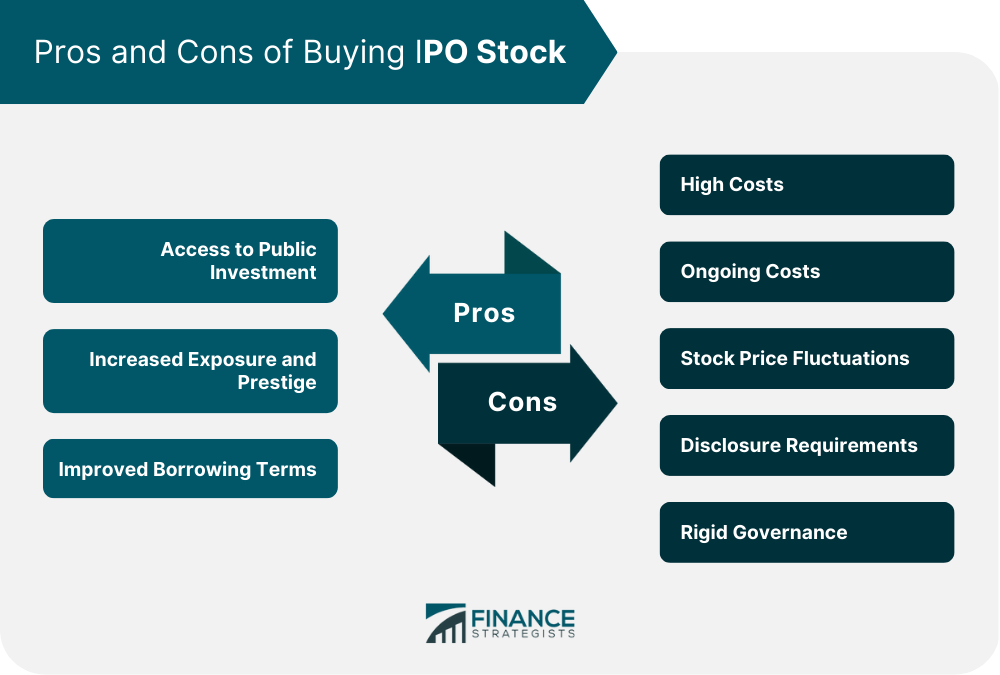
An initial public offering (IPO) is a process by which a private company makes its shares available to the public for the first time, usually with the objective of raising capital to support growth and expansion. An IPO marks a significant turning point for a company as it transitions from private to public, subject to increased scrutiny, regulation, and transparency. IPOs offer a unique opportunity for individual and institutional investors to invest in newly public companies with the potential for significant growth and profits. Investing in IPOs can be an attractive opportunity for investors, especially those seeking to capitalize on a company's potential growth and profitability. As new companies go public, they often experience significant demand from investors looking to buy their shares, which can increase the stock price. One of the main reasons to invest in an IPO is the potential for high returns. Early investors in IPOs can benefit from the "IPO discount," as the initial share price is often lower than the price at which the stock is later traded on the open market. This provides an opportunity for investors to purchase shares at a lower price and potentially sell them at a higher price, generating a significant profit. Moreover, investing in IPOs can provide investors access to companies with strong growth potential. Newly public companies often have innovative products, services, and business models that can disrupt traditional industries and capture market share. By investing in these companies, investors can participate in their growth and potentially benefit from a significant increase in their stock price. Participating in an IPO can be an exciting opportunity for investors to buy shares in a company at the initial offering price. However, participating in an IPO can also be a complicated and risky process. Here are some steps investors should take to participate in an IPO. Before investing in an IPO, it is important to understand the process. An IPO occurs when a private company decides to go public and offer shares of its stock for sale to the public. The company will hire an underwriter, which is usually a major investment bank, to handle the IPO process. The underwriter will work with the company to determine the initial offering price and the number of shares to be offered to the public. Investors who want to participate in an IPO must go through a broker or investment firm. This is because IPO shares are usually unavailable for direct purchase by individual investors. To participate in an IPO, an investor must first open an account with a broker or investment firm. The account must be in good standing, and the investor must meet certain eligibility requirements. These requirements vary depending on the broker or investment firm and the specific IPO. To participate in an IPO, an investor must meet certain eligibility requirements determined by the underwriter handling the IPO. These requirements may include a minimum net worth, annual income, or investment amount. Some brokers or investment firms may also require that an investor have a certain amount of trading experience or a certain number of trades per year. Once an investor has opened an account with a broker or investment firm, they can express interest in participating in an IPO. This is typically done by filling out an IPO application. The application usually requires the investor to provide personal information, including their name, address, and Social Security number. It may also require the investor to provide financial information, such as their annual income and net worth. Once the investor has completed the IPO application, they must submit it to their broker or investment firm. The broker or investment firm will then review the application to determine if the investor meets the eligibility requirements for the IPO. If the investor is eligible, the broker or investment firm will submit the application to the underwriter handling the IPO. If the investor is allocated shares in the IPO, they will be notified by their broker or investment firm. The investor will then be required to provide payment for the shares. Payment for IPO shares is usually due within a few days of notification. It is important to note that the allocation of IPO shares is not guaranteed, and many IPOs are oversubscribed, meaning that there are more investors interested in buying shares than there are shares available. In this case, the underwriter will usually allocate shares based on a predetermined formula, such as pro rata allocation based on the size of the investor's order. To analyze an IPO investment, you will need to gather and analyze relevant information about the company issuing the IPO. This information may include the following: Company's Financial Statements. The company's financial statements, including its balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement, can provide valuable insights into the company's financial health, profitability, and cash flow. Business Plan and Strategy. You should review the company's business plan and strategy, including its market position, competitive landscape, target market, growth prospects, and any potential risks to the business. Management Team. Analyzing the company's management team is essential to understanding their experience, expertise, and track record in managing a business, as well as their plans for the future of the company. Industry and Market Analysis. You should thoroughly analyze the industry and market in which the company operates, including any trends or changes that may impact the company's performance. IPO Prospectus. The IPO prospectus is a legal document that provides detailed information about the company's financials, management, business strategy, and risks. It is essential to review this document carefully before investing in an IPO. Analyst Research. You can also consider analyst research and opinions about the company and the IPO, which can provide valuable insights into the company's prospects and valuation. Once you have gathered this information, you can use various valuation techniques to determine whether the IPO is priced fairly and represents a good investment opportunity. These techniques may include comparing the company's financial metrics to similar companies in the industry, evaluating the company's growth potential, and assessing the quality of the management team. Ultimately, analyzing an IPO investment aims to determine whether the company has a strong business model, growth potential, and a competitive advantage that will enable it to generate long-term value for its investors. Investing in an IPO can be an exciting opportunity to potentially get in on the ground floor of a company's growth. Here are the general steps to follow to buy IPO stock. Research the IPO. Before investing in an IPO, it is important to research the company going public. You should review the company's prospectus, which provides detailed information about the business, financials, management, and risks. Determine if the IPO Is a Good Fit for Your Portfolio. Consider if the IPO aligns with your investment strategy and goals. Determine if you are comfortable with the risks associated with investing in a new company. Open an Account With a Brokerage Firm. If you do not already have one, you will need a brokerage account to purchase shares of the IPO. You should research and compare brokerage firms to find one that best meets your needs. Place an Order for the IPO. Once the IPO is priced, your broker will enable you to place an order for the shares at the offering price. This can be done online or over the phone. Wait for the Stock to Start Trading. After the IPO is complete, the stock will begin trading on an exchange. The stock may trade higher or lower than the offering price, so monitoring the stock's performance is important. Consider the Risks. Investing in IPOs carries risks, such as the potential for the stock price to decline significantly or for the company to fail to meet expectations. It is important to consider these risks before investing in an IPO. It is important to note that IPOs can be highly competitive and difficult to purchase, particularly for individual investors. You may also want to consult with a financial advisor before making any investment decisions. Before investing in an IPO, it is important to consider the potential benefits and drawbacks. Here are some pros and cons to keep in mind: Access to Public Investment. An IPO provides access to investment from the public, which can help a company raise capital easily and more quickly than other methods. Increased Exposure and Prestige. Going public can increase a company's exposure and enhance its public image, which can help drive sales and profits. Improved Borrowing Terms. Companies that go public are required to report quarterly, which increases transparency and can lead to more favorable borrowing terms. High Costs. Going public is expensive and requires significant investment in legal and accounting fees, marketing, and underwriting fees. Ongoing Costs. Maintaining a public company involves ongoing costs such as regulatory compliance, shareholder communication, and accounting fees. Stock Price Fluctuations. Fluctuations in a company's stock price can be a distraction for management, which may be evaluated based on stock performance rather than actual financial results. Disclosure Requirements. Public companies are required to disclose significant financial, accounting, tax, and business information, which could reveal business secrets and methods that competitors can use. Rigid Governance. Companies that go public are subject to more rigid governance and board oversight, which can make it more difficult to retain good managers and take risks. While going public has its advantages, companies may also explore other options, such as remaining private or soliciting bids for a buyout. Ultimately, the decision to go public should be carefully evaluated, taking into account the company's financial position, growth prospects, and long-term goals. An IPO is when a private company makes its shares available to the public for the first time to raise capital for growth and expansion. IPOs can offer an opportunity for investors to benefit from potential growth and profitability. However, investing in IPOs can be complicated and risky. Investors should research the IPO, understand the eligibility requirements, and analyze the company's financials, business plan, management team, industry, and market before investing. While buying IPO stock has pros, such as increased exposure and access to public investment, there are also cons, such as high costs, ongoing costs, stock price fluctuations, disclosure requirements, and rigid governance. As investing in IPOs can be challenging, consulting a financial advisor before making any investment decisions is recommended.Overview of Initial Public Offerings
How to Participate in an IPO
Understanding the IPO Process
Registering With a Broker
Eligibility Requirements
Filling Out an IPO Application
Submitting the Application
Allocating Shares

Analyzing the IPO
How to Buy IPO Stock
Pros and Cons of Buying IPO Stock
Pros of Buying IPO Stock
Cons of Buying IPO Stock
The Bottom Line
How to Buy IPO Stock FAQs
An IPO is a process by which a private company makes its shares available to the public for the first time, usually with the objective of raising capital to support growth and expansion.
You must go through a broker or investment firm to participate in an IPO. You will need to open an account with them, meet certain eligibility requirements, and fill out an IPO application.
Before investing in an IPO, you should research the company's prospectus, financial statements, business plan and strategy, management team, industry and market analysis, and analyst research.
To buy IPO stock, you should research the IPO, determine if it is a good fit for your portfolio, open an account with a brokerage firm, place an order for the IPO, and wait for the stock to start trading.
Buying IPO stock carries risks, such as the potential for the stock price to decline significantly or for the company to fail to meet expectations. It is important to consider these risks before investing in an IPO.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.















