Education tax credits are financial incentives the federal government provides to help offset the costs of higher education for eligible students and their families. These credits reduce the income tax taxpayers owe, potentially resulting in a refund. The U.S. Internal Revenue Service (IRS) administers these tax credits, and taxpayers must meet specific eligibility requirements to claim them. The primary purpose of education tax credits is to alleviate the financial burden of pursuing higher education and to encourage more individuals to attend college or vocational training. By providing tax relief, these credits help make higher education more accessible and affordable for millions of students and their families. Promoting education contributes to a better-educated workforce, which benefits the economy as a whole. The American Opportunity Tax Credit (AOTC) is designed for students enrolled in their first four years of postsecondary education. To be eligible for the AOTC, the student must be enrolled at least half-time in a degree or certificate program at an eligible institution. Additionally, the student must not have completed the first four years of postsecondary education at the beginning of the tax year, and they can only claim the credit for up to four tax years. The AOTC covers a range of education-related expenses, including tuition, fees, and course materials required for enrollment. However, the credit does not cover expenses for room and board, transportation, or other personal costs. Keeping records of all qualified expenses is essential to calculate the credit when filing tax returns accurately. The Lifetime Learning Credit (LLC) is available to students enrolled in any level of postsecondary education, including undergraduate, graduate, and professional degree courses and job training courses. There is no limit to the number of years a taxpayer can claim the LLC. However, unlike the AOTC, the LLC cannot be claimed for expenses paid with tax-free assistance, such as scholarships or grants. Like the AOTC, the LLC covers tuition, fees, and other required enrollment expenses, but it does not cover room and board or personal costs. Additionally, the LLC only applies to course materials if they must be purchased directly from the educational institution as a condition of enrollment. As with the AOTC, keeping accurate records of qualified expenses is crucial for claiming credit. While both the AOTC and LLC help offset higher education costs, they have different eligibility requirements. The AOTC is limited to the first four years of postsecondary education and requires the student to be enrolled at least half-time. The LLC is available for any level of postsecondary education, with no requirement for a minimum course load. Both credits cover tuition and fees but differ in what they consider qualified expenses. The AOTC includes required course materials as qualified expenses, regardless of where they are purchased. At the same time, the LLC only covers course materials if they must be purchased directly from the educational institution as a condition of enrollment. To claim either the AOTC or LLC, taxpayers must obtain a Form 1098-T, Tuition Statement, from their educational institution. This form outlines the tuition and fees paid during the tax year and any scholarships or grants received. Reviewing the form for accuracy and reporting any discrepancies to the educational institution is essential. In addition to Form 1098-T, taxpayers should maintain records of all qualified expenses, such as receipts for tuition, fees, and course materials. These records are necessary for accurately calculating the tax credit and may be requested by the IRS in the event of an audit. To claim either the AOTC or LLC, taxpayers must complete Form 8863, Education Credits, and attach it to their Form 1040, U.S. Individual Income Tax Return. This form includes sections for calculating both credits and requires information from Form 1098-T and records of qualified expenses. Taxpayers must file Form 1040, U.S. Individual Income Tax Return, to claim education tax credits. The total amount of the credit is reported on the appropriate line of Form 1040, reducing the taxpayer's total tax liability. It's crucial to carefully follow the instructions for Form 8863 and Form 1040 to ensure accurate reporting of the credits. Education tax credits can affect the amount of financial aid a student receives. Scholarships and grants may reduce the amount of eligible expenses for the AOTC or LLC. Taxpayers should carefully review their financial aid packages and consult with a tax professional to determine the best approach for claiming education tax credits. Education tax credits do not directly affect student loans, as loan disbursements are considered a form of payment rather than income. However, claiming an education tax credit may reduce a student's overall tax liability, potentially freeing up additional funds to repay student loans. There may be proposed legislation at the federal or state level that could affect education tax credits. Staying informed about potential changes can help taxpayers plan for future tax years and maximize their potential benefits. Various advocacy groups and organizations may push for expanded or modified education tax credits better to serve the needs of students and their families. Understanding these proposals can help taxpayers advocate for changes that benefit them and the broader community. Education tax credits can significantly reduce the financial burden of higher education for eligible students and their families. By understanding and taking advantage of these credits, taxpayers can make postsecondary education more accessible and affordable, contributing to a better-educated workforce and a stronger economy. Staying informed about changes to education tax credits is essential for maximizing potential benefits. Taxpayers should monitor IRS announcements, consult tax professionals, and follow reputable news sources to stay up-to-date on any changes that may affect their eligibility or the amount of credit they can claim. Given the complexities of education tax credits and their potential impact on taxpayers' financial situation, consulting with a tax services professional is highly recommended. A qualified tax expert can provide personalized guidance on claiming credits, maximizing benefits, and navigating the ever-changing tax landscape.What Are Education Tax Credits?
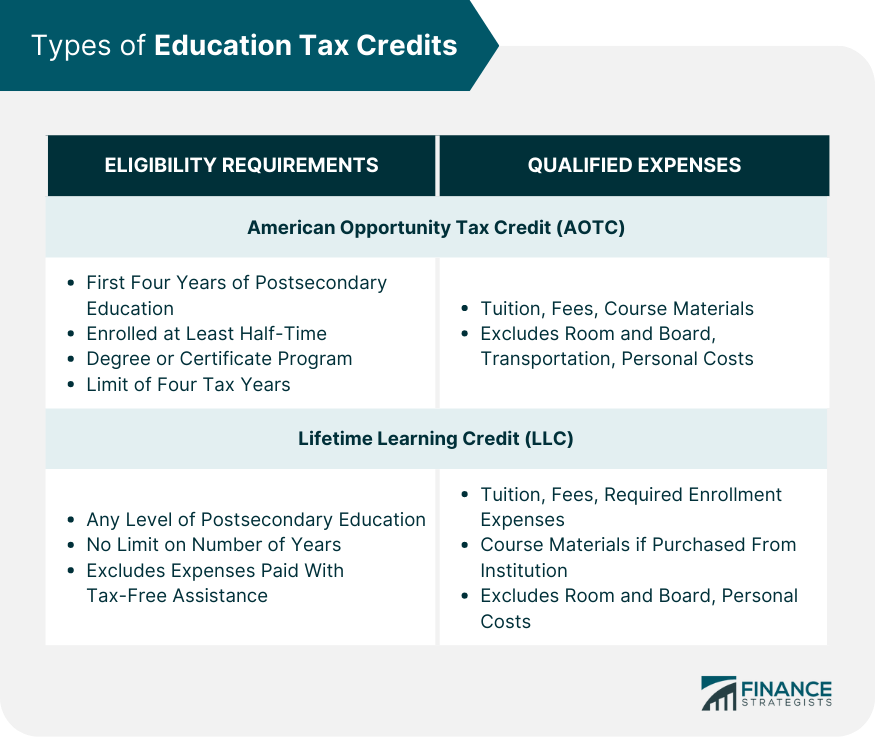
Types of Education Tax Credits
American Opportunity Tax Credit (AOTC)
Eligibility Requirements
Qualified Expenses
Lifetime Learning Credit (LLC)
Eligibility Requirements
Qualified Expenses
Comparing AOTC and LLC
Differences in Eligibility Requirements
Differences in Qualified Expenses
How to Claim Education Tax Credits
Documentation Required
Form 1098-T: Tuition Statement
Records of Qualified Expenses
Tax Forms to Complete
Form 8863: Education Credits
Form 1040: US Individual Income Tax Return
Impact of Education Tax Credits on Financial Aid
Interaction With Scholarships and Grants
Effect on Student Loans
Potential Changes to Education Tax Credits
Proposed Legislation
Advocacy for Expanded or Modified Tax Credits
Conclusion
Education Tax Credits FAQs
Education tax credits are financial incentives the federal government provides to help offset the cost of education expenses. They can reduce the amount of income tax you owe, potentially leading to a larger tax refund.
There are two main types of education tax credits: the American Opportunity Tax Credit (AOTC) and the Lifetime Learning Credit (LLC). The AOTC is for undergraduate education expenses, while the LLC can be used for undergraduate, graduate, and continuing education expenses.
Eligibility for education tax credits depends on factors such as your modified adjusted gross income (MAGI), enrollment status, and eligible education expenses. You must also be enrolled in an eligible educational institution. Specific eligibility requirements vary between the AOTC and LLC.
To claim education tax credits, you must file IRS Form 8863, "Education Credits (American Opportunity and Lifetime Learning Credits)," along with your federal income tax return. You'll need to provide information about your education expenses and the educational institution you attended.
No, you cannot claim both the American Opportunity Tax Credit (AOTC) and the Lifetime Learning Credit (LLC) for the same student in the same tax year. However, if you have multiple students in your household, you can claim one credit for one student and the other credit for a different student.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.















