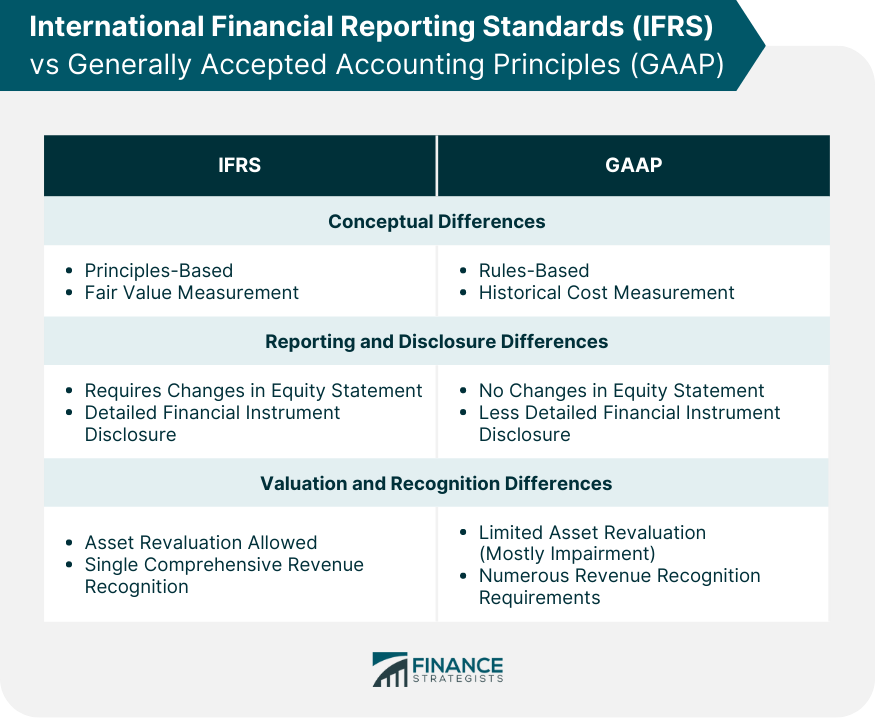
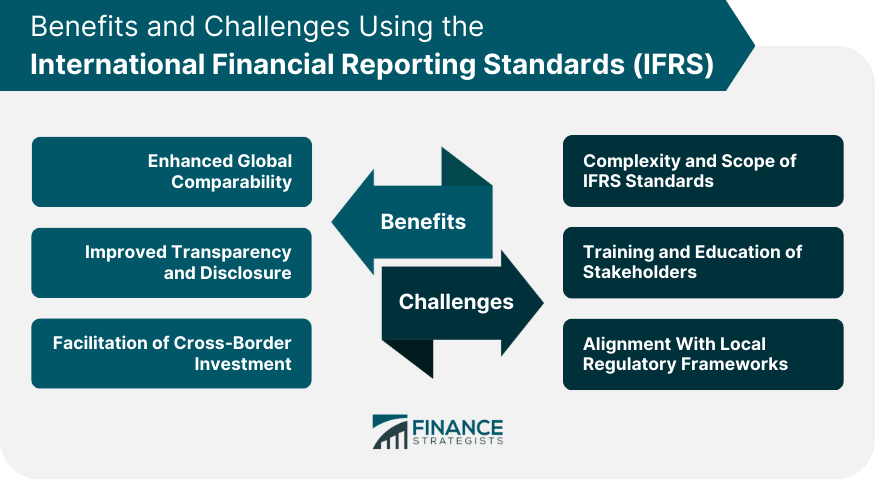
International Financial Reporting Standards, or IFRS, is a set of accounting standards aiming to provide transparency, accountability, and efficiency to financial markets across the globe. Adherence to IFRS standards allows for easy apples-to-apples comparisons of the financial state of different companies, and comparisons of the same company at multiple points in time. These standards aim to bring consistency to accounting language, practices and statements, enabling companies and their financial statements to be consistent, transparent, and comparable around the world. IFRS is increasingly adopted worldwide due to globalization and the need for a common language for financial reporting. The adoption of IFRS has facilitated better comparison and understanding of financial statements globally, making it easier for companies to attract foreign investment and enter foreign capital markets. IFRS originated in the European Union to bring consistency to accounting practices across the continent. It was soon adopted widely by other countries as a kind of universal accounting language, and is currently used by more than 120 countries. That being said, not all countries use IFRS; the US, for example, instead follows Generally Accepted Accounting Principles, or GAAP. Since 2002, however, the US-based Financial Accounting Standards Board, or FASB, and the EU-based International Accounting Standards Board, or IASB, have been working on marrying IFRS and GAAP in response to the increase in companies entering the global market. While the Securities Exchange Commission, or SEC, has said that it will not adopt IFRS in the US, some economists argue that switching to a more universally recognized system would save money on both duplicative reporting work and the cost of comparing countries internationally. The SEC has said, however, that it will continue reviewing proposals to allow IFRS information to supplement GAAP reports for US-based companies. In 2007, they also removed the requirement of non-US companies operating within the states to comply with GAAP reporting if they already comply with IFRS. Under IFRS, financial statements must present fairly the financial position, financial performance, and cash flows of an entity. Fair presentation requires faithfulness, substance over form, neutrality, prudence, and completeness. To achieve compliance with IFRS, entities must apply all applicable standards and interpretations. Non-compliance can lead to a fundamental error, which may require restatement of prior-period financial statements. Therefore, achieving fair presentation and compliance is critical in the realm of international financial reporting. The principle of substance over form requires financial transactions to be accounted for and presented according to their substance and economic reality, not merely their legal form. This principle ensures the financial statements provide a clear, comprehensive picture of the financial position of the company. This principle becomes particularly relevant in transactions that are designed to mask the true financial position or performance of a company. The substance over form principle requires these transactions to be accounted for in accordance with their true substance, thus promoting transparency and integrity in financial reporting. The going concern concept assumes that a company will continue its operations in the foreseeable future. It implies that the entity has neither the intention nor the need to liquidate or curtail materially the scale of its operations. The going concern principle impacts several aspects of financial reporting, including the valuation of assets and the presentation of liabilities. For instance, assets are not typically reported at their liquidation value (which might be the case if a company is not a going concern), while liabilities are not presented as immediately due (unless the business is ceasing operations). Under this method, transactions and other events are recognized when they occur, not when cash or its equivalent is received or paid. Therefore, the financial effects of transactions and other events are recognized and recorded in the financial statements of the periods to which they relate. The accrual basis of accounting provides a more accurate picture of a company's current and future financial position than the cash basis of accounting. It ensures that financial statements reflect all the expenses associated with the reported income for a period, not merely those that have been paid. The principle of materiality suggests that all relevant and material facts should be disclosed in the financial statements. Materiality depends on the size and nature of the item or error judged in the particular circumstances of its omission or misstatement. Aggregation involves adding together items with similar characteristics. The IFRS requires that a minimum line of items, such as assets, liabilities, equity, income, and expenses, should be presented separately on the face of the financial statements. But items that are not individually material within these categories may be aggregated. Consistency refers to the consistent application of accounting principles from one accounting period to another. It ensures that financial statements can be easily compared within a company over time. Comparability allows for comparisons of financial statements across different companies. This principle is especially important in the context of IFRS, as it allows investors and other users of financial statements to compare financial performance and position across different companies operating in different countries. The statement of financial position, commonly known as the balance sheet, provides information about an entity's financial position at a specific point in time. It presents an entity's economic resources, financial structure, liquidity and solvency, and its capacity to adapt to changes in the environment in which it operates. The balance sheet comprises assets, liabilities, and equity. Assets include items of value that the company owns, such as property, plant, and equipment, and intangible assets. Liabilities encompass what the company owes to others, including loans and payables. Equity, also known as net assets, is the residual interest in the assets of the entity after deducting liabilities. The statement of comprehensive income, also known as the income statement, presents the financial performance of an entity over a period of time. It provides information about an entity's profitability, financial sustainability, and the return to its investors. This statement consists of revenue, costs, gains, and losses. The bottom line, or net income, is calculated as revenue minus expenses. The income statement also includes other comprehensive income, which encompasses items that are not recognized in profit or loss, such as revaluation of property, plant, and equipment or gains from hedging activities. The statement of changes in equity presents an entity's changes in equity items during the reporting period. This includes profit or loss, each item of other comprehensive income, and the effects of changes in accounting policies and corrections of errors recognized in accordance with IFRS. This statement provides a bridge between the opening and closing balances of equity. By reading this statement, users of financial statements can understand how the equity position of a company has changed over a period and what transactions or other events have caused those changes. The statement of cash flows provides information about an entity's cash inflows and outflows during a reporting period from operating, investing, and financing activities. It also provides information about changes in cash and cash equivalents. By examining the statement of cash flows, users can evaluate an entity's ability to generate cash and cash equivalents and the needs of the entity to utilize those cash flows. This statement is especially important for users when assessing an entity's liquidity and solvency. IFRS is principles-based, which means it relies on a broad set of principles to guide financial reporting. On the other hand, GAAP is rules-based and relies on detailed and specific rules to guide financial reporting. Conceptual differences also extend to areas such as the measurement of assets and liabilities, where IFRS often requires or allows a fair value measurement basis, while GAAP typically relies on a historical cost basis. IFRS requires a statement of changes in equity, while GAAP does not. IFRS also requires an entity to present an analysis of expenses recognized in profit or loss using a classification based on either their nature or their function within the entity. IFRS is generally considered more detailed in its disclosure requirements, particularly regarding the nature and extent of an entity's use of financial instruments, its exposures to risks, and its capital management objectives, policies, and procedures. IFRS allows the revaluation of assets such as property, plant, and equipment and intangible assets, which can significantly impact the carrying value of these assets. On the contrary, GAAP generally only allows for the downward revaluation (impairment) of these assets. Similarly, differences exist in revenue recognition, where IFRS has a single, comprehensive revenue recognition standard, while GAAP has numerous revenue recognition requirements depending on the nature of the revenue. By using a single set of high-quality international standards, investors and other stakeholders can make more informed decisions as they can better compare companies' financial performance and position across different jurisdictions. This benefit extends beyond investors. Regulators can more effectively monitor financial markets across borders, while companies can compete on a more level playing field in raising capital, attracting investment, and expanding their operations. IFRS also promotes transparency and full disclosure, which can lead to better governance and accountability. The comprehensive and detailed disclosure requirements under IFRS can provide stakeholders with a fuller picture of a company's financial position and performance. Moreover, IFRS requires management to make judgments and estimates, promoting greater transparency about the company's unique circumstances. This can provide stakeholders with better insights into management's view of the company's future prospects. The use of IFRS can facilitate cross-border investment and transactions. It can make it easier for companies to list their securities on foreign exchanges. Investors can more confidently invest in foreign companies, knowing that the financial statements comply with globally recognized standards. Moreover, multinational corporations can more easily consolidate financial statements from their subsidiaries around the world. This can reduce the cost and complexity of preparing and auditing financial statements, thus promoting greater efficiency and cost savings. The complexity and scope of IFRS standards can pose significant hurdles, particularly for companies used to a rules-based system like GAAP. IFRS requires significant judgments and estimates, which can introduce a level of uncertainty and variability into financial statements. Companies need to understand the principles and interpretations underlying each standard and apply them consistently and accurately. Transitioning to IFRS requires extensive training and education of various stakeholders, including accountants, auditors, management, and even investors. The cost and time involved in training and education can be significant. Moreover, there is a need to educate investors and other users of financial statements to understand IFRS-compliant financial statements, particularly given the greater use of judgments and estimates. This can be a challenge, particularly in countries where stakeholders are not familiar with IFRS. Aligning IFRS with local regulatory frameworks can also be a challenge. Countries have their unique regulatory environments and accounting traditions. Thus, adoption of IFRS often requires not only changes in accounting standards but also changes in legislation and regulation, corporate governance, tax rules, and even business practices. Moreover, some countries may resist full adoption of IFRS due to concerns about loss of national sovereignty over accounting standards. These countries might opt for convergence rather than full adoption, which can result in variations from full IFRS. International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) is a set of accounting standards that aims to bring transparency, consistency, and efficiency to financial markets worldwide. The adoption of IFRS offers several benefits. It enhances global comparability, enabling stakeholders to make informed decisions by easily comparing companies' financial performance across different jurisdictions. Also, it improves transparency and disclosure, promoting better governance and accountability. IFRS's comprehensive disclosure requirements provide stakeholders with a fuller picture of a company's financial position and prospects. IFRS facilitates cross-border investment and transactions, making it easier for companies to attract foreign investment and expand their operations internationally. The complexity and scope of IFRS standards can be daunting for companies accustomed to a rules-based system. Training and education of stakeholders are necessary to understand and apply IFRS accurately. Aligning IFRS with local regulatory frameworks can be cumbersome, as it may require changes in legislation and business practices.Define IFRS in Simple Terms
What Does IFRS Mean in Finance?
Key Principles and Concepts of IFRS
Fair Presentation and Compliance
Substance Over Form
Going Concern Concept
Accrual Basis of Accounting
Materiality and Aggregation
Consistency and Comparability

IFRS Financial Statements
Balance Sheet
Income Statement
Changes in Equity
Cash Flows
Differences Between IFRS and Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP)
Conceptual Differences
Reporting and Disclosure Differences
Valuation and Recognition Differences
Benefits of IFRS Adoption
Enhanced Global Comparability
Improved Transparency and Disclosure
Facilitation of Cross-Border Investment
Challenges of Transitioning to IFRS
Complexity and Scope of IFRS Standards
Training and Education of Stakeholders
Alignment With Local Regulatory Frameworks
Conclusion
International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) FAQs
IFRS is an acronym for International Financial Reporting Standards.
International Financial Reporting Standards, or IFRS, is a set of accounting standards aiming to provide transparency, accountability, and efficiency to financial markets across the globe.
Not all countries use IFRS. The US, for example, instead follows Generally Accepted Accounting Principles, or GAAP.
The Securities Exchange Commission, or SEC, has said that it will not adopt IFRS in the US.
Since 2002, the US based Financial Accounting Standards Board, or FASB, and the EU based International Accounting Standards Board, or IASB, have been working on marrying IFRS and GAAP in response to the increase in companies entering the global market.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











