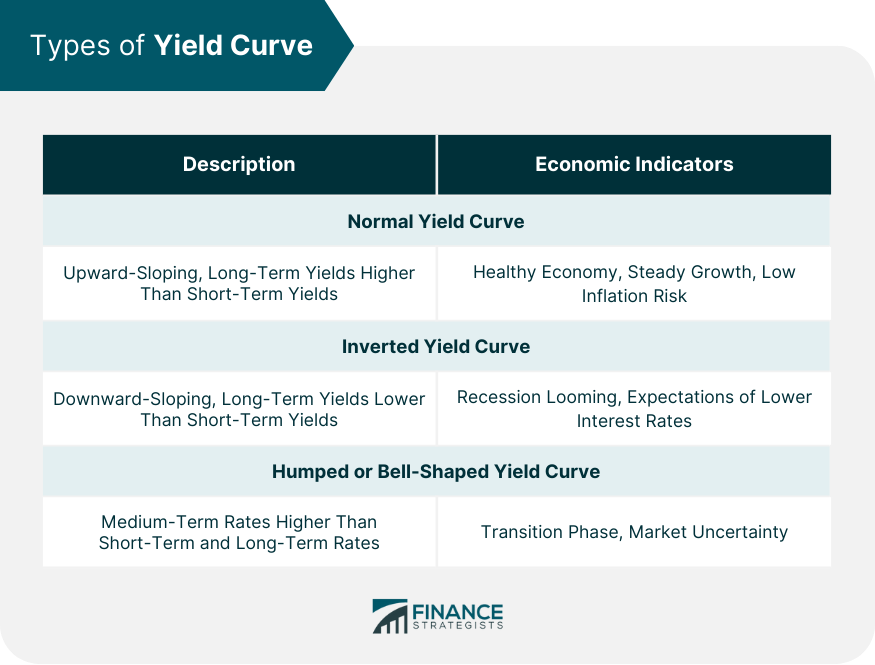
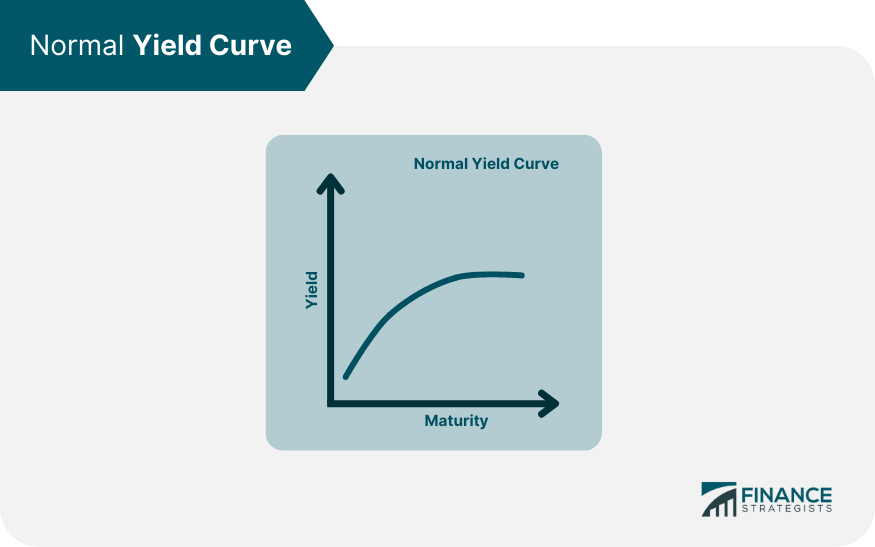
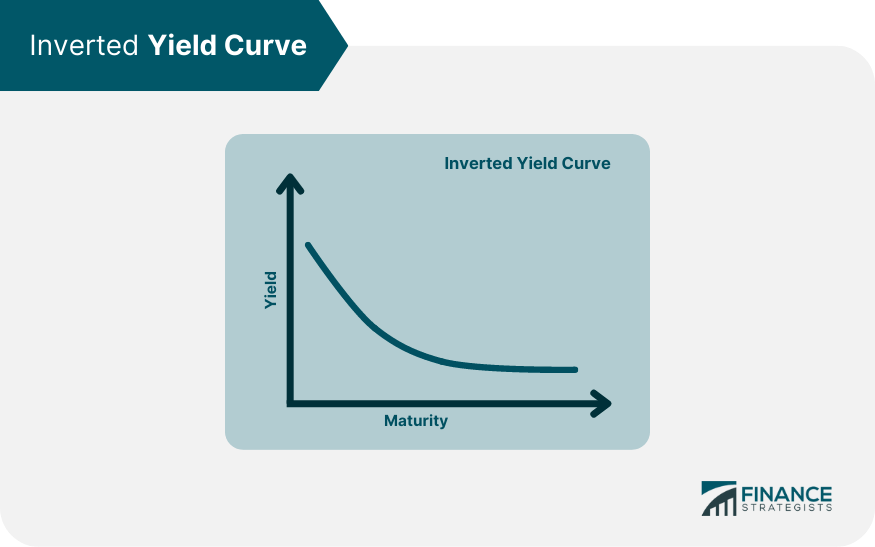
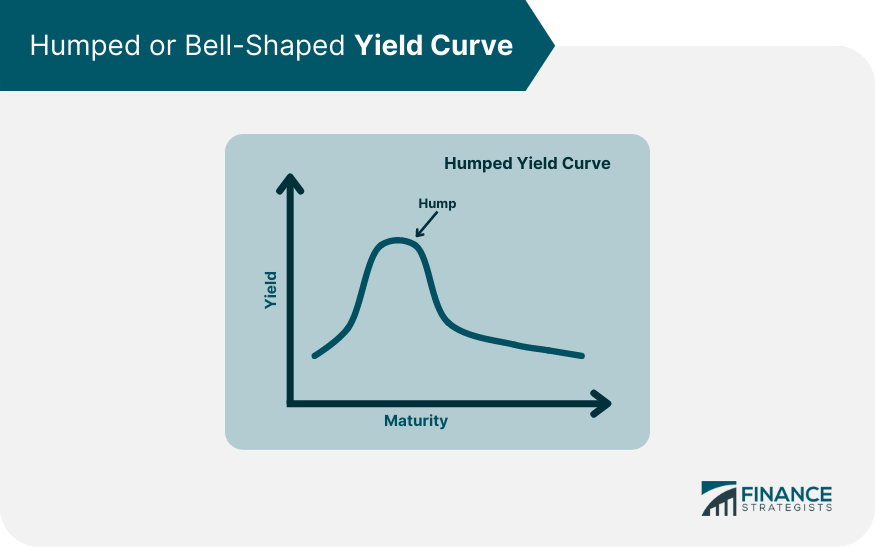
A yield curve is a graphical representation that plots the interest rates of a similar quality bond against their maturities. It serves as a crucial tool for investors and economists to gauge the direction of an economy. The yield curve can take several shapes, which can provide different economic outlooks. A humped yield curve, also known as a bell-shaped curve, represents a situation where medium-term debt instruments have higher yields compared to both short-term and long-term bonds. This type of yield curve is relatively rare and typically suggests economic transition and potential uncertainty. A normal, or upward-sloping, yield curve indicates that long-term securities have a higher yield compared to short-term securities. This is the most common type of yield curve, and it suggests an economy in good health, with expectations of steady economic growth and a low risk of inflation. An inverted or downward-sloping yield curve, on the other hand, happens when long-term bonds have lower yields than short-term bonds. This scenario is infrequent and usually signals a looming recession, as it indicates that investors expect lower interest rates in the future due to a downturn in the economy. The humped yield curve is a scenario where medium-term interest rates are higher than both short-term and long-term rates. This type of yield curve would imply that the economy is in a transition phase, perhaps from a period of growth to a slowdown or vice versa. It can also suggest market uncertainty, with investors having mixed feelings about future economic conditions. Interest rates play a significant role in shaping the yield curve. Central banks adjust interest rates to control inflation and stabilize the economy. When the central bank increases interest rates, short-term yields rise more than long-term yields, leading to a flatter or inverted yield curve. Conversely, when the central bank lowers rates, short-term yields tend to decrease more, causing the curve to steepen. Inflation expectations significantly influence the long end of the yield curve. If investors anticipate higher inflation, they demand higher yields on long-term bonds to compensate for the decrease in purchasing power, leading to an upward-sloping yield curve. If they expect lower inflation, the curve may flatten or invert. The yield curve can also be influenced by changes in supply and demand for different maturities. If investors prefer long-term bonds, their prices will rise, and yields will fall, flattening the yield curve. Conversely, if investors favor short-term securities, their prices go up, and yields go down, steepening the curve. A humped yield curve typically indicates economic uncertainty. Investors may be uncertain about future interest rates, inflation, or economic growth. As a result, they demand higher yields for medium-term bonds to compensate for the risk of holding these securities during uncertain times. The humped yield curve may also suggest that the economy is in a transition phase. For instance, the economy might be moving from a period of expansion to contraction or from low inflation to high inflation. During such times, investors might demand higher yields for medium-term bonds due to the potential changes in economic conditions. Market instability is another reason for the formation of a humped yield curve. In periods of market volatility or instability, investors might prefer medium-term securities, causing their yields to rise relative to short-term and long-term bonds. The humped yield curve reflects the market's uncertain outlook on future economic conditions. Investors may be unsure about the direction of interest rates, inflation, or economic growth, leading to fluctuations in bond prices and yields. A humped yield curve may signal a potential slowdown in economic growth, as it reflects the market's perception that medium-term risks are higher than short-term and long-term risks. This situation could cause businesses and consumers to reduce spending, leading to slower economic growth. The presence of a humped yield curve can impact investors' strategies, as it may suggest adjustments in asset allocation or risk management techniques. Investors may choose to shift their focus toward safer assets or diversify their portfolios to mitigate the potential risks associated with uncertain economic conditions. A humped yield curve can influence central banks' decisions on monetary policy. In response to a humped yield curve, central banks might adjust interest rates or implement other policy measures to stabilize the economy and restore investor confidence. The shape of the yield curve, including a humped yield curve, can provide valuable information for central banks when making monetary policy decisions. For instance, if the yield curve suggests economic uncertainty or potential slowdown, central banks may adopt a more cautious approach, such as lowering interest rates or implementing quantitative easing to stimulate the economy. In the presence of a humped yield curve, investors should prioritize risk management, as market conditions could be volatile and uncertain. This might include adjusting their asset allocation, employing hedging strategies, or using stop-loss orders to protect against potential losses. Diversification is a key strategy for investors in uncertain economic environments. By diversifying their investment portfolio, investors can spread risk across different asset classes and maturities, reducing the potential impact of a single market event or economic shift. Investors should consider their bond selection strategies when faced with a humped yield curve. They might choose to focus on bonds with attractive risk-reward profiles, taking into account factors such as credit quality, duration, and yield. Additionally, investors could explore opportunities in other fixed-income instruments or markets that may offer better returns or lower risk in the presence of a humped yield curve. A humped yield curve, an essential element in the financial world, represents a unique situation where medium-term interest rates are higher than both short-term and long-term rates. It signifies potential economic uncertainty, a transition phase, or market instability. Investors, traders, and policymakers can utilize this information to adjust their strategies and decisions accordingly. The implications of a humped yield curve, such as potential economic slowdown and uncertain future economic conditions, necessitate careful interpretation and proactive risk management strategies. Investors might find value in diversifying their portfolios, adjusting their bond selection strategies, and employing robust risk management techniques. Policymakers, particularly central banks, may need to adjust monetary policies in response to the signals from a humped yield curve. Whether you're an investor seeking to navigate through uncertain economic conditions or a policy-maker needing to comprehend market sentiments, understanding the humped yield curve and its implications is crucial. For personalized wealth management services and to navigate complex financial scenarios like these, consider seeking professional guidance.What Is a Humped Yield Curve?
Understanding the Yield Curve
Normal Yield Curve
Inverted Yield Curve
Humped or Bell-Shaped Yield Curve
Factors Affecting the Shape of Yield Curve
Interest Rates
Inflation Expectations
Market Demand and Supply
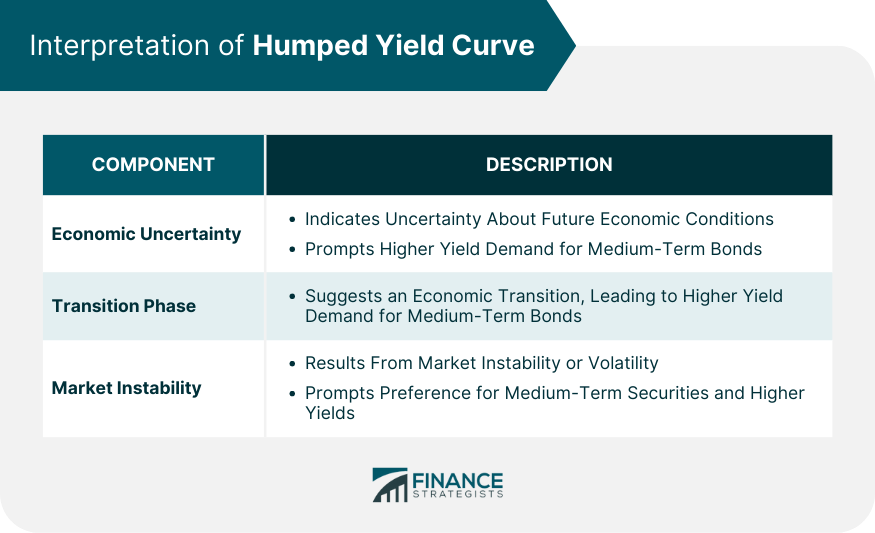
Interpretation of Humped Yield Curve
Economic Uncertainty
Transition Phase
Market Instability
Economic Implications of Humped Yield Curve
Uncertain Future Economic Conditions
Possibility of Slowdown in Economic Growth
Effect on Investment Strategies
Humped Yield Curve and Monetary Policy
Central Bank's Response
Effects on Monetary Policy Decisions
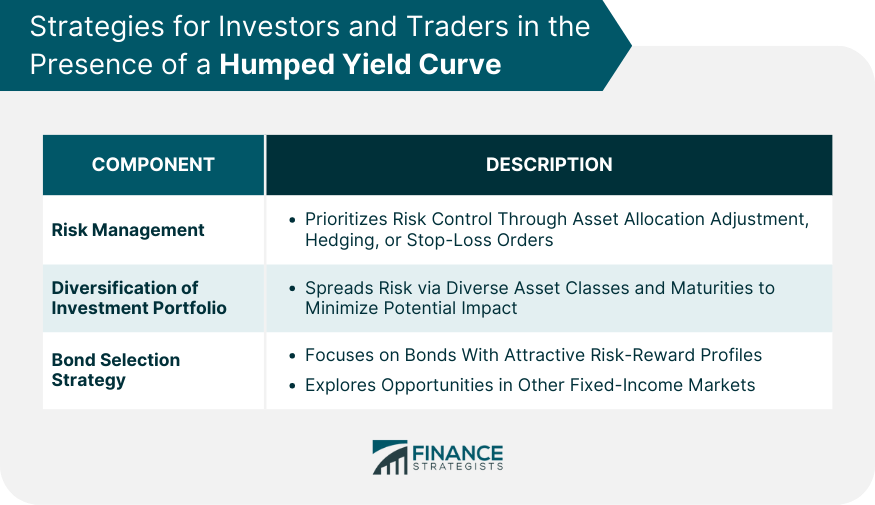
Strategies for Investors and Traders in the Presence of a Humped Yield Curve
Risk Management
Diversification of Investment Portfolio
Bond Selection Strategy
Final Thoughts
Humped Yield Curve FAQs
A humped yield curve is a type of yield curve where medium-term debt instruments have higher yields compared to both short-term and long-term bonds. It typically suggests economic transition and potential uncertainty.
A humped yield curve typically indicates economic uncertainty or a transition phase. It could suggest that the economy is moving from a period of expansion to contraction or vice versa.
The presence of a humped yield curve can lead to adjustments in investment strategies. Investors might shift towards safer assets, diversify their portfolios, or modify their bond selection strategies to mitigate potential risks associated with uncertain economic conditions.
A humped yield curve can influence central banks' decisions on monetary policy. Central banks might adjust interest rates or implement other policy measures to stabilize the economy and restore investor confidence in response to a humped yield curve.
In the presence of a humped yield curve, investors should prioritize risk management and diversification of their investment portfolio. They might also need to reconsider their bond selection strategies, focusing on bonds with attractive risk-reward profiles.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.















