Active Share is a metric that measures the degree of active management in a portfolio. It is calculated by comparing the holdings in a portfolio to its benchmark index. The higher the Active Share, the greater the difference between the portfolio and its benchmark. This metric is often used by investors to determine the level of risk associated with a portfolio. Active Share has become increasingly important in investment management. It provides a way for investors to measure a manager's skill and assess the level of risk associated with a portfolio. This metric also allows investors to distinguish between actively managed funds and passive index funds. Active share is a crucial metric for investors and fund managers as it measures the degree of active management being applied to a portfolio. It helps investors understand whether they are getting active management or just a passive investment. High active share means the fund is making bold bets, and investors need to evaluate whether the strategy employed aligns with their risk appetite and investment objectives. Active share also provides an important measure of accountability for fund managers. It allows them to justify their fees by demonstrating that they are applying active management to the portfolio and seeking to generate alpha. It can help them to identify potential risks in their investment strategy by analyzing the factors contributing to active share. Overall, active share plays a critical role in the investment management industry by providing a simple and objective way to measure the extent of active management being applied to a portfolio. Active Share is calculated by taking the absolute value of the difference between the weight of a portfolio's holdings and the weight of its benchmark holdings. Active Share is expressed as a percentage, with a range of 0 to 100. A score of 0 indicates that the portfolio is identical to its benchmark, while a score of 100 indicates that the portfolio has no holdings in common with its benchmark. In general, an Active Share score of 60 or higher is considered high, indicating a high level of active management. Active Share provides insight into a manager's investment style. A high Active Share indicates that a manager is taking an active approach to investing, while a low Active Share indicates a more passive approach. This metric allows investors to choose managers whose investment style aligns with their investment objectives. Active Share helps investors distinguish between actively managed funds and passive index funds. Passive funds generally have a low Active Share, as they are designed to track their benchmark closely. Conversely, actively managed funds typically have a higher Active Share, as managers aim to outperform their benchmark. Active Share can be used to measure a manager's skill. Managers with a high Active Share who consistently outperform their benchmark may be considered skilled investors. Conversely, managers with a low Active Share who consistently underperform their benchmark may be considered unskilled. Active Share does not consider the performance of the benchmark index. A manager with a high Active Share may still underperform their benchmark, while a manager with a low Active Share may outperform their benchmark. Therefore, investors should not rely solely on Active Share to evaluate a portfolio's performance. Active Share may not be suitable for all investment strategies. For example, some strategies may require a low Active Share, such as factor-based investing or quant strategies. Additionally, some investment products, such as ETFs or index funds, may not have a meaningful Active Share score. Active Share is not a guarantee of outperformance. While a high Active Share may indicate a manager's skill, it does not guarantee that the manager will outperform their benchmark. The success of an investment strategy is dependent on a multitude of factors, including market conditions, economic factors, and geopolitical risks. Active Share and Tracking Error are two metrics that measure different aspects of a portfolio's performance. Active Share measures the degree of active management in a portfolio, while Tracking Error measures the deviation of a portfolio's returns from its benchmark. While Active Share is expressed as a percentage, Tracking Error is expressed as a standard deviation. Active Share and Tracking Error are complementary measures. Active Share provides insight into a manager's investment style, while Tracking Error measures the volatility of a portfolio relative to its benchmark. By considering both metrics, investors can gain a more complete understanding of a portfolio's risk and performance. Active Share is a valuable tool for investors to assess the level of active management in a portfolio, and to differentiate between active and passive investment strategies. It provides insight into a manager's investment style, and can be used to measure a manager's skill. However, Active Share has its limitations, and investors should not rely solely on this metric to evaluate a portfolio's performance. Active Share is defined as the percentage of a portfolio's holdings that differ from its benchmark index, with a score of 60 or higher indicating a high degree of active management. The advantages of Active Share include providing insight into a manager's investment style, helping investors identify actively managed funds, and measuring a manager's skill. However, Active Share has limitations, including its inability to consider the performance of the benchmark index, and its potential unsuitability for some investment strategies. Investors should consider using Active Share in conjunction with other metrics, such as Tracking Error, to gain a more complete understanding of a portfolio's risk and performance. By considering a range of metrics and factors, investors can make informed investment decisions and achieve their investment objectives.Definition of Active Share
Importance of Active Share
Calculation of Active Share
Formula for Active Share
Interpretation of Active Share
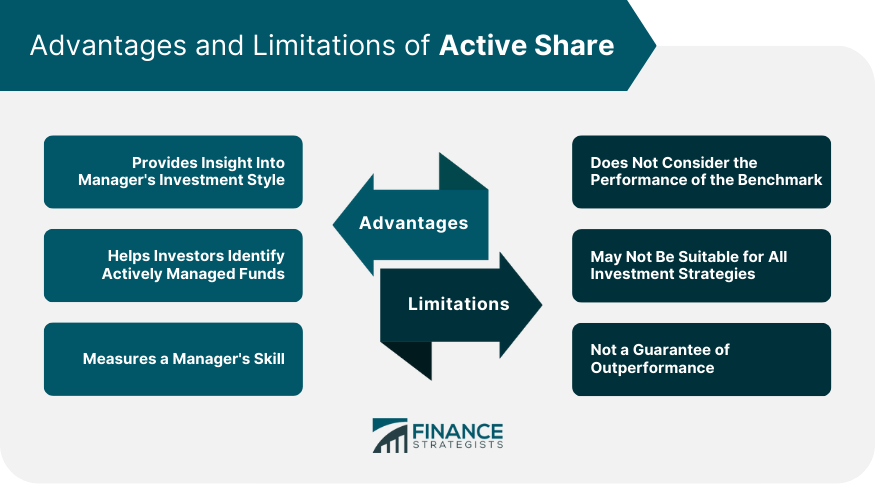
Advantages of Active Share
Provides Insight Into Manager’s Investment Style
Helps Investors Identify Actively Managed Funds
Measures a Manager’s Skill
Limitations of Active Share
Does Not Consider the Performance of the Benchmark
May Not Be Suitable for All Investment Strategies
Not a Guarantee of Outperformance
Active Share vs Tracking Error
Differences Between Active Share and Tracking Error
Complementary Measures
Conclusion
Active Share FAQs
Active Share is a metric used in investment management to measure the percentage of a portfolio's holdings that differ from its benchmark index.
Active Share is calculated by subtracting the weight of benchmark holdings from the weight of the portfolio holdings, then summing the absolute value of the differences.
Active Share provides insight into a manager's investment style, helps investors identify actively managed funds, and can be used to measure a manager's skill.
Active Share does not consider the performance of the benchmark, may not be suitable for all investment strategies, and is not a guarantee of outperformance.
Active Share measures the degree of active management, while Tracking Error measures the deviation of a portfolio's returns from its benchmark. They are complementary measures.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











