The energy industry is a complex and fascinating one, characterized by dynamic changes, high-risk ventures, and significant returns on investment. A significant component of this sector is the oil and gas industry, which relies heavily on efficient asset management. Asset management is essentially the coordinated activity of an organization to realize value from its assets. In the context of oil and gas, it involves handling, optimizing, and maintaining resources like reserves, wells, pipelines, and refineries, which have a crucial role in the exploration, production, and distribution of these energy sources. Managing these assets effectively is not just beneficial—it's essential to the industry's success. Companies that fail to effectively manage their assets can face operational inefficiencies, financial losses, and even reputational damage. The history of oil and gas asset management mirrors the journey of the oil and gas industry itself. Initially, during the advent of the oil boom, the primary concern was locating and extracting these resources. The approach to managing assets during this period was relatively rudimentary and heavily labor-intensive. However, as the industry grew, so did the need for more efficient asset management practices. As more resources were discovered and extracted, it became evident that more structured and systematic methods of managing these resources were necessary. In the mid-twentieth century, as more sophisticated extraction methods were developed and global demand for energy grew, companies had to shift their focus. The focus expanded from mere extraction to managing the available resources more effectively, maximizing productivity, and minimizing wastage. With the ever-growing demand and the increasing complexity of operations, asset management in the oil and gas industry began to evolve into a discipline of its own, complete with its methodologies and strategies. The last few decades have seen tremendous technological advancements that have significantly reshaped oil and gas asset management. From advanced seismic technology for resource detection to automated systems for production optimization, technology has enabled companies to maximize their returns from their assets. Today, digital technologies like data analytics, machine learning, and artificial intelligence are revolutionizing the field, enabling companies to monitor and manage their assets in real time and make data-driven decisions. Lifecycle analysis involves understanding the full spectrum of an asset's life, from the procurement of the resource to its depletion. It includes assessing and predicting an asset's performance, costs, and risks at each stage of its lifecycle. This allows for effective planning, reduces unforeseen costs, and ultimately enhances asset value. A thorough lifecycle analysis helps in creating robust asset management strategies that can ensure an asset's maximum potential is reached. In an industry characterized by substantial risks, both financial and operational, risk management forms a core principle of asset management. This includes identifying potential threats to asset performance, developing strategies to mitigate these risks, and establishing contingency plans for unforeseen situations. A well-thought-out risk management strategy can protect a company from significant losses and ensure the smooth operation of its assets. Optimization strategies involve fine-tuning operations to extract maximum value from assets. This could mean enhancing production efficiency, reducing downtime, or improving asset longevity. Optimization requires continuous monitoring, analysis, and adjustments based on changing market conditions and asset performance. It involves a delicate balance of maintaining operational efficiency, minimizing costs, and maximizing productivity. Upstream assets are related to the exploration and production of oil and gas. This includes reserves, drilling rigs, and production facilities such as oil wells and gas fields. These assets are where the journey of oil and gas begins, and their effective management is crucial for ensuring the efficiency and profitability of the entire operation. Midstream assets are responsible for the transportation and storage of crude oil, natural gas, and refined products. These assets include pipelines, storage tanks, and transportation vessels. Managing these assets efficiently is key to ensuring that the oil and gas produced at upstream facilities reach the downstream facilities safely and timely, ensuring a continuous supply to the market. Downstream assets are involved in the refining of crude oil and the purifying of natural gas, as well as the distribution of products derived from crude oil and natural gas to consumers. Refineries and retail outlets are examples of downstream assets. Managing these assets effectively can impact the quality of the end product and customer satisfaction, thereby influencing a company's market share and profitability. A key aspect of oil and gas asset management is accurately valuing these assets. Various factors such as the quantity and quality of the resource, the cost of extraction and production, the prevailing market prices, and potential future trends are considered in this process. Accurate valuation helps companies make informed decisions about investing in new assets, divesting existing assets, or improving the efficiency of current assets. Investment analysis forms a vital part of financial considerations in asset management. It involves evaluating the profitability of investing in specific assets or projects. This includes performing cost-benefit analyses, assessing the return on investment, and understanding the risk associated with the investment. This analysis is crucial for companies to allocate their resources effectively and ensure that their investments yield maximum returns. Given the substantial revenues and profits involved in the oil and gas industry, taxation plays a significant role in the financial considerations of asset management. Additionally, the industry is highly regulated, and compliance with these regulations often has substantial financial implications. Understanding the tax implications and regulatory requirements of asset management can help companies avoid hefty fines and penalties, optimize their tax strategies, and maintain good relations with regulatory bodies. Market dynamics such as supply and demand, geopolitical events, and economic policies can significantly impact oil and gas asset management. For example, a surge in demand or supply disruption can result in price volatility, influencing the value of assets and investment decisions. Companies need to closely monitor these dynamics to adapt their asset management strategies accordingly. Oil and gas assets are often located in regions characterized by political instability. These geopolitical issues can impact the accessibility and value of these assets and hence need to be factored into the asset management strategy. Companies need to understand the geopolitical landscape and incorporate strategies to manage the potential risks associated with geopolitical issues. The growing global focus on climate change and sustainability also impacts oil and gas asset management. Transitioning towards cleaner energy sources could potentially devalue oil and gas assets. On the other hand, it opens opportunities for investment in technologies that reduce the environmental impact of these resources. Therefore, sustainability considerations are becoming an increasingly important aspect of asset management in the oil and gas industry. Given the hazardous nature of oil and gas operations, health and safety risks are paramount. Asset management strategies need to ensure the safety of the workforce and the public, and any accident or mishap can have significant repercussions on a company's reputation and financial position. Hence, companies need to have robust safety protocols and procedures in place as part of their asset management strategy. The industry's potential impact on the environment presents significant environmental risks. These include potential oil spills, gas leaks, and other forms of environmental contamination. Asset management strategies should include measures to prevent such incidents and contingencies for addressing any incidents that do occur. Being proactive in managing environmental risks can help companies avoid costly cleanups, legal consequences, and damage to their reputation. The oil and gas industry is subject to various local and international regulations and standards. Non-compliance can lead to hefty fines and penalties and damage a company's reputation. Hence, effective asset management requires a comprehensive understanding of these regulations and strategies to ensure compliance. Regular audits, continuous monitoring, and timely updates of asset management practices can help in maintaining compliance with these standards. Efficient asset management is pivotal in the complex, high-risk, yet highly rewarding realm of the oil and gas industry. From the lifecycle analysis of assets, risk management, optimization strategies to the effective administration of upstream, midstream, and downstream assets, a carefully crafted strategy is critical for success. Given the ever-evolving landscape of technology, regulatory compliance, market dynamics, and geopolitical issues, these strategies must remain flexible and adaptable. A deep understanding of asset valuation, investment analysis, taxation, and the industry's inherent risks and compliance requisites further underpins successful asset management. As the world focuses increasingly on sustainability and climate change, companies must also consider the environmental impact of their operations and potentially explore opportunities in cleaner technologies. To navigate this intricate and volatile landscape, seeking professional wealth management services can provide invaluable guidance, ensuring your investments in the oil and gas industry are maximized and protected. Overview of Oil and Gas Asset Management
Evolution of Oil and Gas Asset Management
Early Years
Growth and Development Over the Years
Impact of Technological Advancements
Key Principles of Asset Management
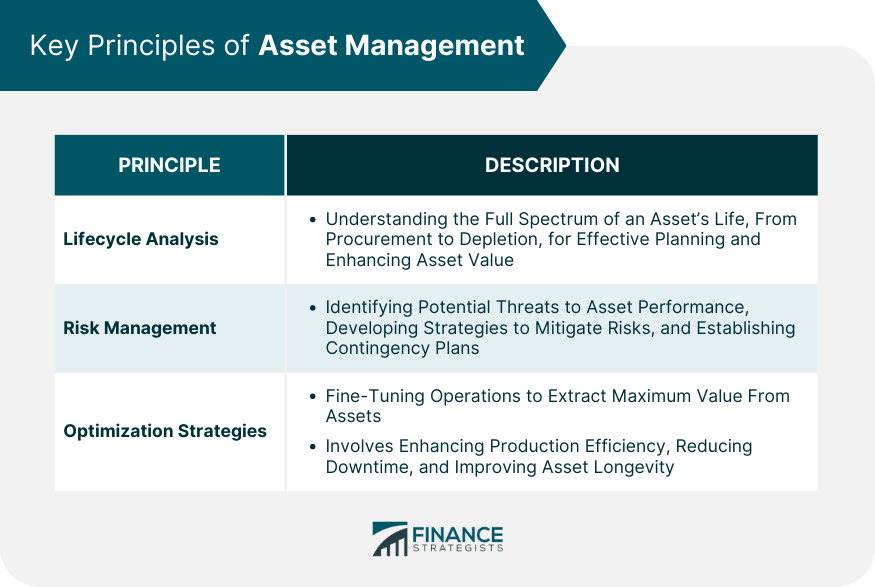
Lifecycle Analysis
Risk Management
Optimization Strategies
Types of Assets in the Oil and Gas Industry
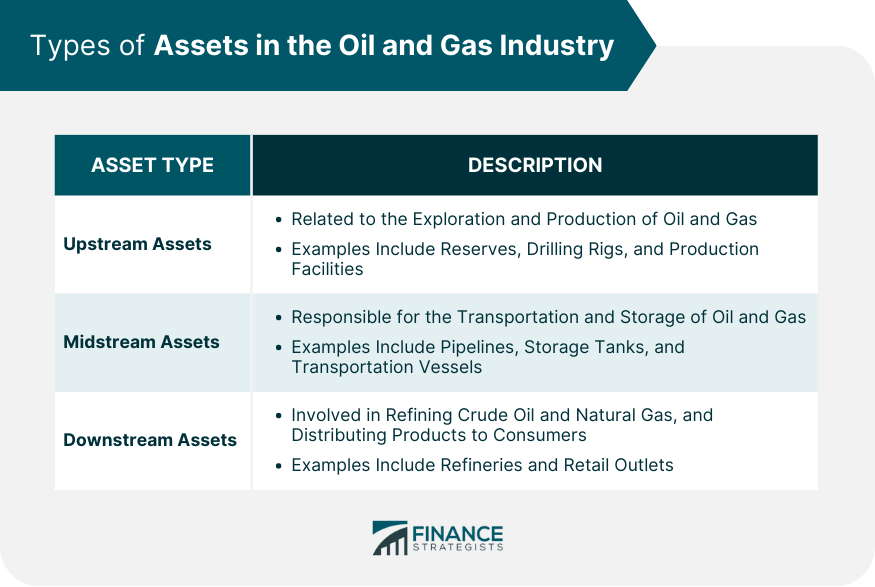
Upstream Assets
Midstream Assets
Downstream Assets
Financial Considerations in Oil and Gas Asset Management
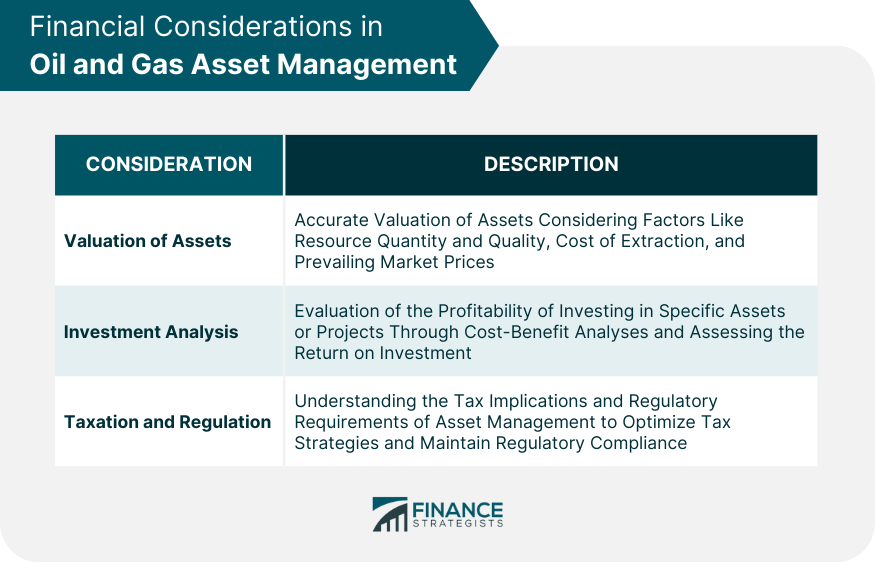
Valuation of Assets
Investment Analysis
Taxation and Regulation
Impact of Global Economic Factors
Market Dynamics
Geopolitical Issues
Climate Change and Sustainability

Risk and Compliance in the Oil and Gas Sector
Health and Safety Risks
Environmental Risks
Compliance With Standards

Bottom Line
Oil and Gas Asset Management FAQs
Oil and gas asset management is the systematic handling, optimizing, and maintaining resources like reserves, wells, pipelines, and refineries to maximize their value and efficiency in the oil and gas industry.
The three key principles of oil and gas asset management are lifecycle analysis, risk management, and optimization strategies. These principles guide the process of managing assets effectively.
Oil and gas assets can be categorized into upstream (reserves, drilling rigs, and production facilities), midstream (pipelines, storage tanks, and transportation vessels), and downstream assets (refineries and retail outlets).
Valuation of assets, investment analysis, and understanding taxation and regulation are vital financial considerations in oil and gas asset management.
Global economic factors such as market dynamics, geopolitical issues, and the growing focus on climate change and sustainability significantly influence oil and gas asset management strategies.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.















