VIX, also known as the CBOE Volatility Index, is a real-time market index created by the Chicago Board Options Exchange (CBOE). It quantifies the market's expectation of 30-day forward-looking volatility derived from the prices of options on the S&P 500 stock index. It provides insights into market expectations and can be used as a tool to assess risk and make investment decisions. The VIX was introduced by the CBOE in 1993, providing the first standard tool for tracking market volatility. Its calculation methodology was updated in 2003 to measure implied volatility from a wider range of S&P 500 index options. Over the years, the VIX has been popularly dubbed the "fear gauge" or "fear index" due to its tendency to spike during periods of financial stress. Market volatility refers to the rate at which the price of an asset, such as an index, security, or commodity, increases or decreases for a set of returns. It's a statistical measure of dispersion and is often expressed through the standard deviation or variance between returns from the same security or market index. The VIX Index calculation aims to depict expected future volatility by aggregating the weighted prices of many S&P 500 put and call options. It provides a measure of market risk and investor sentiments by projecting the expected volatility of the S&P 500 index over the next 30 days. High VIX levels typically indicate increased fear among investors, while low VIX levels suggest complacency. As a rule of thumb, a VIX level above 30 is generally associated with a high level of fear due to increased uncertainty, while a value below 20 corresponds to a stable or complacent market. In wealth management, the VIX is often used as a risk measurement tool. By indicating how much volatility investors anticipate, it provides a sense of the risk and uncertainty they perceive in the market. Thus, it can inform decisions around risk tolerance, asset allocation, and portfolio diversification. The VIX can significantly influence investment strategies. For instance, when the VIX is high, wealth managers might shift towards defensive strategies, moving assets into less volatile securities or cash. Conversely, a low VIX may signal an opportune time to implement more aggressive investment strategies. VIX-related products can be used to diversify a portfolio. Because the VIX tends to be negatively correlated with the S&P 500, VIX futures and options can provide a hedge against equity market downturns, thus serving as a powerful tool for portfolio diversification. The VIX is often seen as a barometer for the stock market. In general, when the stock market is bullish, the VIX tends to drop. Conversely, when the stock market falls, the VIX usually rises. This inverse relationship makes the VIX an invaluable tool for gauging market sentiment. Being a forward-looking measure, the VIX is often used to predict future market volatility. A rising VIX suggests that traders expect increased volatility, while a falling VIX indicates expectations of decreased volatility. Therefore, it serves as a valuable predictor of market sentiment. Stock investors can utilize the VIX in various ways. For example, they can use it to hedge their portfolios against market downturns or to speculate on future market movements. Moreover, by observing the VIX, investors can gain insights into the market's risk and fear levels, helping them make more informed investment decisions. VIX-related financial products include VIX futures, options, Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs), and Exchange-Traded Notes (ETNs). These products allow investors to trade volatility directly, providing opportunities for hedging, speculation, and portfolio diversification. VIX futures are contracts that allow traders to speculate on the future direction of the VIX index. These futures contracts have monthly expirations and can be used for hedging or speculating on future changes in market volatility. VIX options are derivative securities that grant the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy (call option) or sell (put option) the VIX at a predetermined price before a specific date. They offer investors a way to bet on future movements in the VIX index. VIX ETFs and ETNs are exchange-traded products that track the VIX index. They provide investors with exposure to volatility without having to deal with the complexities of trading futures or options. Trading VIX-related products has its pros and cons. On the one hand, these products offer a way to profit from changes in market volatility, hedge against market downturns, and diversify a portfolio. On the other hand, they can be complex and risky, especially for inexperienced traders. Furthermore, VIX-related products can be susceptible to contango, a situation where the futures price is higher than the expected future spot price, which can lead to losses over time. While the VIX is a powerful tool, it has its limitations. One criticism lies in its calculation, which is based on the implied volatilities of S&P 500 index options. It doesn't consider real-world events or the actual volatility of individual stocks, making it a somewhat abstract measure. Another critique is that the VIX can be misinterpreted. For instance, a low VIX doesn't necessarily mean that the market is safe, just as a high VIX doesn't automatically signal an impending market crash. The VIX measures expected volatility, not the direction of market movements. While the VIX is widely used, it's not the only tool for risk management. Other volatility indices, such as the NASDAQ-100 Volatility Index (VXN) and the Russell 2000 Volatility Index (RVX), can also provide insights into market volatility. Additionally, traditional risk management tools, such as diversification and asset allocation, remain crucial. The VIX (CBOE Volatility Index), often known as the "fear index," is a real-time market index that represents the anticipated volatility in the stock market over the next 30 days. This forward-looking measure, based on S&P 500 stock index option prices, provides valuable insights into market sentiment and risk. Understanding the VIX is fundamental for both investors and wealth managers. High VIX levels usually indicate increased fear, while low levels suggest complacency, helping to gauge the pulse of the market. Moreover, in the realm of wealth management, the VIX serves as a powerful risk measurement tool. It influences investment strategies and aids in portfolio diversification, thus playing a critical role in effective wealth management. Hence, mastering the dynamics of the VIX provides a significant edge in navigating the complex world of financial markets.What Is VIX (CBOE Volatility Index)?
Brief History of the VIX
Understanding the VIX (CBOE Volatility Index)
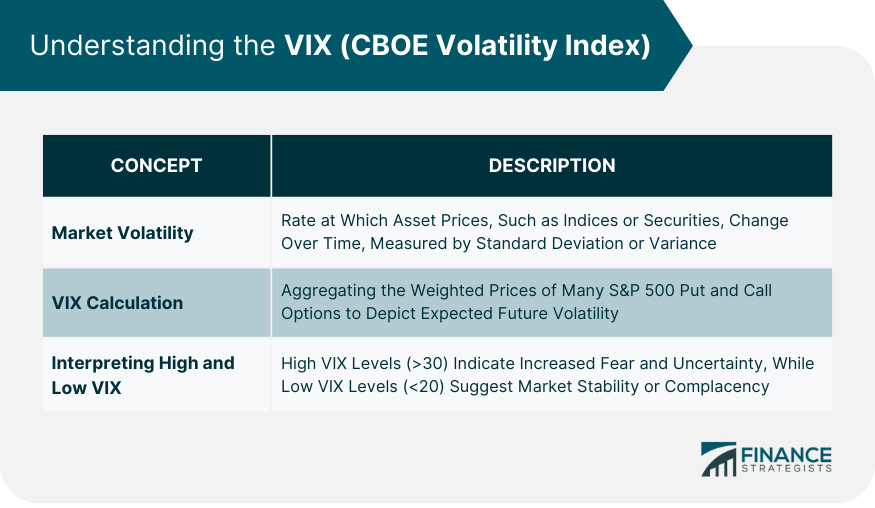
Concept of Market Volatility
How the VIX Is Calculated
Interpreting VIX Levels: High VIX and Low VIX Explained
Role of VIX in Wealth Management
VIX as a Risk Measurement Tool
Influence of VIX on Investment Strategies
VIX in Portfolio Diversification
VIX and Stock Market
Relationship Between the VIX and Stock Market
VIX as a Predictor of Market Sentiment
How Stock Investors Can Utilize the VIX
Trading VIX-Related Products
Overview of VIX-Related Financial Products
VIX Futures
VIX Options
VIX ETFs and ETNs
Pros and Cons of Trading VIX-related Products

Critiques and Limitations of the VIX
Limitations in VIX Calculations
Misinterpretations of the VIX
Alternatives to the VIX in Risk Management
Final Thoughts
VIX (CBOE Volatility Index) FAQs
The VIX, or the CBOE Volatility Index, is a real-time market index that measures the market's expectation of 30-day forward-looking volatility. It is based on S&P 500 stock index option prices and is often referred to as the "fear index."
In wealth management, the VIX is used as a risk measurement tool. By indicating the market's anticipated volatility, it provides a sense of the risk and uncertainty perceived by investors, which can inform decisions around risk tolerance, asset allocation, and portfolio diversification.
High VIX levels typically suggest increased fear among investors, indicating a potential market downturn. Conversely, low VIX levels suggest complacency and potentially bullish market conditions. Therefore, the VIX serves as a valuable barometer for gauging market sentiment.
VIX-related financial products include VIX futures, options, ETFs, and ETNs. These products allow investors to trade volatility directly, offering opportunities for hedging, speculation, and portfolio diversification.
While the VIX is a powerful tool, it has its limitations. Its calculation is based on the implied volatilities of S&P 500 index options and doesn't consider actual events or individual stock volatilities. Additionally, a low VIX doesn't necessarily mean the market is safe, and a high VIX doesn't automatically signal an impending crash. It's crucial to use the VIX wisely and in conjunction with other investment tools.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.















