A Non-Qualified Annuity is a long-term investment product issued by an insurance company. Unlike a Qualified Annuity, it doesn't offer tax-deductible contributions but allows for unrestricted deposit amounts. The investor funds it with after-tax dollars, allowing growth to be tax-deferred until withdrawal. Upon withdrawal, only the earnings part of the annuity is taxable. A unique feature is its lack of annual contribution limits, making it attractive to those who wish to invest substantial sums for retirement. The investor chooses between immediate or deferred payouts, providing a level of income flexibility. Non-Qualified Annuities can play a pivotal role in enhancing retirement income strategies and supplementing other income sources. It's important to understand the potential fees, surrender charges, and the overall impact on one's financial planning goals before investing. Non-qualified annuities are typically purchased with after-tax dollars, meaning the money you've already paid taxes on. You can buy these annuities from insurance companies, and the funds you invest can be allocated to various investment options based on your risk tolerance and financial goals. A key advantage of non-qualified annuities is tax deferral. The income and gains from these annuities are not taxed until they are withdrawn, which could potentially be years or decades in the future. Non-qualified annuities have specific rules for withdrawals. In general, you can start taking distributions at age 59½ without incurring a 10% early withdrawal penalty, although the income portion of your withdrawal will be taxed as ordinary income. An immediate annuity provides income right after you purchase it. You make a lump-sum payment, and in return, the insurer guarantees a certain amount of income for a specified period or the rest of your life. Deferred annuities accumulate income over time. The income payments begin at a future date, often after retirement, allowing your money to grow tax-deferred in the meantime. Fixed annuities offer a guaranteed rate of return, providing you with steady, predictable income. They are a lower-risk investment compared to other types of annuities. Variable annuities allow you to choose your investments, so your return depends on their performance. While these offer the potential for higher returns, they also carry more risk. During this phase, you invest in the annuity using after-tax dollars. Your money grows on a tax-deferred basis. This phase is when you start receiving income payments. These payments can last for a set period or the remainder of your life, depending on the contract terms. Many annuities have a surrender period, a set number of years during which you would incur a penalty for withdrawals above a certain limit. Understanding these charges and the surrender period is essential before investing. During the accumulation phase, your investment grows tax-deferred. You don't pay taxes on the gains until you make a withdrawal. During the distribution phase, your income is taxed as ordinary income. It's important to note that only the income portion is taxed, not the portion representing your original investment. If you make an early withdrawal before age 59½, you may incur a 10% penalty in addition to regular income taxes. Non-qualified annuities can be a valuable tool for retirement planning. They offer a guaranteed income stream, providing stability and predictability in retirement. The tax-deferred growth offered by non-qualified annuities can be a significant advantage, especially for individuals in higher tax brackets. Annuities can provide a lifetime income stream, reducing the risk of outliving your savings—a crucial benefit for those with longevity in their family. Annuities often come with various fees and charges, including surrender charges, management fees, and mortality and expense risk charges. These fees can eat into your returns. Annuities are not very liquid, and early withdrawals can result in hefty penalties. This lack of liquidity can be a disadvantage for those needing frequent access to their funds. Variable annuities carry market risk. The value of your investment can fluctuate based on the performance of the investment options you choose. Non-qualified annuities can play a key role in your financial planning, particularly in diversifying your investment portfolio, planning for retirement income, and long-term care planning. Diversifying Investment Portfolio: Non-qualified annuities can provide a layer of diversification to your investment portfolio, helping to spread risk and potentially enhance returns. Planning for Retirement Income: With the potential for a guaranteed lifetime income, non-qualified annuities can form a central part of your retirement income planning. Long-Term Care Planning: Some non-qualified annuities come with long-term care benefits, offering a way to fund potential long-term care expenses. Non-qualified annuities are subject to various regulations, including insurance company regulations, federal and state tax laws, and consumer protection laws. Insurance Company Regulations: Insurance companies offering annuities must adhere to regulations set by state insurance commissions and other regulatory bodies to ensure financial solvency and protect consumers. Federal and State Tax Laws: Non-qualified annuities are subject to federal tax laws and, potentially, state tax laws, depending on where you live. Consumer Protection Laws: There are numerous laws in place to protect consumers from misleading sales practices and to ensure they have all the necessary information to make informed decisions. Your financial goals and risk tolerance should guide your decision. If you're close to retirement and seek stability, a fixed annuity may be more suitable. But if you're younger and willing to take on more risk for potentially higher returns, a variable annuity might be a better fit. Comparing different annuity products can help you find the best fit for your needs. Look at the fees, surrender charges, guaranteed rate of return, and other features. Reading and understanding the annuity contract is essential. The contract outlines your rights and the obligations of the insurance company, providing clarity on how the annuity works. Non-qualified annuities, a type of long-term investment product, provide unique benefits, including tax-deferred growth and an unrestricted contribution limit. Funded with after-tax dollars, these annuities allow for flexible payout options, enhancing retirement income strategies. They come in various forms, including immediate, deferred, fixed, and variable, each catering to different investor needs. Despite the benefits, potential investors should be mindful of possible fees, lack of liquidity, and market risks. Crucial to understanding these complex financial products are their tax implications, the surrender period, and charges. Key to successful investment is aligning with personal financial goals, risk tolerance, and careful product comparison. Understanding the contract terms is vital. Overall, non-qualified annuities can serve as an effective tool for diversifying an investment portfolio, planning retirement income, and even facilitating long-term care planning.Non-Qualified Annuity Overview
Features of Non-Qualified Annuities
Funding and Investment Options
Tax Deferral Benefits
Withdrawal Rules

Types of Non-Qualified Annuities
Immediate Annuities
Deferred Annuities
Fixed Annuities
Variable Annuities
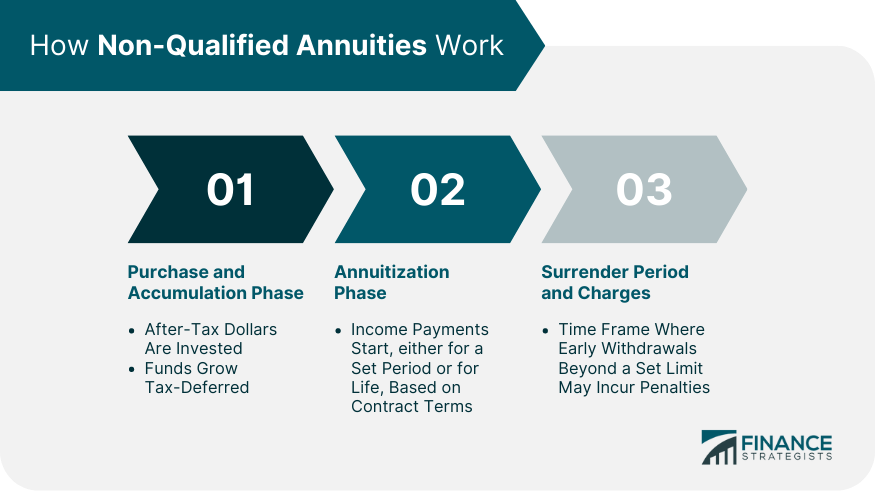
How Non-Qualified Annuities Work
Purchase and Accumulation Phase
Annuitization Phase
Surrender Period and Charges
Tax Implications of Non-Qualified Annuities
Tax Treatment During Accumulation Phase
Tax Treatment During the Distribution Phase
Impact of Early Withdrawals
Benefits of Non-Qualified Annuities
Retirement Planning
Tax Advantages
Lifetime Income Stream
Drawbacks and Risks of Non-Qualified Annuities
Possible Fees and Charges
Lack of Liquidity
Market Risk for Variable Annuities
Role of Non-Qualified Annuities in Financial Planning
Regulations for Non-Qualified Annuities
Evaluating Non-Qualified Annuities
Consideration of Financial Goals and Risk Tolerance
Comparison of Annuity Products
Understanding the Annuity Contract
Final Thoughts
Non-Qualified Annuity FAQs
Non-qualified annuities are a type of annuity that is purchased with after-tax dollars. Unlike qualified annuities, they do not comply with the Internal Revenue Code's requirements for a tax-advantaged retirement account, resulting in different tax implications.
With non-qualified annuities, your investments grow on a tax-deferred basis, meaning you do not pay taxes on the income and gains until you withdraw the funds. If withdrawals are made before age 59½, there might be a 10% early withdrawal penalty in addition to regular income taxes.
Non-qualified annuities can be a valuable tool for retirement planning because they can provide a guaranteed income stream for a specific period or the remainder of your life. This can offer stability and predictability in retirement.
Non-qualified annuities often come with various fees and charges, including surrender charges for early withdrawals. They also lack liquidity due to penalties associated with early withdrawals. For variable annuities, there's also the risk associated with market fluctuations.
When evaluating non-qualified annuities, it's crucial to consider your financial goals and risk tolerance. Comparing different annuity products and considering their fees, surrender charges, guaranteed rate of return, and other features are also key. Understanding the annuity contract is vital to know your rights and the obligations of the insurance company.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











