Entity-purchase agreements are legal contracts that outline the terms and conditions of a transaction involving the sale and purchase of a business entity, such as a corporation, partnership, or limited liability company. These agreements detail the responsibilities and rights of the buyers and sellers and address various aspects of the transaction, including purchase price, payment terms, assets and liabilities being transferred, representations and warranties, and pre-closing and post-closing covenants. Entity-purchase agreements play a critical role in mergers and acquisitions, business restructurings, and other transactions involving the transfer of ownership or control of a business entity. They help to provide a framework for the negotiation, due diligence, and completion of the transaction, while also serving to protect the interests of both buyers and sellers.
I'm Taylor Kovar, a Certified Financial Planner (CFP), specializing in helping business owners with strategic financial planning. Entity-Purchase Agreements are crucial for businesses to ensure a smooth transition of ownership in case a key member exits. To effectively manage these, start by accurately valuing your business and ensuring the agreement is funded, often through life insurance policies on the members involved. This approach guarantees liquidity for purchasing the departing member's share, securing the business's future. It's crucial to consult with a financial advisor to tailor the agreement to your specific needs. Contact me at (936) 899 - 5629 or [email protected] to discuss how we can achieve your financial objectives. WHY WE RECOMMEND: IDEAL CLIENTS: Business Owners, Executives & Medical Professionals FOCUS: Strategic Planning, Alternative Investments, Stock Options & Wealth Preservation These are the entities or individuals who acquire the ownership or a portion of the target entity. Their responsibilities and rights are clearly defined in the agreement. The buyer's primary responsibilities include conducting due diligence, negotiating the terms, and making the necessary payments as agreed upon. The sellers are the current owners or shareholders of the target entity. They are responsible for providing accurate information about the business, its assets, and liabilities. The seller must also ensure that all the necessary legal and regulatory requirements are met. Depending on the specific transaction, other stakeholders may also be involved. These could include lenders, investors, advisors, and regulatory bodies. Several methods can be employed to determine the value of the target entity. Common valuation approaches include discounted cash flow analysis, comparable company analysis, and precedent transactions analysis. The payment terms in an entity-purchase agreement should clearly outline the timing and methods of payment. This may include a combination of cash, stocks, or other forms of consideration. The agreement may also include provisions for milestone payments, escrow arrangements, or earn-out provisions based on the target's future performance. Escrow arrangements can be used to secure a portion of the purchase price to ensure that certain conditions or contingencies are met. This can provide additional protection for both the buyer and the seller in the event of disputes or unforeseen circumstances. The entity-purchase agreement must clearly list and describe the assets being transferred, which may include tangible assets, such as property, equipment, and inventory, as well as intangible assets, such as intellectual property, contracts, and goodwill. The agreement should also specify which liabilities the buyer is assuming from the seller. This may include outstanding debts, obligations, and legal liabilities. In some cases, certain assets or liabilities may be excluded from the transaction or reserved for future disposition. These should be clearly identified and addressed in the agreement. The seller typically makes certain representations and warranties to the buyer regarding the target entity's operations, financial condition, and compliance with applicable laws and regulations. These may cover topics such as the accuracy of financial statements, the absence of undisclosed liabilities, and the ownership of intellectual property rights. The buyer also makes representations and warranties to the seller, which may include the buyer's financial capability to complete the transaction, the absence of litigation, and compliance with applicable laws and regulations. The entity-purchase agreement may include disclosure schedules that list specific exceptions to the representations and warranties. These schedules help to clarify the scope of the representations and warranties and provide a basis for indemnification claims if any inaccuracies are discovered. These covenants outline the actions that both parties agree to take before closing the transaction. This may include obtaining regulatory approvals, maintaining the target entity's business operations, or satisfying any other pre-closing conditions. Closing conditions are specific requirements that must be met before the transaction can be finalized. These may include regulatory approvals, the completion of due diligence, or the fulfillment of certain financial or operational benchmarks. These covenants outline the parties' obligations and commitments after the transaction is complete. They may include agreements on non-competition, non-solicitation, indemnification, or transition support. Certain transactions may require regulatory approvals or filings with the appropriate authorities. These may include antitrust or competition clearances, securities filings, or industry-specific approvals. Entity-purchase agreements may be subject to review by antitrust or competition authorities to ensure that the transaction does not result in an undue concentration of market power. Parties must be mindful of these laws and ensure that their transaction is structured in a manner that complies with applicable regulations. The transfer of ownership in an entity-purchase agreement may have implications for the employees of the target entity. Parties should be aware of and address any potential issues related to employment contracts, labor laws, and employee benefits. The buyer must ensure that the target entity complies with all relevant environmental and safety regulations. This may include conducting environmental assessments, obtaining permits, or addressing any existing non-compliance issues. The transfer of intellectual property rights and licenses is a critical aspect of many entity-purchase agreements. Parties must carefully address the transfer and protection of these rights, as well as any potential issues related to third-party licenses or infringements. A thorough legal due diligence process is essential for both the buyer and the seller to identify potential risks and liabilities associated with the target entity. This process typically includes a review of the target's contracts, litigation history, and regulatory compliance. Financial due diligence involves a comprehensive examination of the target entity's financial statements, tax filings, and other financial records. This process helps the buyer assess the financial health and stability of the target and identify any potential risks or liabilities. Operational due diligence focuses on the target entity's business operations, including its processes, systems, and infrastructure. This can help the buyer identify potential efficiency improvements and assess the compatibility of the target's operations with its own. The entity-purchase agreement should include indemnification provisions that protect both parties from losses arising from breaches of representations, warranties, or covenants. These provisions should clearly define the scope and limitations of each party's liability. Purchase price adjustments and earn-outs can be used as mechanisms to manage risks and uncertainties associated with the target entity's future performance. These provisions should be carefully negotiated and structured to align the interests of both parties. The agreement should include dispute resolution mechanisms, such as arbitration or mediation, to address any disputes that may arise during the transaction process. These mechanisms can provide a more efficient and cost-effective alternative to litigation. The entity-purchase agreement should specify the required closing deliverables and conditions precedent that must be satisfied before the transaction can be finalized. This may include executed contracts, regulatory approvals, or other documentation. Post-closing adjustments may be necessary to account for any changes in the target entity's financial condition or operations that occur between signing and closing. Additionally, the parties may be required to provide notifications to relevant stakeholders, such as customers, suppliers, or regulatory authorities, following the completion of the transaction. Effective integration and transition planning is crucial to the success of an entity-purchase agreement. This may involve the development of a detailed integration plan, addressing issues such as employee communication, systems integration, and the alignment of business processes. Both buyers and sellers should approach negotiations with a clear understanding of their objectives and priorities. This includes being well-prepared with accurate information, a strong understanding of the target entity's operations, and a willingness to compromise when necessary. Conducting thorough due diligence is essential to identify and address potential risks and liabilities associated with the target entity. Inadequate due diligence can lead to unforeseen problems and disputes after the transaction has closed. To ensure a smooth transaction process, parties should take care to avoid common drafting errors in the entity-purchase agreement. This includes using clear and unambiguous language, consistently defining terms, and ensuring that all necessary provisions are included. Clear communication and alignment of expectations between the parties are vital for a successful transaction. This includes regular updates on the progress of the transaction, addressing concerns or questions promptly, and maintaining open lines of communication throughout the process. Entity-purchase agreements play a crucial role in transactions involving the sale and purchase of a business entity. Key components include clearly defining the parties involved, addressing the purchase price and payment terms through proper valuation methods, identifying assets being transferred and liabilities being assumed, and establishing representations, warranties, and disclosure schedules. Pre-closing and post-closing covenants and conditions, along with legal and regulatory considerations, such as obtaining regulatory approvals and complying with antitrust, labor, environmental, and intellectual property laws, are also essential. Risk management and mitigation involve conducting thorough due diligence, incorporating indemnification and liability provisions, and implementing dispute resolution mechanisms. The closing process and post-closing obligations, including adjustments, notifications, and integration planning, should be carefully managed. To ensure a successful transaction, parties should follow best practices such as effective negotiation strategies, thorough due diligence, avoiding drafting errors, and maintaining clear communication and alignment of expectations.What Are Entity-Purchase Agreements?
Learn From Taylor

Fee-Only Financial Advisor
Certified Financial Planner™
3x Investopedia Top 100 Advisor
Author of The 5 Money Personalities & Keynote Speaker
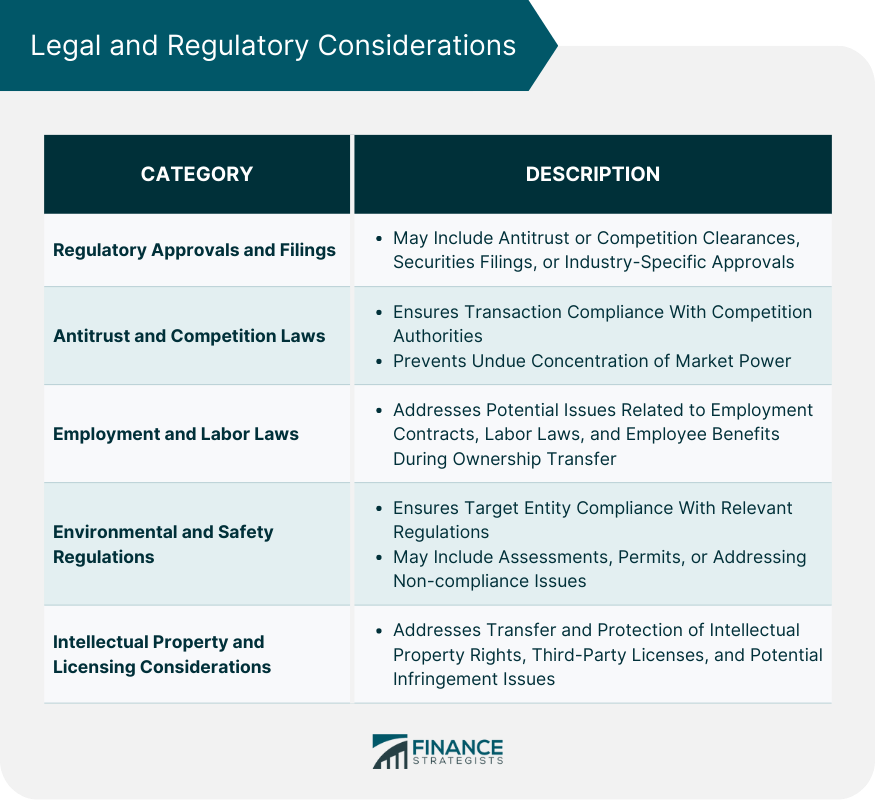
Key Components of Entity-Purchase Agreements
Parties Involved
Buyers
Sellers
Other Relevant Stakeholders
Purchase Price and Payment Terms
Valuation Methods
Payment Schedule and Methods
Escrow Arrangements, if Applicable
Assets and Liabilities
Identification of Assets Being Transferred
Assumption of Liabilities
Exclusions or Reservations of Specific Assets or Liabilities
Representations and Warranties
Seller's Representations and Warranties
Buyer's Representations and Warranties
Disclosure Schedules and Exceptions
Covenants and Conditions
Pre-Closing Covenants
Closing Conditions
Post-Closing Covenants
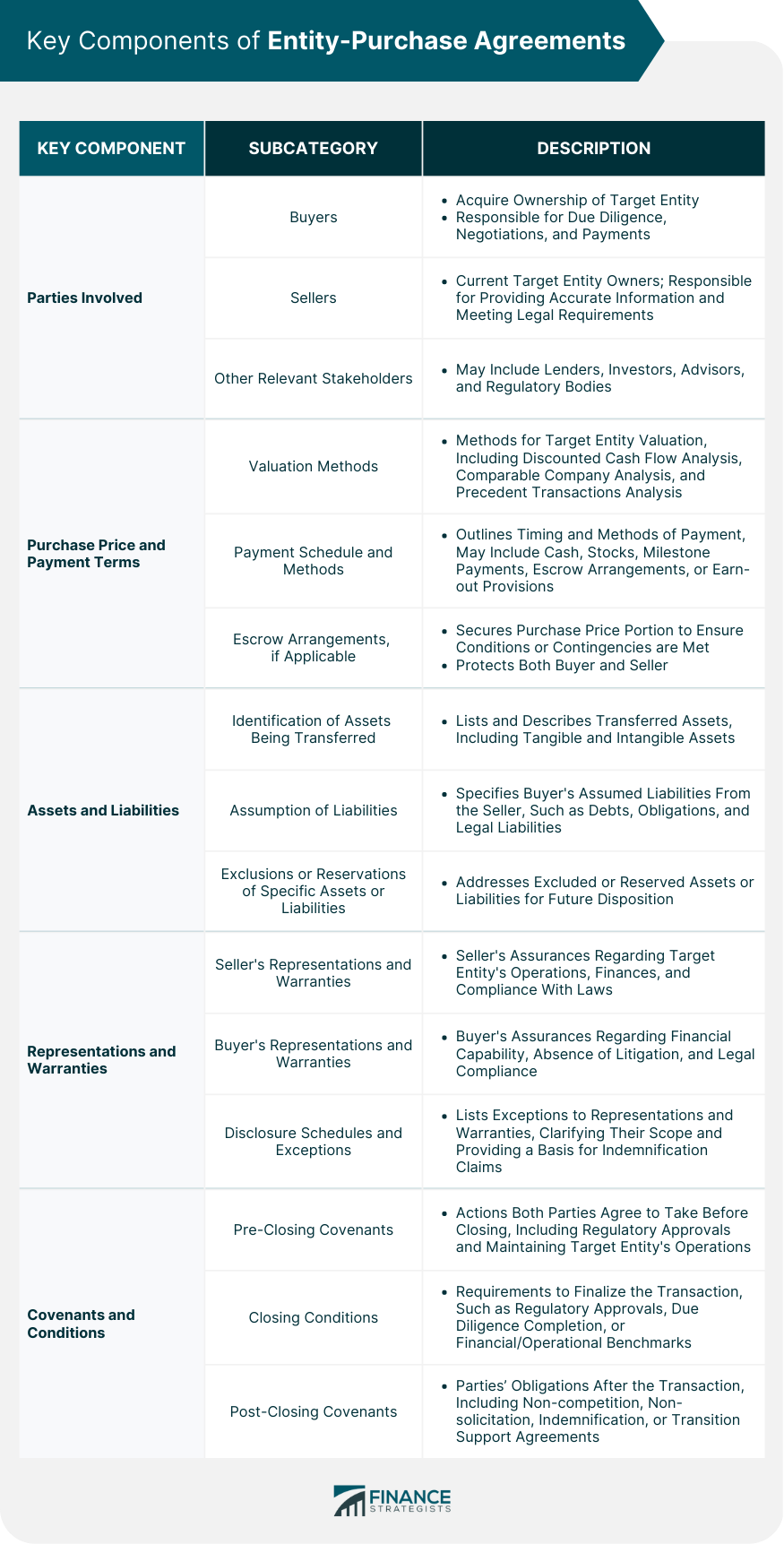
Legal and Regulatory Considerations
Regulatory Approvals and Filings
Antitrust and Competition Laws
Employment and Labor Laws
Environmental and Safety Regulations
Intellectual Property and Licensing Considerations
Risk Management and Mitigation
Due Diligence Process
Legal
Financial
Operational
Indemnification and Liability Provisions
Purchase Price Adjustments and Earn-Outs
Dispute Resolution Mechanisms
Closing Process and Post-Closing Obligations
Closing Deliverables and Conditions Precedent
Post-Closing Adjustments and Notifications
Integration and Transition Planning
Entity-Purchase Agreement Best Practices and Common Pitfalls
Effective Negotiation Strategies
Importance of Thorough Due Diligence
Avoiding Common Drafting Errors
Ensuring Clear Communication and Alignment of Expectations
Conclusion
Entity-Purchase Agreements FAQs
An entity-purchase agreement is a legally binding contract between the owners of a business entity, such as a corporation or limited liability company, which outlines the terms and conditions of a potential sale of the entity's ownership interests in the event of the death, disability, retirement, or other triggering events of one of the owners.
An entity-purchase agreement is important because it helps ensure a smooth transfer of ownership in the event of an owner's death, disability, or retirement. It provides a mechanism for the remaining owners to purchase the departing owner's share of the business and prevent unwanted or unfamiliar parties from becoming co-owners.
Owners of businesses structured as corporations, limited liability companies (LLCs), or other types of entities can enter into entity-purchase agreements. It is particularly important for businesses with multiple owners or partners, as it can help prevent disputes and provide a clear exit strategy.
An entity-purchase agreement should include details such as the purchase price of the departing owner's share, how the purchase price will be determined, and the payment terms. It should also address how the purchase will be funded, such as through insurance policies or other financing arrangements. The agreement should outline the triggering events that would require a purchase, the procedure for conducting the purchase, and any restrictions on transferring ownership interests.
Yes, it is recommended that you work with an experienced attorney to draft an entity-purchase agreement that meets your specific needs and requirements. An attorney can help ensure that the agreement complies with applicable laws and regulations and addresses all potential issues that may arise in the future.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.















