Reinvestment risk is the possibility that an investor will be unable to reinvest cash flows from an investment, such as interest or dividends, at a rate equal to or higher than the investment's original rate of return. This can negatively impact the investor's overall returns and financial goals. Understanding reinvestment risk is crucial for investors, as it can impact the long-term performance of their investment portfolios. By being aware of reinvestment risk, investors can make informed decisions and implement strategies to manage and mitigate this risk. Various factors influence reinvestment risk, including interest rate fluctuations, changes in market conditions, economic cycles, and monetary policy. Bonds, particularly those with regular coupon payments, are subject to reinvestment risk. As interest rates change, the rates at which investors can reinvest their coupon payments may differ from the bond's initial yield. CDs, which pay interest at a fixed rate until maturity, also face reinvestment risk. When a CD matures, an investor may have to reinvest the principal and accumulated interest at a lower rate if interest rates have declined. Dividend-paying stocks are subject to reinvestment risk, as the rates at which investors can reinvest their dividends may vary depending on market conditions and available investment opportunities. Income-generating mutual funds and ETFs, such as bond funds and dividend funds, also face reinvestment risk. The rates at which the fund's income distributions can be reinvested may differ from the fund's initial yield, impacting the investor's total return. Falling interest rates are a primary cause of reinvestment risk, as they can result in lower reinvestment rates for cash flows from investments. Changes in market conditions, such as increased market volatility or shifts in the economic landscape, can also impact reinvestment risk by affecting the available investment opportunities and their associated returns. Economic cycles, including periods of expansion and contraction, can influence reinvestment risk by impacting interest rates and market conditions. Monetary policy, such as central banks' decisions to raise or lower interest rates, can impact reinvestment risk by affecting the overall interest rate environment. Bond laddering involves constructing a portfolio of bonds with staggered maturities, allowing investors to reinvest the principal and interest payments at varying interest rates and reducing reinvestment risk. Diversifying across asset classes and investment products can help investors manage reinvestment risk by spreading cash flows across various investments with different reinvestment rate sensitivities. Active portfolio management involves continuously monitoring and adjusting investments in response to changes in market conditions, interest rates, and other factors that influence reinvestment risk. Floating-rate securities, such as floating-rate bonds or notes, have interest rates that adjust periodically based on a reference rate. Investing in these securities can help mitigate reinvestment risk, as their interest payments adjust in response to changes in market interest rates. Zero-coupon bonds do not make regular interest payments, but instead, are issued at a discount and redeemed at face value at maturity. This structure eliminates reinvestment risk, as there are no cash flows to reinvest before the bond's maturity. Matching investment horizons with liabilities involves aligning the maturity or investment period with the investor's financial obligations or goals, reducing the potential impact of reinvestment risk on the investor's overall financial plan. Interest rate risk is the potential for changes in interest rates to negatively impact the value of an investment, such as bonds. Both interest rate risk and reinvestment risk are influenced by fluctuations in interest rates but affect investments in different ways. Inflation risk is the potential for rising inflation to erode the purchasing power of an investment's returns. Reinvestment risk can exacerbate inflation risk if investors are forced to reinvest cash flows at lower rates that do not keep pace with inflation. Credit risk is the potential for an issuer to default on its financial obligations, such as bond coupon payments or principal repayment. While credit risk does not directly influence reinvestment risk, it may impact the available investment opportunities and their associated returns. Market risk is the potential for changes in market conditions to negatively impact the value of an investment. Market risk can influence reinvestment risk by affecting the available investment opportunities and their associated returns. Evaluating reinvestment risk alongside other investment risks, such as interest rate risk, credit risk, and market risk, is crucial in determining an investor's overall portfolio risk and implementing appropriate risk management strategies. Understanding reinvestment risk and its potential impact on an investment portfolio can help investors align their investment strategies with their risk tolerance and financial goals, ensuring a balanced approach to risk management. Regularly reviewing and adjusting investment portfolios can help investors manage reinvestment risk by identifying and addressing any changes in market conditions, interest rates, or the investor's financial goals. Reinvestment risk is an important consideration for investors in managing their investment portfolios. By understanding and managing reinvestment risk, investors can better navigate the challenges associated with fluctuating interest rates and market conditions, optimizing their long-term returns. Understanding and managing reinvestment risk is crucial for achieving long-term financial success. Implementing effective risk management strategies can help investors protect their wealth and meet their financial goals. Utilizing various risk management strategies, such as bond laddering, diversification, active portfolio management, and matching investment horizons with liabilities, can help investors mitigate reinvestment risk and optimize their investment portfolios.What Is Reinvestment Risk?
Types of Investments Affected by Reinvestment Risk
Fixed-Income Securities
Bonds
Certificates of Deposit (CDs)
Dividend-Paying Stocks
Mutual Funds and ETFs With Income Distributions
Causes and Impact of Reinvestment Risk
Falling Interest Rates
Changes in Market Conditions
Economic Cycles
Monetary Policy
Strategies for Managing Reinvestment Risk
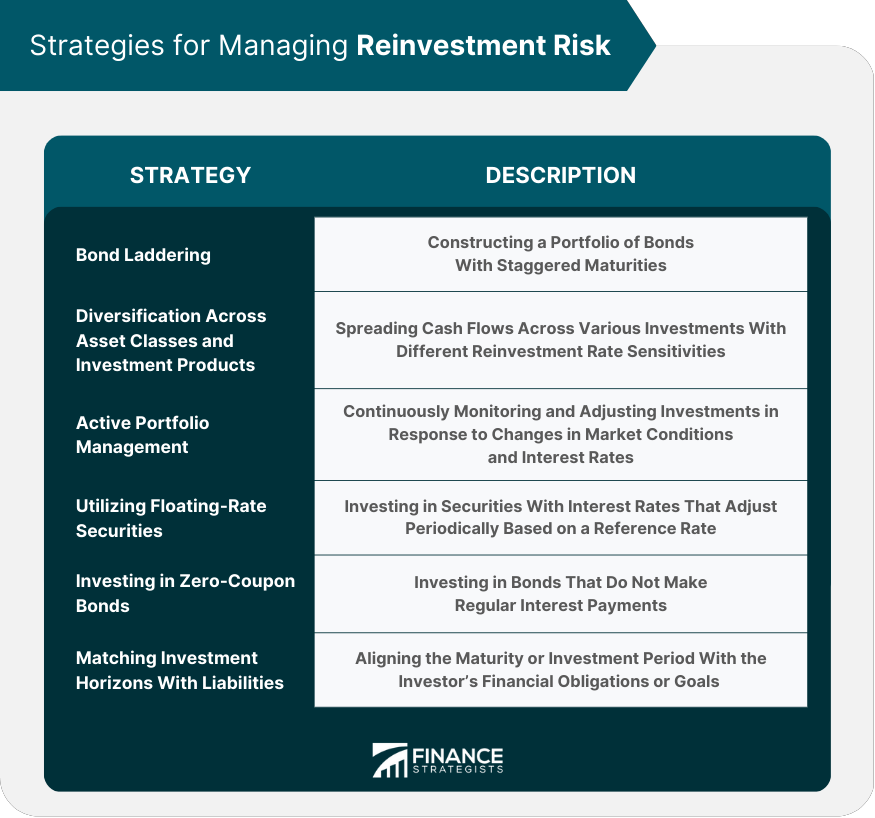
Bond Laddering
Diversification Across Asset Classes and Investment Products
Active Portfolio Management
Utilizing Floating-Rate Securities
Investing in Zero-Coupon Bonds
Matching Investment Horizons With Liabilities
The Relationship Between Reinvestment Risk and Other Investment Risks
Interest Rate Risk
Inflation Risk
Credit Risk
Market Risk
Importance of Reinvestment Risk in Investment Decision-Making
Assessing Reinvestment Risk in the Context of Overall Portfolio Risk
Aligning Investment Strategies With Risk Tolerance and Financial Goals
Periodic Portfolio Review and Adjustments
Conclusion
Reinvestment Risk FAQs
Reinvestment risk is the risk that an investor may not be able to reinvest the cash flows from an investment at the same rate of return as the original investment due to changes in market conditions or interest rates.
Reinvestment risk affects bonds when interest rates decline. When a bond's coupon payments are reinvested at a lower interest rate than the bond's yield, the bond's overall return will decrease.
One strategy to manage reinvestment risk is to invest in bonds with shorter maturities. This way, the investor can reinvest the cash flows at more frequent intervals, reducing the impact of changing interest rates. Another strategy is to ladder bond investments, which involves investing in bonds with staggered maturities to spread out the reinvestment risk.
Reinvestment risk is the risk that the cash flows from an investment cannot be reinvested at the same rate of return as the original investment, while interest rate risk is the risk that changes in interest rates will affect the value of an investment. Reinvestment risk is specific to cash flows and the reinvestment of those cash flows, while interest rate risk is a more general risk that affects the overall value of an investment.
No, reinvestment risk can apply to any investment that generates cash flows that must be reinvested to maintain the investment's overall return. This can include stocks that pay dividends, real estate investments that generate rental income, and other types of investments that generate regular cash flows.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.















