The calculation of self-employment taxes is based on the net income earned from self-employment activities. This includes any revenue generated from business activities conducted as a sole proprietor, freelancer, contractor, or partner in a partnership. To calculate your self-employment tax, you must first determine your net income. This is calculated by subtracting your business expenses from your business income. Once you have your net income, multiply it by the self-employment tax rate, which is currently 15.3%. You can use several techniques to reduce your self-employment tax burden. Maximizing deductions is one of the most effective ways to reduce self-employment taxes. As a self-employed individual, you can deduct certain business expenses from your income, lowering your taxable income and reducing the self-employment taxes you owe. Some common business expenses that may be tax-deductible include office rent, supplies, equipment, travel expenses, and advertising. To ensure that you maximize your deductions, keeping accurate records of all business expenses is essential. This encompasses the practice of preserving receipts and maintaining comprehensive records of all business-related transactions. This can aid in maximizing the tax deductions that are applicable to your situation. Another effective way to reduce self-employment taxes is to consider incorporating your business. By incorporating your business, you can take advantage of certain tax benefits unavailable to sole proprietors. For example, corporations may deduct certain expenses, such as health insurance premiums, that are not deductible for sole proprietors. There are several different business structures to choose from when incorporating your business, including sole proprietorship, LLC, and S-corporation. Each structure has its advantages and disadvantages, and it is essential to carefully consider which one is right for your business. For example, an S-corporation may be the best choice for a small business owner who wants to reduce self-employment taxes because it allows for pass-through taxation, which means that the business's profits and losses are passed through to the owner's tax return. Making retirement contributions is another effective way to reduce self-employment taxes. By contributing to a retirement account, you can reduce your taxable income and lower the amount of self-employment taxes you owe. Several different retirement account options are available to self-employed individuals, including SEP IRAs, Solo 401(k)s, and SIMPLE IRAs. A SEP IRA is a type of retirement account that allows self-employed individuals to contribute up to 25% of their net income (up to a maximum of $69,000 in 2024) to their retirement account. Contributions to a SEP IRA are tax-deductible and can help reduce your taxable income. A Solo 401(k) is another retirement account option for self-employed individuals. With a Solo 401(k), you can contribute up to $69,000 in 2024 ($7,500 catch up contribution if you are 50 or older) or 100% of your net earnings from self-employment, whichever is less. Like a SEP IRA, Solo 401(k) contributions are tax-deductible and can help lower your taxable income. Finally, a SIMPLE IRA is a retirement account for small businesses. With a SIMPLE IRA, you and your employees can contribute to the account, and contributions are tax-deductible. Timing your income and expenses can also be an effective way to reduce self-employment taxes. By deferring income and accelerating expenses, you can lower your taxable income and reduce the amount of self-employment taxes you owe. For example, if you have a large client payment coming in at the end of the year, you can defer receipt until the following year to reduce your taxable income for the current year. Similarly, you can accelerate certain business expenses, such as office rent or equipment purchases, to reduce your taxable income for the current year. It is important to note that you should only defer income and accelerate expenses if it makes financial sense for your business. It is likewise beneficial to be aware of IRS rules and regulations regarding the timing of income and expenses to ensure compliance with tax laws. Finally, seeking professional advice regarding reducing self-employment taxes is always a good idea. Consulting with an expert in tax services or a financial advisor can help you identify tax-saving opportunities and ensure you comply with all tax laws and regulations. A professional can also help you evaluate different tax planning strategies and determine which ones are best for your business. In addition to the strategies outlined above, there are several other tips for the self-employed on reducing self-employment taxes. For example, you may take advantage of the home office deduction if you use a portion of your home exclusively for business purposes. You can also deduct the cost of health insurance premiums as a business expense. It is important to remember that reducing self-employment taxes requires careful planning and attention to detail. By implementing the above mentioned strategies and seeking professional advice when necessary, you can lower your tax burden and keep more of your hard-earned money. While there are several ways to reduce self-employment taxes, there are both advantages and disadvantages to doing so. Lower Tax Liability: One of the most obvious advantages of reducing self-employment taxes is that it lowers your tax liability. This means you get to keep more of your hard-earned money and have more funds available to invest back into your business or personal life. Increased Cash Flow: By lowering your tax liability, you also increase your cash flow. This can help you manage your business more effectively, invest in new equipment or software, or even take a much-needed vacation. Retirement Savings: By maximizing your retirement contributions, you can reduce your current tax liability and increase your retirement savings. This can help ensure that you have enough money saved for retirement and reduce your reliance on Social Security benefits. Improved Financial Stability: By reducing your tax liability, you may be able to improve your financial stability. This can help you weather financial storms or unexpected expenses and give you greater peace of mind. Reduced Benefits: Social Security benefits, for example, are based on your total earnings over your lifetime, and reducing your self-employment taxes could reduce the amount of benefits you are eligible for. Reduced Savings: While maximizing retirement contributions can help increase your retirement savings, it also means that you have less cash available for immediate expenses. Complex Tax Planning: Reducing self-employment taxes requires careful tax planning and a good understanding of tax laws and regulations. This can be time-consuming and may require the assistance of a professional tax advisor. Reduced Credibility: Reducing self-employment taxes may result in reduced credibility with lenders, investors, or potential business partners. This is because it may be seen as an attempt to reduce tax liability at the expense of other obligations or responsibilities. Reducing self-employment taxes requires careful planning and attention to detail. By implementing strategies such as maximizing deductions, incorporating your business, making retirement contributions, timing income and expenses, and seeking professional advice, you can lower your tax burden and keep more of your hard-earned money. It is important to remember that each strategy has its advantages and disadvantages, and the best approach will depend on your unique business needs and financial situation. Therefore, it is highly recommended that you seek the services of a tax accountant or financial professional to help you identify the best tax-saving opportunities and ensure compliance with tax laws and regulations. Refrain from letting taxes take a significant chunk of your self-employment income. Take action today and consult a professional to help maximize your deductions and reduce your self-employment taxes.Calculation for Self-Employment Taxes
Strategies to Reduce Self-Employment Taxes

Maximize Deductions
Consider Incorporating Your Business
Make Retirement Contributions
Time Income and Expenses
Seek Professional Advice
Advantages and Disadvantages of Reducing Self-Employment Taxes
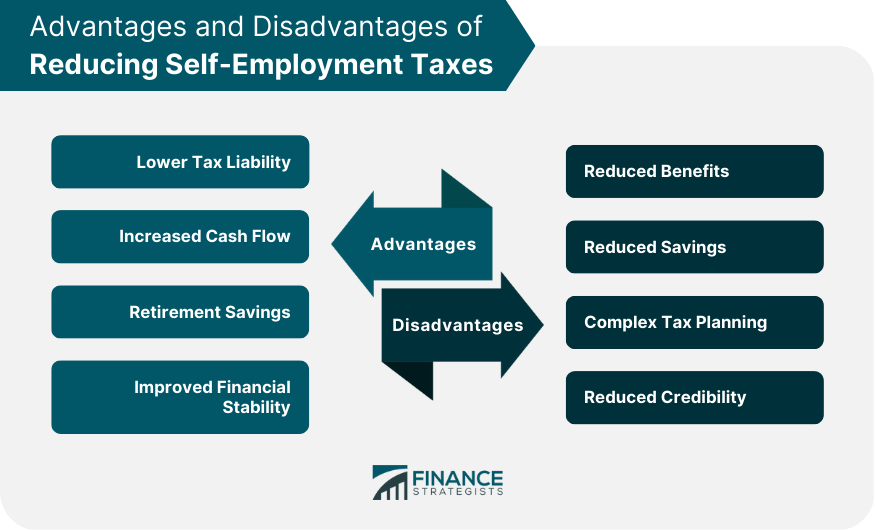
Advantages
Disadvantages
This can be a disadvantage if you have unexpected expenses or need to invest in your business.Final Thoughts
How to Reduce Self-Employment Taxes FAQs
You can reduce your self-employment taxes by maximizing deductions, incorporating your business, making retirement contributions, timing income and expenses, and seeking professional advice.
You can use retirement accounts such as SEP IRAs, Solo 401(k)s, and SIMPLE IRAs to reduce self-employment taxes.
By deferring income and accelerating expenses, you can lower your taxable income and reduce the amount of self-employment taxes you owe.
Incorporating your business may allow you to take advantage of certain tax benefits not available to sole proprietors, such as deducting certain expenses like health insurance premiums.
A tax advisor can help you identify tax-saving opportunities, evaluate different tax planning strategies, and ensure compliance with tax laws and regulations. They can also provide advice and guidance tailored to your unique business needs and financial situation.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.













