A back-end load, also known as a contingent deferred sales charge (CDSC), is a fee charged to investors when they sell or redeem shares of a mutual fund, annuity, or life insurance product. The fee is typically a percentage of the investment amount and decreases over time, eventually reaching zero. The purpose of the back-end load is to encourage long-term investing and align the interests of investors and advisors. Back-end load fees aim to incentivize investors to hold onto their investments for a more extended period, thereby providing stability to the fund or financial product. This stability allows fund managers to implement long-term strategies that may generate better returns. Additionally, back-end loads help align the interests of investors and financial advisors by rewarding both parties for long-term investment commitments. There are several types of load fees associated with investment products, such as front-end loads and level loads. Front-end loads are charged when investors purchase shares, while level loads are ongoing fees charged annually. Back-end loads differ from these fees in that they are charged when investors sell or redeem their shares. Back-end load fees are calculated as a percentage of the investment amount. This percentage typically decreases over time, as laid out in the contingent deferred sales charge schedule provided by the investment product. The CDSC schedule outlines the specific percentage charged as a back-end load, depending on the holding period of the investment. The fees associated with back-end loads can impact the overall returns of an investment. Investors must carefully consider the CDSC schedule and its potential effects on their investment returns before committing to a back-end load investment product. Back-end load fees are typically associated with mutual funds, annuities, and life insurance products. These fees are applied when investors sell or redeem their shares in these investment products. One significant advantage of back-end load fees is the lower initial investment cost compared to front-end load fees. This lower cost can make it easier for investors to enter the market and build their portfolios. Back-end load fees promote long-term investing as the fees decrease over time. This incentive encourages investors to hold onto their investments, which can lead to more stable, long-term returns. As the back-end load fees decrease over time, investors who hold onto their investments for an extended period may ultimately pay lower fees than they would with other load structures. Back-end load fees help align the interests of investors and financial advisors by rewarding both parties for long-term investment commitments. Investors in back-end load investments may need more liquidity due to the fees associated with selling or redeeming their shares. This reduction in liquidity can limit investors' ability to access their funds if needed quickly. The fee structures associated with back-end load investments can be complicated and challenging to understand. Investors must carefully consider the CDSC schedule and its potential impact on their investment returns before committing to a back-end load investment product. Investors who need to sell or redeem their shares in a back-end load investment product early may face high costs due to the fees. These costs can erode the overall returns on their investments. Back-end load fees may limit investors' flexibility to move their investments between different funds or financial products. These fees can make it costly for investors to change their investment strategies. Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA) regulates back-end load fees and other fees associated with investment products. They establish rules and guidelines to protect investors and ensure fair practices in the industry. The Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) also regulates back-end load fees and requires investment companies to disclose these fees to investors. The SEC's rules aim to protect investors by providing them with transparent information about the costs associated with investment products. Investment companies are required to disclose back-end load fees in their prospectuses and marketing materials. This disclosure helps investors make informed decisions about whether to invest in a particular product. Investor protection measures, such as those enforced by FINRA and the SEC, help ensure that back-end load fees are disclosed transparently and that investment companies follow fair practices. Investors should carefully review the fee structure and CDSC schedule associated with a back-end load investment product. This information can help them understand the potential costs and impact on their investment returns. Before investing in a back-end load investment product, investors should evaluate the fund's or financial product's performance and management. This evaluation can help them determine whether the potential returns justify the fees. Investors should compare different investment options with similar objectives to identify the best fit for their investment goals and risk tolerance. This comparison should include an analysis of fees, performance, and management. Investors who are still determining the suitability of a back-end load investment product should consult with a financial advisor. A professional advisor can help them understand the potential risks, benefits, and costs associated with the investment. No-load mutual funds are an alternative to back-end load investments. These funds do not charge front-end or back-end load fees, allowing investors to keep more of their returns. However, no-load funds may still have other ongoing fees, such as management fees. Low-load or front-end load investments charge fees when investors initially purchase shares but do not charge back-end load fees. These investments may be more suitable for investors who prioritize liquidity and flexibility over long-term investment commitments. Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) are another alternative to back-end load investments. They are traded like stocks on an exchange, allowing investors to buy and sell shares throughout the trading day. ETFs typically have lower fees than mutual funds and offer more flexibility and liquidity for investors. Investors who want to avoid the potential conflicts of interest associated with load fees can consider seeking fee-based investment advice. Fee-based advisors charge a flat fee or a percentage of assets under management rather than earning commissions from selling investment products. Back-end load fees are essential to financial investing, particularly in mutual funds, annuities, and life insurance products. Investors must carefully consider the advantages and disadvantages of back-end load fees and the alternatives available to them. By understanding the fee structure, regulatory environment, and disclosure requirements, investors can make informed decisions about their investments. The importance of informed decision-making must be considered when considering back-end load investments. Investors must weigh the potential benefits of long-term investing against the fees and limited flexibility associated with these investment products. As the financial industry continues to evolve, the future may bring changes to back-end load fee structures and investment products. Investors should stay informed and regularly review their investments to ensure they continue to align with their financial goals and risk tolerance. By doing so, they can optimize their investment portfolios and better navigate the complexities of the financial market.What Is a Back-End Load?
How Back-End Load Fees Work
Calculation of Back-End Load Fees
Impact on Investment Returns
Situations When Back-End Load Fees Apply
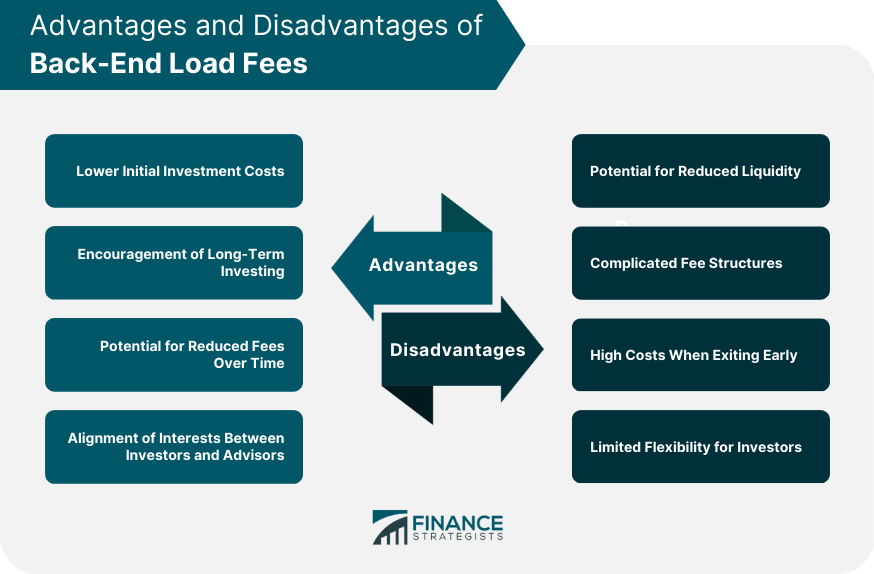
Advantages of Back-End Load Fees
Lower Initial Investment Costs
Encouragement of Long-Term Investing
Potential for Reduced Fees Over Time
Alignment of Interests Between Investors and Advisors
Disadvantages of Back-End Load Fees
Potential for Reduced Liquidity
Complicated Fee Structures
High Costs When Exiting an Investment Early
Limited Flexibility for Investors
Regulatory Environment of Back-End Load Fees
Financial Industry Regulatory Authority Regulations
Securities and Exchange Commission Rules
Disclosure Requirements for Back-End Load Fees
Investor Protection Measures
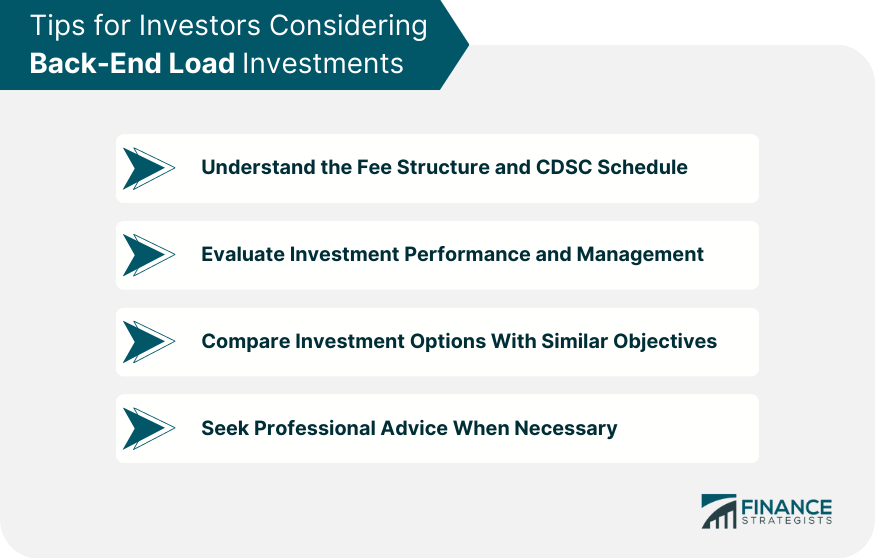
Tips for Investors Considering Back-End Load Investments
Understand the Fee Structure and CDSC Schedule
Evaluate Investment Performance and Management
Compare Investment Options With Similar Objectives
Seek Professional Advice When Necessary
Alternatives to Back-End Load Fee Investments
No-Load Mutual Funds
Low-Load or Front-End Load Investments
Exchange-Traded Funds
Fee-Based Investment Advice
Conclusion
Back-End Load FAQs
A back-end load, also known as deferred sales charge, is a fee charged by mutual funds or insurance companies when an investor sells their shares within a certain period of time after purchasing them. This fee is meant to discourage short-term trading and compensate the company for the costs associated with selling the shares.
Back-end load is a fee charged when an investor sells their shares, while front-end load is a fee charged at the time of purchase. The front-end load is deducted from the initial investment, while the back-end load is deducted from the proceeds of the sale.
Some mutual funds and insurance companies may offer back-end load fee waivers under certain circumstances, such as if the investor has held the shares for a certain period of time or if the investor is making a certain type of transaction.
Back-end load balancing can help reduce downtime, increase performance, and improve the security of a web application. It can also enable easier management and maintenance of servers, as well as better utilization of resources.
Some common back-end load balancing techniques include round-robin, least connections, IP hash, and weighted round-robin. These techniques distribute incoming traffic based on various criteria, such as server availability, connection count, client IP address, and server capacity.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.















