment periods and implementing effective strategies, borrowers can successfully manage their loans and achieve their financial goals.What Is a Loan Repayment Period?
Types of Loans and Their Repayment Periods
Personal Loans
Secured Loans
Unsecured Loans
Mortgages
Fixed-Rate Mortgages
Adjustable-Rate Mortgages
Student Loans
Federal Student Loans
Private Student Loans
Auto Loans
Business Loans
Short-Term Loans
Long-Term Loans
SBA Loans
Factors Influencing Loan Repayment Periods
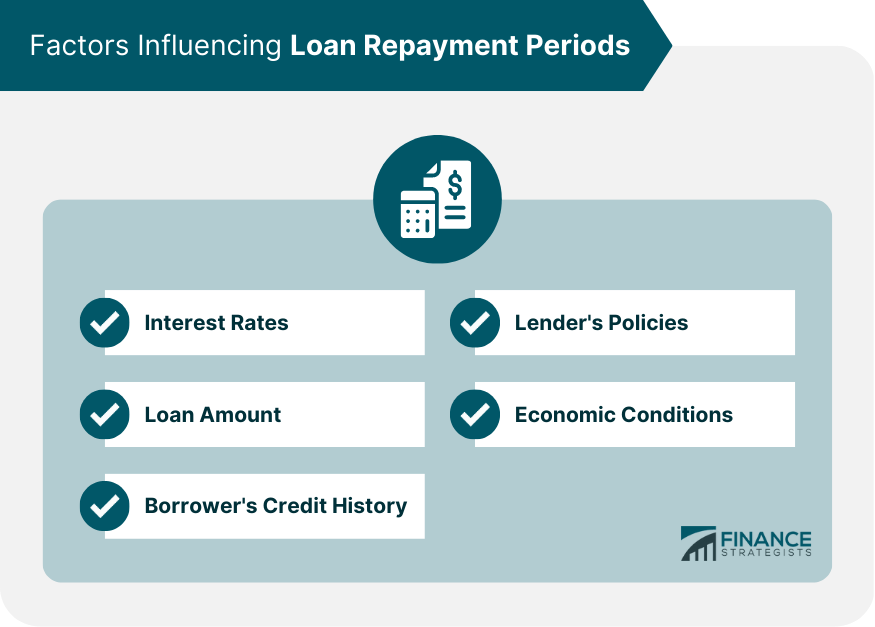
Interest Rates
Loan Amount
Borrower's Credit History
Lender's Policies
Economic Conditions
Impact of Loan Repayment Periods on Borrowers
Monthly Payment Amount
Total Interest Paid
Impact on Credit Score
Financial Planning and Budgeting
Strategies for Managing Loan Repayment Periods

Choosing the Right Loan Term
Prepayment and Refinancing Options
Consolidating Loans
Income-Driven Repayment Plans
Loan Forgiveness Programs
Regulatory Environment and Legal Considerations
Government Policies on Loan Repayment Periods
Consumer Protection Laws and Regulations
Penalties for Early Repayment or Default
Conclusion
Loan Repayment Period FAQs
Loan repayment periods vary depending on the type of loan. Some common types include personal loans (secured and unsecured) with repayment periods ranging from 1 to 10 years, mortgages (fixed-rate and adjustable-rate) with repayment periods of 15 to 30 years, student loans (federal and private) with repayment periods from 10 to 30 years, auto loans with repayment periods of 2 to 7 years, and business loans (short-term, long-term, and SBA loans) with repayment periods between 3 months and 25 years.
Interest rates and loan amounts directly influence loan repayment periods. Generally, loans with lower interest rates have longer repayment periods, while loans with higher interest rates have shorter repayment periods. Larger loan amounts typically require longer repayment periods to ensure affordability for the borrower.
Loan repayment periods affect borrowers in several ways, including their monthly payment amount, total interest paid, credit score, and overall financial planning and budgeting. Longer repayment periods result in lower monthly payments but the higher total interest paid, while shorter repayment periods lead to higher monthly payments and lower total interest paid.
Borrowers can manage loan repayment periods effectively by choosing the right loan term, considering prepayment and refinancing options, consolidating loans, opting for income-driven repayment plans (for federal student loans), and exploring loan forgiveness programs.
Government policies, such as regulations on maximum loan terms or caps on interest rates, can influence loan repayment periods. Consumer protection laws and regulations, like the Truth in Lending Act (TILA), ensure that borrowers have access to clear and accurate information about loan terms and repayment periods, helping them make informed decisions.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.















