Tax equalization is a policy or mechanism implemented by multinational corporations to ensure that their employees who are working on international assignments pay a similar amount of taxes as they would if they were working in their home country. When an employee is sent on an international assignment, they may be subject to multiple tax jurisdictions and face complex tax issues, which can result in an unequal tax burden. Tax equalization aims to balance the tax burden by reimbursing or paying the additional tax liabilities of the employee. It ensures that the employee is not financially disadvantaged or advantaged by working in a foreign country and that the corporation is compliant with tax laws and regulations in both the host and home countries. Horizontal equity refers to the principle that taxpayers with similar income levels should be subject to similar tax burdens. This principle is essential for maintaining a fair tax system, as it prevents arbitrary differences in taxation based on irrelevant factors, such as marital status or employment type. Vertical equity, on the other hand, posits that taxpayers with higher incomes should pay a larger proportion of their income in taxes compared to those with lower incomes. This principle is rooted in the idea that those who have a greater ability to pay should contribute more to public finances. The ability to pay principle suggests that taxes should be levied according to an individual's capacity to contribute. This principle is closely linked to both horizontal and vertical equity, as it ensures that taxes are fair and proportionate to taxpayers' financial resources. The benefits received principle holds that taxpayers should contribute to public finances in proportion to the benefits they receive from public goods and services. While this principle can be challenging to apply in practice, it can help guide policy decisions regarding user fees and targeted taxation. Progressive taxation is a method of tax equalization wherein tax rates increase as income levels rise. This system ensures that higher-income individuals contribute more to public finances, promoting vertical equity and reducing income inequality. Proportional taxation, also known as a flat tax, is a system in which all taxpayers pay the same percentage of their income in taxes. While this method may not directly promote vertical equity, it can contribute to horizontal equity by treating taxpayers with similar incomes equally. Regressive taxation is a system where tax rates decrease as income levels increase. This type of taxation can exacerbate income inequality and is generally considered to be contrary to the principles of tax equalization. Lump-sum taxation is a tax equalization method in which all taxpayers pay a fixed amount, regardless of their income. While this system can be simple to administer, it tends to be regressive and does not promote the principles of horizontal or vertical equity. Expatriate tax equalization aims to ensure that employees working abroad are not disadvantaged or unduly benefited by differences in tax systems between their home and host countries. Methods include hypothetical tax, tax protection, and tax reimbursement. Double tax treaties are agreements between countries designed to prevent taxpayers from being subject to taxation in both their country of residence and country of income source. These treaties can promote tax equalization by reducing the potential for double taxation and encouraging cross-border investment. Transfer pricing adjustments are used to prevent multinational corporations from manipulating the prices of goods and services traded between their subsidiaries to avoid taxation. By ensuring that these transactions are conducted at arm's length, tax equalization can be promoted across international borders. Harmonization of tax rates refers to the process of aligning tax rates and structures across countries or regions. This approach can enhance tax equalization by reducing tax competition and ensuring that taxpayers face similar tax burdens regardless of their location. Economic inequality can undermine the effectiveness of tax equalization efforts. Disparities in wealth and income make it difficult to establish tax systems that are both fair and effective in raising revenue. Tax evasion and avoidance are significant challenges to achieving tax equalization. When taxpayers use illegal or aggressive methods to reduce their tax liabilities, the burden of taxation shifts to other taxpayers, resulting in an inequitable distribution of the tax burden. The complexity of tax systems can lead to high compliance costs for taxpayers and tax authorities alike. These costs can disproportionately affect lower-income taxpayers and small businesses, undermining efforts to achieve tax equalization. Political factors can hinder the implementation of tax equalization measures. Tax policies are often influenced by powerful interest groups and public opinion, which may not always align with the principles of tax equalization. Simplifying tax systems can reduce compliance costs and make it more difficult for taxpayers to engage in tax evasion or avoidance. A simpler tax code also promotes transparency, which can lead to greater public trust in the tax system. Improving tax administration is essential for achieving tax equalization. By investing in technology, staff training, and efficient processes, tax authorities can enhance their ability to detect and deter tax evasion and avoidance. A global minimum corporate tax can help to promote tax equalization by reducing tax competition between countries and ensuring that multinational corporations contribute their fair share of taxes. International cooperation is vital for addressing tax evasion, avoidance, and competition. By sharing information and coordinating policies, countries can work together to promote tax equalization and ensure that taxpayers are treated fairly across borders. Tax equalization is a policy or mechanism implemented by multinational corporations to balance the tax burden on employees working on international assignments. Its principles include horizontal equity, vertical equity, ability to pay, and benefits received. The methods include progressive, proportional, regressive, and lump-sum taxation. Achieving tax equalization in an international context involves expatriate tax equalization, double tax treaties, transfer pricing adjustments, and harmonization of tax rates. Challenges to achieving tax equalization include economic inequality, tax evasion and avoidance, compliance costs, and political factors. Solutions to enhance tax equalization include simplifying tax systems, strengthening tax administration, implementing a global minimum corporate tax, and encouraging international cooperation.What Is Tax Equalization?
Tax Equalization Principles
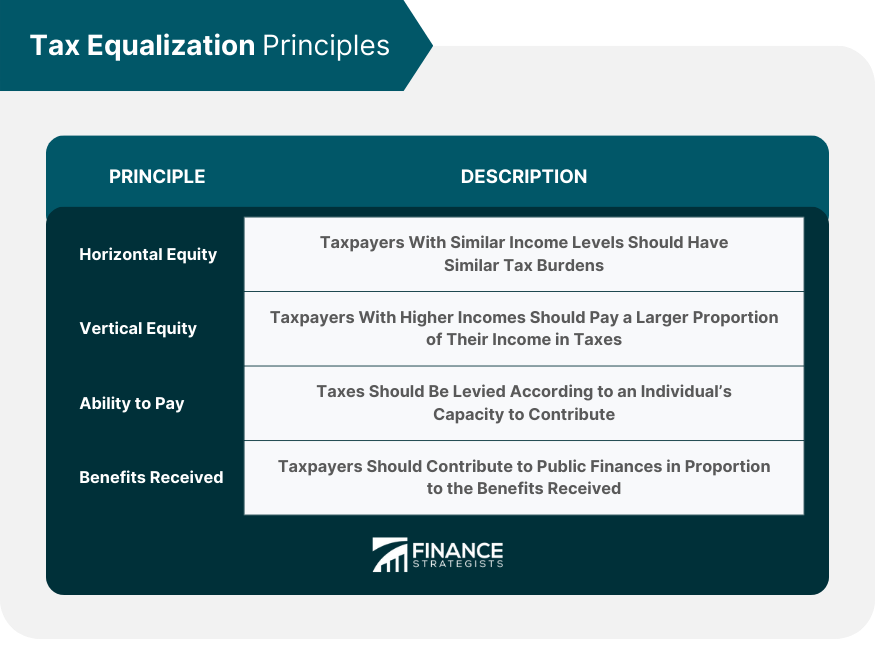
Horizontal Equity
Vertical Equity
Ability to Pay
Benefits Received
Tax Equalization Methods
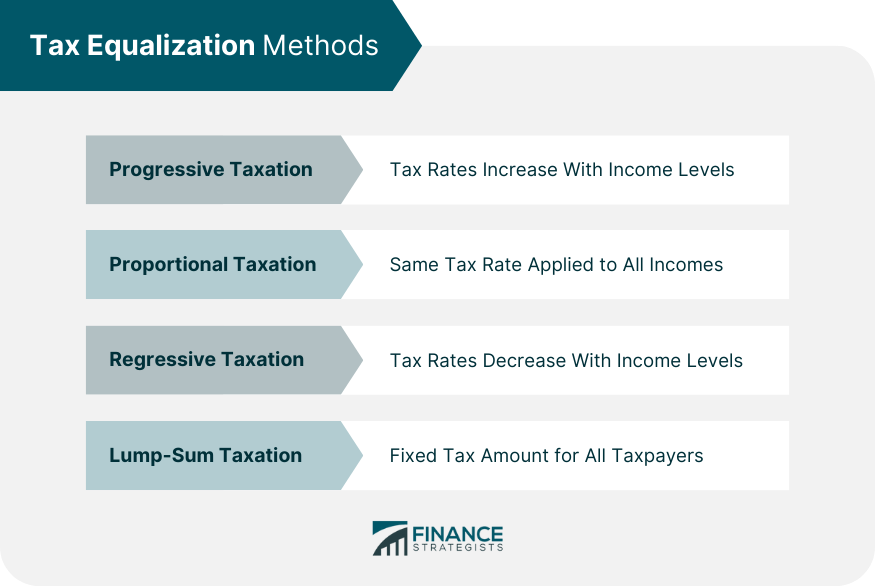
Progressive Taxation
Proportional Taxation
Regressive Taxation
Lump-Sum Taxation
Tax Equalization in International Context
Expatriate Tax Equalization
Double Tax Treaties
Transfer Pricing Adjustments
Harmonization of Tax Rates
Challenges in Achieving Tax Equalization
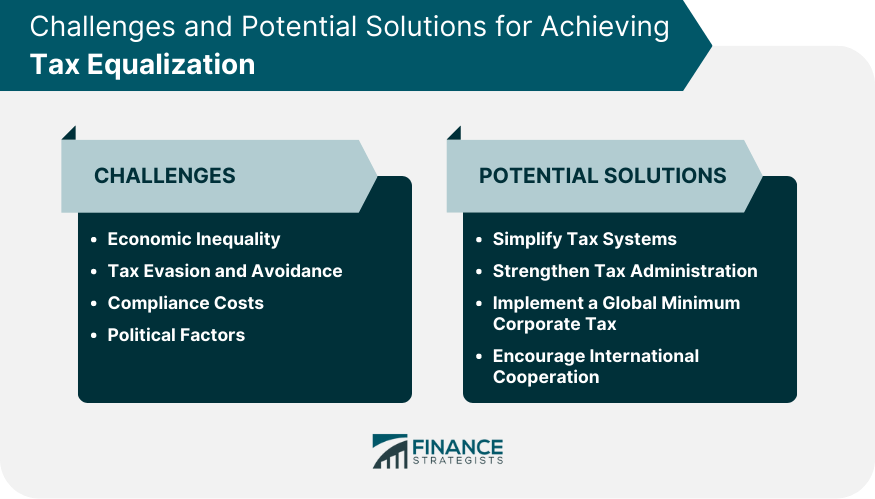
Economic Inequality
Tax Evasion and Avoidance
Compliance Costs
Political Factors
Potential Solutions for Enhancing Tax Equalization
Simplifying Tax Systems
Strengthening Tax Administration
Implementing a Global Minimum Corporate Tax
Encouraging International Cooperation
Conclusion
Tax Equalization FAQs
Tax equalization is a fiscal policy approach aimed at ensuring fairness and promoting social cohesion within a society by creating a more equitable distribution of the tax burden. It is important because it helps reduce income inequality and fosters a sense of shared responsibility for public goods and services
Progressive taxation supports tax equalization by imposing higher tax rates on individuals with higher incomes. This method ensures that those who have a greater ability to pay contribute more to public finances, which promotes vertical equity and helps reduce income inequality.
Some challenges in achieving tax equalization include economic inequality, tax evasion and avoidance, high compliance costs, and political factors. These challenges can undermine efforts to establish fair and effective tax systems that promote equity and social cohesion.
International cooperation can help achieve tax equalization by sharing information, coordinating policies, and harmonizing tax rates across countries. This collaborative approach can reduce tax competition, address tax evasion and avoidance, and ensure that taxpayers are treated fairly across borders.
Expatriate tax equalization aims to ensure that employees working abroad are not disadvantaged or unduly benefited by differences in tax systems between their home and host countries, thus promoting fairness and equity in the taxation of international workers.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











