Blockchains are digital ledgers that store transaction records across multiple computers. They ensure transparency, security, and immutability by using cryptography to validate and secure data. Blockchains address challenges in traditional centralized systems by providing a decentralized and efficient way to store and verify transactions. Blockchains operate through key components and network architecture. Blockchain technology combines decentralization, consensus mechanisms, and cryptography. It enables participants to agree on the state of the ledger without relying on a central authority. Decentralization: Blockchains distribute authority and decision-making power, reducing the risk of a single point of failure. Consensus Mechanisms: These protocols enable participants to agree on the validity of transactions, maintaining the integrity of the blockchain. Cryptography: Blockchain uses cryptographic algorithms to secure transactions, authenticate participants, and protect data. Blockchain networks can be categorized into three main types: Public blockchains like Bitcoin and Ethereum are open to anyone and allow permissionless participation. They offer high levels of decentralization and transparency. Private blockchains restrict participation and are typically controlled by a single entity or a consortium. They prioritize privacy and are commonly used in enterprise settings. Consortium blockchains are governed by a group of organizations working together to maintain the network. They strike a balance between decentralization and control. Blockchain technology provides robust security measures that enhance trust among participants. The immutability of blockchain ensures that once a transaction is recorded, it becomes nearly impossible to alter or tamper with the data. This guarantees data integrity and prevents unauthorized changes. By eliminating intermediaries and enforcing transparent and auditable transactions, blockchains reduce fraudulent activities such as identity theft, financial fraud, and document forgery. Blockchain-based identity systems empower individuals to control their personal data securely. Self-sovereign identity solutions enable secure and private identity management, reducing the risk of identity theft and unauthorized access. Blockchains offer several advantages, making transactions more efficient and transparent. Traditional financial systems involve lengthy settlement and clearing processes. Blockchain enables near real-time settlements and clearing, reducing delays and improving overall efficiency. By eliminating intermediaries, blockchain significantly reduces transaction fees, especially in cross-border payments and remittances. Blockchain's transparent nature allows auditors and regulators to access a comprehensive and immutable record of transactions. This improves auditing capabilities and enhances traceability across supply chains, financial transactions, and other industries. Blockchain has the potential to revolutionize supply chain management by introducing transparency and efficiency. Blockchain records and verifies each step of the supply chain, allowing stakeholders to trace the origin and movement of goods. This enhances transparency and helps combat issues like counterfeit products and unauthorized substitutions. Blockchain-based systems enable real-time inventory tracking, reducing errors and providing accurate data on stock levels. This leads to better demand forecasting, optimized supply chains, and reduced costs. By recording and verifying product information on the blockchain, it becomes difficult to counterfeit or tamper with goods. Customers can verify the authenticity of products, leading to increased trust and consumer protection. Blockchain technology can revolutionize the way digital identities are managed, providing increased privacy and security. Self-sovereign identity on the blockchain allows individuals to control their personal data and selectively share it with trusted parties. This reduces reliance on centralized identity providers and gives individuals greater autonomy. Blockchain's decentralized nature, combined with cryptographic techniques, ensures the privacy and security of personal data. It offers an alternative to centralized databases vulnerable to data breaches and unauthorized access. Blockchain-based identity systems simplify verification processes by providing trusted and verifiable credentials. This streamlines procedures such as KYC (Know Your Customer) and reduces the burden on individuals and businesses. While blockchain technology holds promise, it faces challenges that need addressing. As blockchain networks grow, scalability becomes a concern. Some blockchains struggle to handle a large volume of transactions efficiently. Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus algorithms, like those used by Bitcoin, require substantial computational power and energy consumption. This raises concerns about the environmental impact of blockchain technology. The legal and regulatory frameworks surrounding blockchain are still evolving. Uncertainty around compliance, taxation, and data privacy can slow down adoption and hinder innovation. Despite the benefits, several factors impede widespread blockchain adoption. Different blockchain platforms often lack interoperability, making it challenging to transfer assets and data seamlessly between networks. This limits the potential benefits of blockchain technology. Many individuals and businesses lack a clear understanding of blockchain and its applications. Education and awareness initiatives are necessary to foster trust and facilitate adoption. Integrating blockchain technology with existing legacy systems can be complex and costly. This integration hurdle may discourage organizations from embracing blockchain solutions. Blockchain technology, with its vast array of applications, has the potential to revolutionize diverse sectors ranging from finance to supply chain management. Its unique features, such as decentralization, consensus mechanisms, and cryptography, deliver enhanced security, efficient transactions, and the promise of a more transparent, equitable future. However, like any evolving technology, blockchain faces hurdles like scalability, energy consumption, regulatory uncertainties, and adoption barriers. These challenges offer an opportunity to the keen observer and thoughtful investor seeking avenues of growth and innovation. If managed effectively, the potential returns from blockchain implementation could be immense. As such, it is increasingly crucial to align one's financial strategy with the opportunities presented by emerging technologies like blockchain. Seek expert guidance to help you navigate these waters. Consider reaching out to a wealth management service today to leverage blockchain's potential in your investment strategy and secure a prosperous future.Overview of Blockchains
Key Components of a Blockchain
Blockchain Network Architecture
Public Blockchains
Private Blockchains
Consortium Blockchains
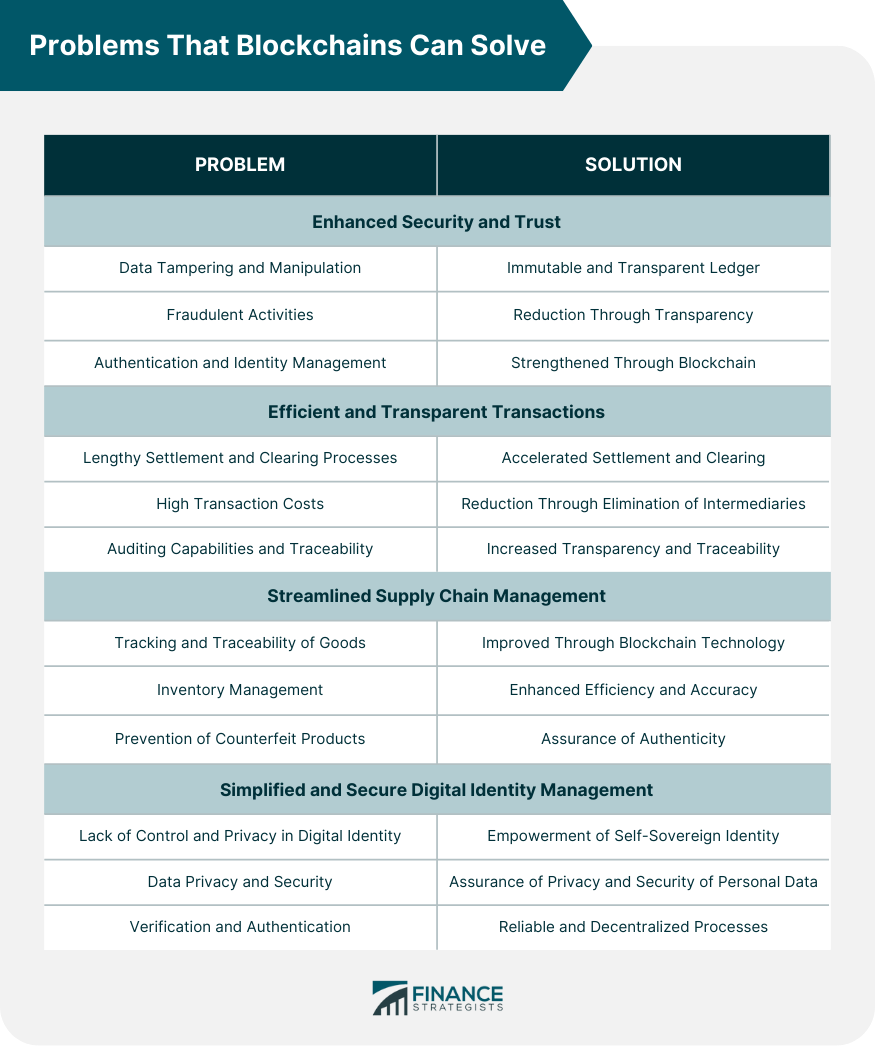
Problems That Blockchains Can Solve
Enhanced Security and Trust
Data Tampering and Manipulation
Fraudulent Activities
Authentication and Identity Management
Efficient and Transparent Transactions
Lengthy Settlements and Clearing Processes
High Transaction Costs
Auditing Capabilities and Traceability
Streamlined Supply Chain Management
Tracking and Traceability of Goods
Inventory Management
Prevention of Counterfeit Products
Simplified and Secure Digital Identity Management
Lack of Control and Privacy in Digital Identity
Data Privacy and Security
Verification and Authentication
Challenges and Limitations of Blockchains
Scalability Issues
Energy Consumption
Regulatory and Legal Uncertainty
Adoption Barriers
Lack of Interoperability
Insufficient Education and Awareness
Integration Challenges with Existing Systems
The Bottom Line
Problems That Blockchains Can Solve FAQs
Blockchains ensure data integrity, reduce fraud, and strengthen authentication and identity management.
Blockchains enable faster settlements, lower transaction costs, and increased auditing capabilities.
Blockchains improve tracking and inventory management and prevent counterfeit products.
Blockchains empower individuals with self-sovereign identity, data privacy, and reliable verification.
Scalability issues, energy consumption, regulatory uncertainty, and integration barriers pose challenges.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











