Trust distribution standards are the guidelines that outline how and when trust assets are distributed to beneficiaries. These standards serve as a roadmap for trustees, helping them make informed decisions about trust distributions. Well-defined trust distribution standards are crucial to ensure that trust assets are managed and distributed according to the grantor's wishes. They provide clarity for trustees and beneficiaries, reducing the risk of misunderstandings and legal disputes. Trust distribution standards are essential for effective trust management, as they guide trustees in fulfilling their fiduciary duties. By adhering to these standards, trustees can protect trust assets, provide for beneficiaries, and comply with relevant laws and regulations. Discretionary trusts grant trustees the power to decide when, how, and to whom trust assets are distributed, within the bounds of the trust document. Purely discretionary distributions give the trustee complete control over trust distributions, without any specific criteria or guidelines. The trustee can make distributions based on their judgment and the best interests of the beneficiaries. Hybrid discretionary distributions provide more structure by specifying certain criteria or conditions that must be met before a trustee can make a distribution. This allows for greater control by the grantor while still maintaining trustee discretion. Mandatory trusts require the trustee to distribute trust assets to beneficiaries according to fixed terms and conditions. Fixed amount distributions mandate that the trustee distributes a specific dollar amount to one or more beneficiaries, usually at set intervals. This ensures that beneficiaries receive a predetermined amount, regardless of the trust's performance or other factors. Fixed percentage distributions require the trustee to distribute a specific percentage of the trust's value to beneficiaries. This method aligns the beneficiaries' interests with the performance of the trust, as their distributions will increase or decrease based on the trust's value. Support trusts are designed to provide financial support to beneficiaries for specific needs, such as health, education, maintenance, and support. The HEMS standard allows trustees to distribute trust assets for the health, education, maintenance, and support of beneficiaries. This standard ensures that trust distributions are used to meet essential needs, while maintaining the trustee's discretion within these parameters. The ascertainable standard is a more restrictive distribution standard that requires trustees to distribute assets based on an objective standard, such as a beneficiary's reasonable needs. This standard helps prevent misuse of trust funds and provides additional protection for beneficiaries. When establishing trust distribution standards, there are several factors to consider, including the trust's purpose, beneficiary needs and circumstances, tax implications, and asset protection. The primary purpose of the trust should guide the creation of distribution standards, ensuring that the trust's objectives are met and the grantor's intentions are fulfilled. Considering the unique needs and circumstances of the beneficiaries is essential when developing distribution standards, as this will help ensure that the trust effectively provides for the beneficiaries as intended. Understanding the tax implications of trust distributions is important, as it can impact both the trust itself and the beneficiaries. Properly structured distribution standards can minimize tax liabilities and maximize benefits for all parties. Trust distribution standards should also consider asset protection, ensuring that trust assets are preserved and safeguarded from potential threats, such as creditor claims or legal disputes. When drafting trust distribution standards, it is essential to use clear and precise language to accurately convey the grantor's intentions. This helps to prevent misunderstandings, conflicts, and potential legal challenges. Trust distribution standards should provide a balance between structure and flexibility, allowing for adaptation to changing circumstances and beneficiary needs. Including provisions for trustee discretion and trust modification can help ensure the trust remains effective over time. Drafting trust distribution standards must comply with applicable laws and regulations to ensure their validity and enforceability. Consulting with legal professionals can help ensure compliance and minimize potential legal challenges. Trustees have a fiduciary duty to act in the best interests of the trust and its beneficiaries, which includes several specific duties. The duty of loyalty requires trustees to act solely in the best interests of the beneficiaries, avoiding any conflicts of interest or self-dealing that could compromise the trust. The duty of care obligates trustees to exercise prudence and diligence in managing trust assets and making trust distributions, ensuring that trust assets are protected and used effectively for the benefit of the beneficiaries. The duty of impartiality mandates that trustees treat all beneficiaries fairly and impartially, particularly when managing trusts with multiple beneficiaries or competing interests. Trustees must exercise discretion and make informed decisions when managing trust distributions, guided by trust distribution standards. Trustees should assess the individual needs and circumstances of beneficiaries when making distribution decisions, ensuring that trust assets are used effectively and in accordance with the grantor's intentions. When managing trusts with multiple beneficiaries, trustees must balance the interests and needs of all beneficiaries, ensuring that distributions are fair and equitable. Trustees must follow the trust distribution standards outlined in the trust document, using their discretion and judgment within these guidelines to make informed distribution decisions. Inadequate or unclear trust distribution standards can lead to confusion, mismanagement, and disputes among trustees and beneficiaries, potentially undermining the trust's effectiveness and the grantor's intentions. Conflicts of interest between beneficiaries and trustees can compromise trust management, resulting in biased decision-making or self-dealing that harms the trust and its beneficiaries. Trustees who fail to properly manage trust assets or make poor investment decisions can jeopardize the trust's financial stability and the well-being of beneficiaries. Unclear or noncompliant trust distribution standards can lead to legal disputes and challenges, which can be costly, time-consuming, and damaging to the trust and its beneficiaries. Trust distribution standards are guidelines outlining when and how trust assets are distributed to beneficiaries, serving as a roadmap for trustees to make informed decisions. Trust distribution standards are essential for effective trust management, serving as a roadmap for trustees to make informed decisions about trust distributions. Well-defined trust distribution standards are crucial to ensure that trust assets are managed and distributed according to the grantor's wishes. When establishing trust distribution standards, it is important to consider factors such as the trust's purpose, beneficiary needs and circumstances, tax implications, and asset protection. Trustees have a fiduciary duty to act in the best interests of the trust and its beneficiaries, which includes several specific duties, such as the duty of loyalty, duty of care, and duty of impartiality. Challenges and potential pitfalls in trust distribution include inadequate or unclear distribution standards, conflicts of interest among beneficiaries and trustees, mismanagement of trust assets, and legal disputes and challenges. Properly structured trust distribution standards, along with the careful and informed decision-making of trustees, can help ensure that trust assets are used effectively for the benefit of the beneficiaries, in accordance with the grantor's intentions. Secure your legacy and protect your loved ones by seeking the expertise of a qualified estate planning lawyer. These professionals can help you navigate the complexities of trust creation, distribution standards, and asset protection, ensuring your trust is tailored to your unique needs and objectives. What Are Trust Distribution Standards?
Types of Trust Distribution Standards
Discretionary Trusts
Purely Discretionary Distributions
Hybrid Discretionary Distributions
Mandatory Trusts
Fixed Amount Distributions
Fixed Percentage Distributions
Support Trusts
Health, Education, Maintenance, and Support (HEMS) Standard
Ascertainable Standard

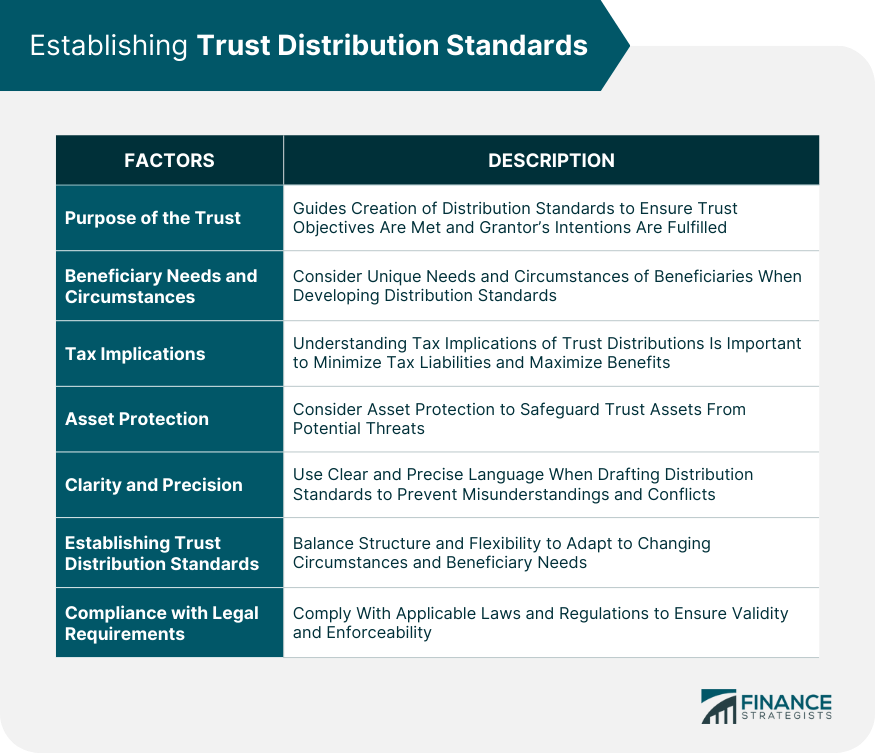
Factors to Consider When Establishing Trust Distribution Standards
Purpose of the Trust
Beneficiary Needs and Circumstances
Tax Implications
Asset Protection
Clarity and Precision
Flexibility and Adaptability
Compliance With Legal Requirements
Role of the Trustee in Trust Distribution
Fiduciary Duties
Duty of Loyalty
Duty of Care
Duty of Impartiality
Trustee Discretion and Decision-Making
Evaluating Beneficiary Needs
Balancing Interests of Multiple Beneficiaries
Adhering to Trust Distribution Standards
Challenges and Potential Pitfalls in Trust Distribution
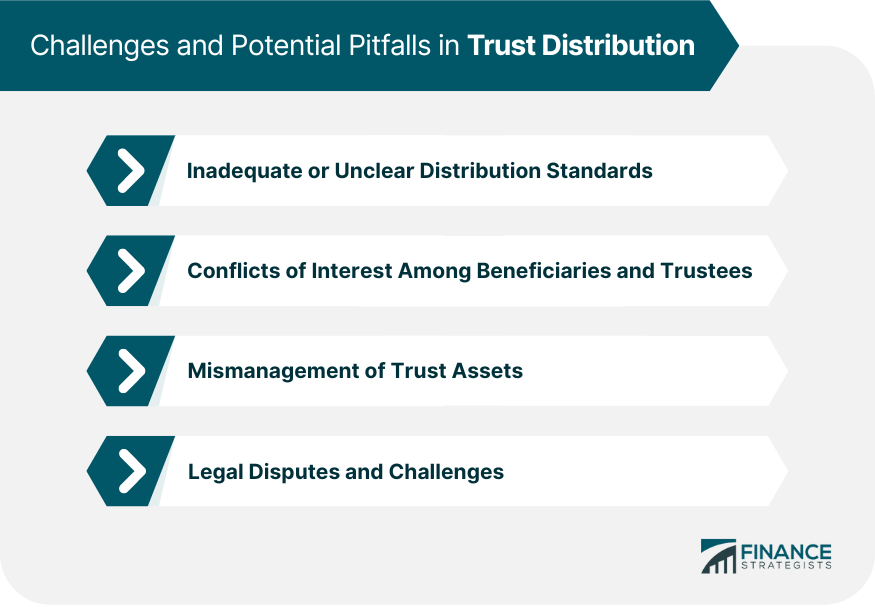
Inadequate or Unclear Distribution Standards
Conflicts of Interest Among Beneficiaries and Trustees
Mismanagement of Trust Assets
Legal Disputes and Challenges
Final Thoughts
Trust Distribution Standards FAQs
Trust income refers to the earnings generated by the trust's assets, such as interest, dividends, or rental income. Principal allocation pertains to the original assets placed in the trust, such as property or investments. Trust distribution standards outline how and when these two components are to be distributed to beneficiaries.
Trust distribution standards guide trustees in making decisions about distributing trust income and principal to beneficiaries. These standards can determine the timing, frequency, and amount of distributions, ultimately affecting the financial support beneficiaries receive from the trust.
Depending on the flexibility of the trust distribution standards and the trustee's level of discretion, a trustee may be able to make changes to trust income and principal allocations. However, any changes must align with the grantor's intentions, comply with the trust document, and meet the beneficiaries' needs.
The allocation of trust income and principal can impact the tax liabilities for both the trust and its beneficiaries. Generally, trust income is subject to taxation, while principal distributions are not. Trust distribution standards that clearly outline income and principal allocations can help minimize tax liabilities and maximize benefits for all parties.
Some common challenges include ensuring clarity and precision in defining income and principal allocations, striking a balance between structure and flexibility, and complying with legal requirements. Properly addressing these challenges when drafting trust distribution standards can minimize disputes, ensure fairness, and maximize the benefits for beneficiaries.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.













