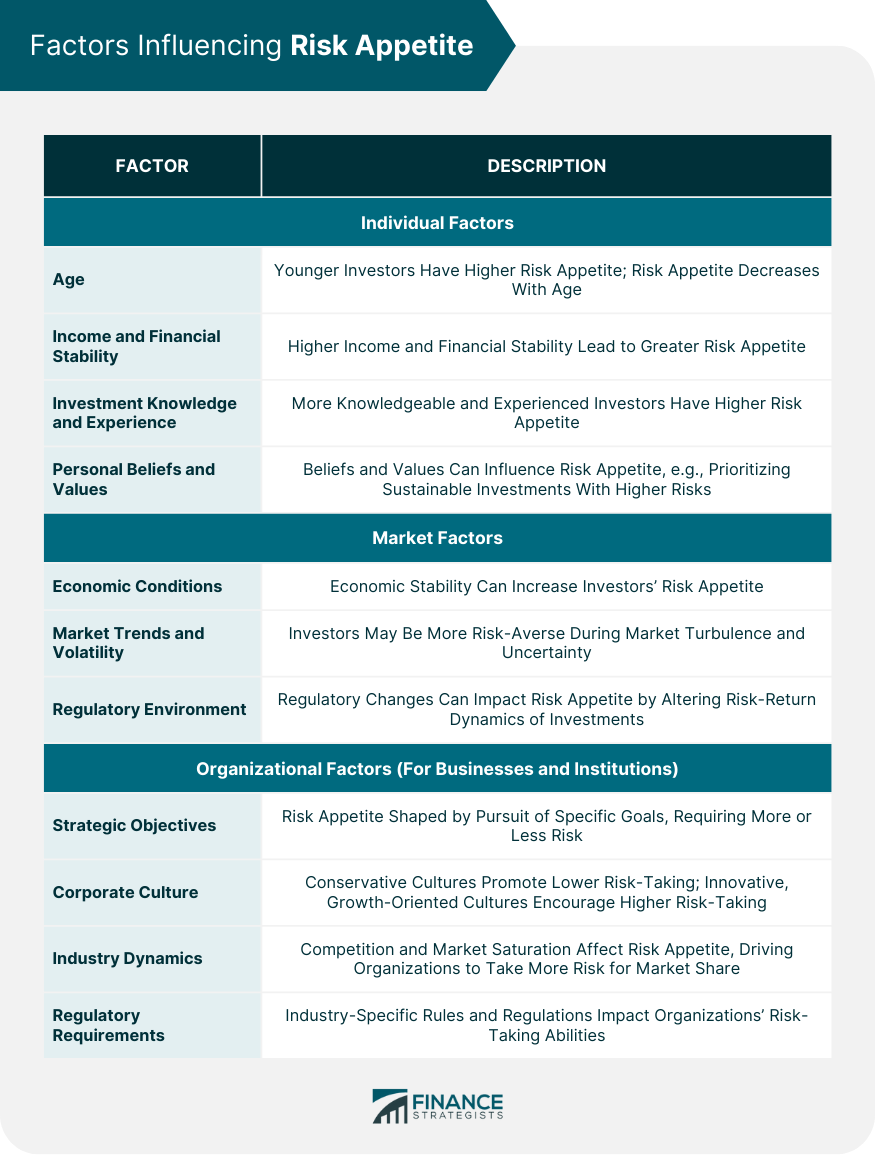
Risk appetite refers to the amount and type of risk that an individual or organization is willing to take on in order to achieve their financial goals. It is a measure of the level of uncertainty or potential loss that is considered acceptable in the pursuit of specific objectives. Risk appetite can vary widely among individuals and organizations, and it is influenced by factors such as financial knowledge, past experiences, personality traits, and current financial circumstances. Risk appetite is often used interchangeably with the term "risk tolerance," although there are subtle differences between the two. Risk tolerance refers to the ability to withstand losses without jeopardizing financial stability. It is a more psychological concept that reflects an individual's emotional comfort with risk. On the other hand, risk appetite focuses more on the desired level of risk-taking. It is a more strategic concept that reflects an organization's deliberate choice to accept a certain level of risk. Understanding both concepts is essential for effective risk management and informed investment decisions. Younger investors generally have a higher risk appetite, as they have a longer investment horizon and more time to recover from potential losses. As investors age, their risk appetite tends to decrease. Higher income and financial stability can lead to a greater risk appetite, as investors can more easily absorb potential losses without jeopardizing their financial well-being. Investors with more knowledge and experience are likely to have a higher risk appetite, as they are better equipped to understand and manage the risks associated with their investments. An individual's personal beliefs and values can also influence their risk appetite. For example, an environmentally conscious investor may prioritize sustainable investments, even if they carry higher risks. Economic conditions, such as growth rates and inflation, can impact investors' risk appetite. During periods of economic stability, investors may be more willing to take on risk. Market trends and volatility can also influence risk appetite. Investors may become more risk-averse during periods of market turbulence and uncertainty. Changes in the regulatory environment can impact investors' risk appetite, as regulatory developments may alter the risk-return dynamics of various investments. An organization's strategic objectives play a significant role in shaping its risk appetite, as the pursuit of specific goals may require taking on more or less risk. Corporate culture can also influence risk appetite, with more conservative cultures promoting lower risk-taking, while more innovative and growth-oriented cultures may encourage higher risk-taking. Industry dynamics, such as competition and market saturation, can affect an organization's risk appetite, as they may need to take on more risk to maintain or gain market share. Organizations must also consider regulatory requirements when determining their risk appetite, as they must comply with industry-specific rules and regulations that may impact their risk-taking abilities. Individual investors can use self-assessment questionnaires to gauge their risk appetite, answering questions related to their financial goals, time horizon, and comfort with risk. Financial advisors can also help investors assess their risk appetite by discussing their financial objectives, risk tolerance, and investment preferences. Organizations can assess their risk appetite through board and management discussions, where key decision-makers consider strategic objectives, industry dynamics, and other relevant factors. Organizations can formalize their risk appetite through risk appetite statements, which outline the desired level of risk-taking in pursuit of strategic objectives. Enterprise risk management frameworks can help organizations systematically assess and manage their risk appetite across different areas of the organization. Investors should consider their risk appetite when determining their asset allocation, aiming to strike the right balance between risk and potential returns. This involves allocating funds among various asset classes, such as stocks, bonds, cash equivalents, and alternative investments. Diversification is a key strategy for managing risk in line with one's risk appetite. By spreading investments across different assets and sectors, investors can reduce the impact of poor-performing investments on their overall portfolio. Investors should evaluate the risk associated with individual investments relative to their potential returns, ensuring that their choices align with their risk appetite. Investment selection should be guided by an investor's risk appetite, with more risk-averse investors focusing on conservative investments, and those with a higher risk appetite considering more aggressive investments. Investors should establish risk limits based on their risk appetite, setting boundaries for acceptable levels of risk within their portfolio. Regular monitoring of investments is crucial for managing risk. Investors should review their portfolios periodically and make adjustments as needed to ensure that their investments remain aligned with their risk appetite. Investors can also employ hedging strategies and other risk mitigation techniques to manage risk in line with their risk appetite. Investors should align their financial goals with their risk appetite, ensuring that their objectives are achievable given their willingness to take on risk. Investors must balance short-term and long-term objectives, considering their risk appetite when determining which goals to prioritize and how to allocate resources accordingly. Financial plans should be tailored to an investor's risk appetite, with investment strategies designed to achieve financial objectives while managing risk effectively. Investors and financial advisors should periodically reassess and adjust financial plans to ensure that they continue to align with the investor's risk appetite and evolving financial objectives. Risk appetite assessments can be subjective, with investors' perceptions of their risk appetite potentially being influenced by biases and emotions. An investor's risk appetite can change over time due to factors such as age, financial circumstances, and market conditions. Regular reassessment is essential to ensure that investment strategies remain aligned with the investor's risk appetite. Cognitive biases and emotional influences can impact an investor's risk appetite, leading to suboptimal investment decisions that do not accurately reflect their true risk preferences. Investors may rely too heavily on historical data and past experiences when assessing their risk appetite, potentially underestimating the impact of future market conditions and economic trends. Understanding risk appetite is crucial for making informed financial decisions, as it helps investors manage risk effectively and select investments that align with their financial goals and preferences. Risk appetite is influenced by a variety of factors, including individual characteristics, market conditions, and organizational factors. Assessing risk appetite can be done through self-assessment questionnaires, financial advisor consultations, and organizational risk management frameworks. Risk appetite should guide investment decisions and financial planning, with investors considering their risk appetite when allocating assets, selecting investments, and managing risk. Investors should be aware of the challenges and limitations associated with risk appetite, such as subjectivity in self-assessment, changing risk appetite over time, cognitive biases and emotional influences, and overreliance on historical data and past experiences. These factors should be considered when making investment decisions and developing financial plans. Risk appetite assessment is not a one-time process but an ongoing practice. Investors and financial advisors should continually monitor and adjust financial strategies to ensure they remain aligned with the investor's risk appetite and evolving financial objectives. By actively managing risk and making informed investment decisions, investors can improve their chances of achieving long-term financial success.What Is Risk Appetite?
Relationship Between Risk Appetite and Risk Tolerance
Factors Influencing Risk Appetite
Individual Factors
Age
Income and Financial Stability
Investment Knowledge and Experience
Personal Beliefs and Values
Market Factors
Economic Conditions
Market Trends and Volatility
Regulatory Environment
Organizational Factors (For Businesses and Institutions)
Strategic Objectives
Corporate Culture
Industry Dynamics
Regulatory Requirements
Assessing Risk Appetite
Methods for Individuals
Self-Assessment Questionnaires
Financial Advisor Consultations
Methods for Organizations
Board and Management Discussions
Risk Appetite Statements
Enterprise Risk Management Frameworks
Applying Risk Appetite to Investment Decisions
Asset Allocation
Balancing Risk and Return
Diversification
Investment Selection
Evaluating Risk vs Potential Returns
Choosing Investments in Line With Risk Appetite
Risk Management
Establishing Risk Limits
Monitoring and Adjusting Investments
Hedging and Other Risk Mitigation Techniques
Role of Risk Appetite in Financial Planning
Goal Setting and Prioritization
Aligning Goals With Risk Appetite
Balancing Short-Term and Long-Term Objectives
Developing Tailored Financial Plans
Ensuring Investment Strategies Align With Risk Appetite
Periodically Reassessing and Adjusting Plans
Challenges and Limitations of Risk Appetite
Subjectivity in Self-Assessment
Changing Risk Appetite Over Time
Cognitive Biases and Emotional Influences
Overreliance on Historical Data and Past Experiences
Conclusion
Factors Influencing Risk Appetite and Methods for Assessment
Application of Risk Appetite to Investment Decisions and Financial Planning
Challenges and Limitations
The Ongoing Process of Monitoring and Adjusting Financial Strategies Based on Risk Appetite
Risk Appetite FAQs
Risk appetite refers to the level of risk that an individual or organization is willing and able to tolerate in pursuit of their financial goals.
Risk appetite is determined by a variety of factors, including an individual's or organization's financial goals, investment experience, time horizon, and overall financial situation. It is often expressed as a range of acceptable risks that an individual or organization is comfortable with.
Understanding risk appetite is important because it helps individuals and organizations make informed investment decisions that align with their financial goals and risk preferences. It also helps manage risk by avoiding investments that are outside of the acceptable risk range.
Risk appetite is the level of risk that an individual or organization is willing and able to take on, while risk tolerance refers to an individual's or organization's ability to handle and cope with risk. Risk tolerance is often influenced by an individual's or organization's financial situation and psychological factors.
Yes, risk appetite can change over time as an individual's or organization's financial situation, investment experience, and risk preferences change. It is important for individuals and organizations to periodically review and adjust their risk appetite to ensure that it remains appropriate for their financial goals and circumstances.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











