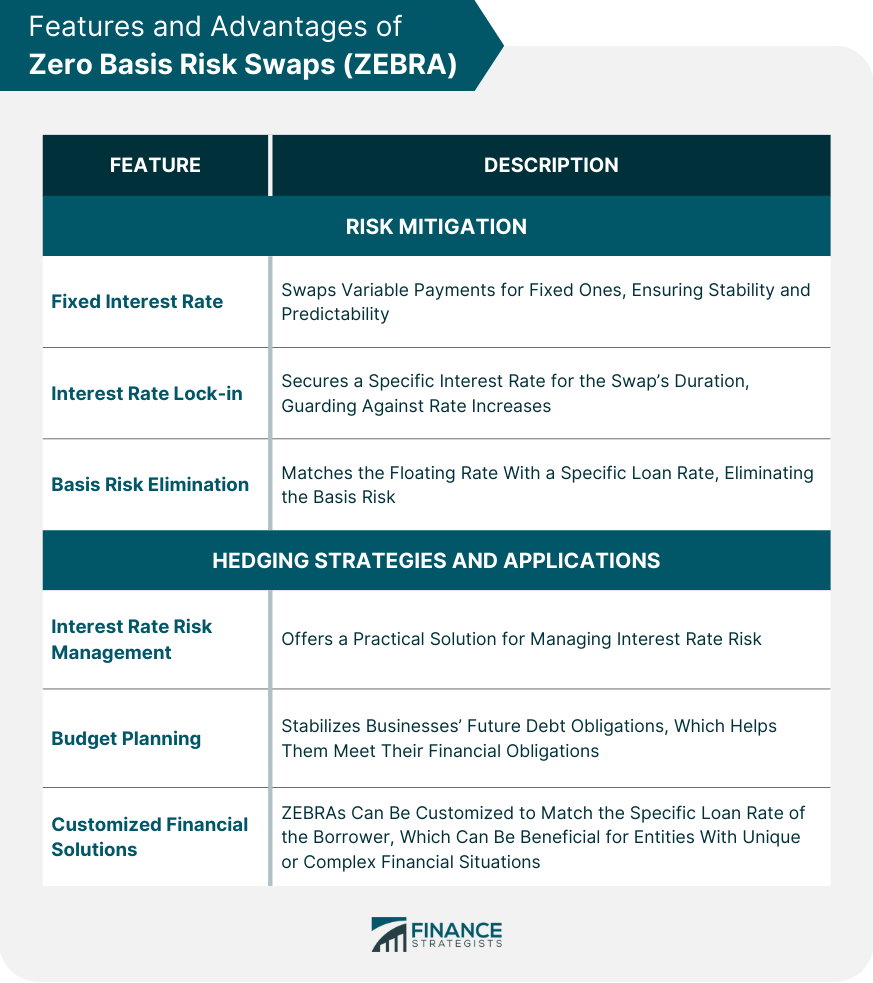
A Zero Basis Risk Swap (ZEBRA) is a unique form of interest rate swap, where the floating rate of the swap aligns with an underlying loan rate. This derivative financial instrument enables businesses and institutions to hedge interest rate risks while eliminating the basis risk inherent in traditional interest rate swaps. Essentially, ZEBRAs provide an efficient method for entities to stabilize their interest rate environment. In the realm of financial management, ZEBRAs are instrumental in maintaining fiscal stability. By creating a swap contract that matches the variable interest rate of an existing loan, entities can convert a variable interest rate to a fixed one. This allows for better planning, budget forecasting, and a reduction in the risk exposure associated with fluctuating interest rates. In a ZEBRA, two parties agree to exchange interest payments on a specific principal amount, the notional principal, over a certain period. The swap involves one party paying a fixed rate while the other paying a floating rate equal to the rate on an outstanding loan. This feature differentiates ZEBRAs from typical interest rate swaps and offers the advantage of zero basis risk. The parties involved in a ZEBRA typically include an entity with a floating rate loan (the borrower) and a counterparty, often a financial institution, willing to engage in the swap. The borrower pays a fixed rate and receives a floating rate that matches the loan rate, thereby eliminating the basis risk. ZEBRAs provide a comprehensive method for risk mitigation. They possess several noteworthy features that collectively contribute to reducing the risk associated with interest rate fluctuations: Fixed Interest Rate: ZEBRAs allow borrowers with a floating rate loan to swap their variable interest payments for fixed ones. This conversion to a fixed rate provides stability and predictability, safeguarding against the risk of interest rate volatility. Interest Rate Lock-In: With ZEBRAs, borrowers can lock in a specific interest rate for the duration of the swap agreement. This feature shields the borrower from potential increases in interest rates, thereby offering a significant measure of protection against market volatility. Basis Risk Elimination: Basis risk, the risk that the floating rate of an interest rate swap won't match the rate of an underlying loan, is entirely removed in ZEBRAs. By aligning the floating rate with the specific loan rate, ZEBRAs eliminate this risk, enhancing their risk mitigation capability. In the context of hedging strategies, ZEBRAs prove to be an invaluable tool for financial risk management. They offer several key advantages: Interest Rate Risk Management: ZEBRAs offer a practical solution for managing interest rate risk. Businesses with large variable-rate loans can use a ZEBRA to mitigate the risk of rising interest rates, thereby securing predictable and stable loan repayments. Budget Planning: With ZEBRAs, businesses can stabilize their future debt obligations, facilitating budget planning. Fixed payments' predictability helps businesses meet their financial obligations without undue strain from interest rate increases. Customized Financial Solutions: Unlike standardized futures and forward contracts, ZEBRAs can be customized to match the specific loan rate of the borrower, providing an exact hedge. This level of customization can be particularly beneficial for entities with unique or complex financial situations. By offering such features and advantages, ZEBRAs are crucial in providing stability and certainty in an entity's financial planning and risk management strategy. The valuation of a ZEBRA follows the general principles of other interest rate swaps. However, its unique feature of matching the floating rate to a specific loan rate demands a distinct approach to the calculation. The difference between the present value of fixed-rate payments and the present value of floating-rate payments determines the swap's value. Several factors can influence the valuation of a ZEBRA. These include the notional principal amount, fixed and floating interest rates, the swap duration, and the parties' creditworthiness. Additionally, the specific characteristics of the loan matched to the swap, such as its term and the frequency of interest payments, can significantly affect the swap's value. Although ZEBRAs and traditional interest rate swaps share similarities, their key difference lies in their treatment of floating rates. While the latter's floating rate is typically tied to a benchmark such as LIBOR, a ZEBRA matches the rate to a specific loan. When compared to futures and forwards, ZEBRAs offer the distinct advantage of customization. Futures and forwards contracts are standardized and may not offer the precise hedging desired. However, a ZEBRA can be tailored to match the specific rate of a borrower's loan, providing an exact hedge. ZEBRAs apply to various sectors such as banking, telecommunications, energy, etc. Any industry where entities have substantial floating rate loans can benefit from the risk management potential of ZEBRAs. Despite their advantages, ZEBRAs have challenges. The most prominent constraint is finding a willing counterparty for the swap. Moreover, ZEBRAs, like other derivatives, are exposed to credit risk — the risk that the counterparty may default on its obligations. ZEBRAs, like other derivative contracts, are subject to specific regulatory oversight in many jurisdictions. Authorities such as the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) and the U.K.'s Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) ensure that these contracts meet stringent transparency, disclosure, and risk management standards. As a result, parties involved in ZEBRA transactions must be aware of and comply with the regulatory requirements in their respective jurisdictions. While not strictly regulatory, ethical considerations play a significant role in the ZEBRA market. All parties are expected to conduct business in a fair and transparent manner, ensuring that neither party manipulates the swap terms to their undue advantage. In a financial world increasingly dominated by complex instruments, the appeal of ZEBRAs and their straightforward risk mitigation will likely grow. Coupled with the shift towards more tailored financial solutions, ZEBRAs are expected to increase, especially among businesses with significant floating-rate debt exposure. Technology's role in the financial sector continues to evolve, including the market for ZEBRAs. Blockchain technology, for example, could streamline the execution and settlement of ZEBRA contracts, making them more accessible and less administratively burdensome. These advancements could further enhance the attractiveness of ZEBRAs in the coming years. A ZEBRA is a unique type of interest rate swap that matches the floating rate to an underlying loan, thereby eliminating the basis risk. It's a powerful financial tool institution use to mitigate interest rate risk, especially in volatile market conditions. ZEBRAs offer significant advantages, such as risk mitigation and aligning interest rates with business objectives. Despite their benefits, they also have limitations, including the need for a willing counterparty and exposure to credit risk. Furthermore, they are subject to regulatory requirements and ethical standards. For institutions seeking to manage their financial risk, it's crucial to consider tools like ZEBRAs as part of a comprehensive wealth management strategy. Contact a trusted financial advisor to understand how ZEBRAs can fit into your risk management plan.What Is a Zero Basis Risk Swap (ZEBRA)?
Mechanism of Zero Basis Risk Swaps
Working Principle
Parties Involved
Features and Advantages of Zero Basis Risk Swaps
Risk Mitigation
Hedging Strategies and Applications
Calculation and Valuation in Zero Basis Risk Swaps (ZEBRA)
Formula and Numerical Explanation
Impact Factors on ZEBRA Valuation
Comparison of Zero Basis Risk Swaps (ZEBRA) With Other Financial Derivatives
ZEBRA vs Interest Rate Swaps
ZEBRA vs Futures and Forwards
Applications and Limitations of Zero Basis Risk Swaps
Usage in Various Sectors
Constraints and Challenges
Regulatory Considerations in Zero Basis Risk Swaps (ZEBRA)
Legal and Regulatory Framework
Ethical Considerations
Future Outlook for Zero Basis Risk Swaps
Emerging Trends
Impact of Technological Advancements
Conclusion
Zero Basis Risk Swap (ZEBRA) FAQs
The primary purpose of a ZEBRA is to hedge against interest rate risk by allowing entities to swap a floating interest rate for a fixed one, thereby providing payment stability.
Unlike traditional interest rate swaps, where the floating rate is often tied to a benchmark, a ZEBRA matches the floating rate to a specific loan, eliminating the basis risk.
ZEBRAs are commonly used across various industries, including banking, telecommunications, and energy, especially where entities have significant floating rate loans.
Like other financial derivatives, ZEBRAs carry certain risks, including the credit risk of the counterparty defaulting on their obligations.
ZEBRAs, like other derivatives, are subject to specific regulatory oversight to ensure transparency, disclosure, and adequate risk management. The regulatory framework can vary by jurisdiction.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











