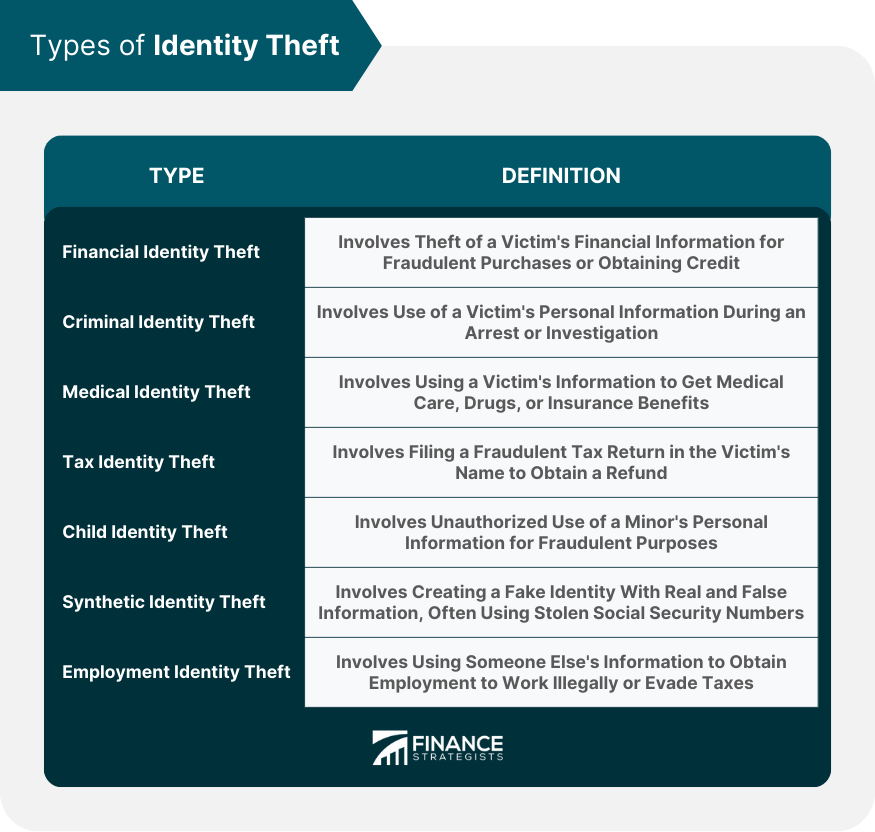
Identity theft is a type of fraud that involves stealing someone's personal information, such as their name, date of birth, social security number, or credit card details, for the purpose of committing fraud or other crimes. Identity theft is a growing concern in today's digital world, where criminals are becoming more sophisticated in their attempts to steal personal information for financial gain or other malicious purposes. Understanding identity theft is essential for individuals and businesses alike in order to protect themselves and minimize the potential damage caused by this crime. Financial identity theft occurs when a criminal uses a victim's personal information to gain access to their financial accounts or obtain credit, loans, or services in the victim's name. Criminal identity theft involves an individual using another person's identifying information during an arrest or investigation, resulting in the victim being wrongfully associated with a criminal record. Medical identity theft occurs when someone uses another person's personal information to obtain medical care, prescription drugs, or insurance benefits. Tax identity theft involves the fraudulent use of a victim's personal information to file a tax return and claim a refund. Child identity theft is the unauthorized use of a minor's personal information for various types of fraud, such as opening credit accounts or obtaining benefits. Synthetic identity theft is the creation of a fake identity using a combination of real and fabricated personal information, often involving the use of stolen Social Security numbers. Employment identity theft occurs when someone uses another person's personal information to obtain employment, often to work illegally or evade taxes. Phishing and spear-phishing are tactics used by criminals to trick individuals into providing personal information through deceptive emails, websites, or phone calls. Data breaches occur when unauthorized individuals gain access to sensitive personal information stored by companies or organizations, exposing the information to potential misuse. Physical theft of personal information can occur through stolen wallets, mail, or documents containing sensitive data. Skimming involves capturing a victim's credit or debit card information using a device placed on an ATM or payment terminal. Hackers may use various techniques, such as exploiting software vulnerabilities or installing malware, to gain unauthorized access to personal information stored on digital devices. Social engineering refers to the manipulation of individuals into divulging personal information through psychological tactics or deception. Insider threats occur when employees or other individuals with legitimate access to sensitive information misuse their access to steal personal data. Unusual or unauthorized bank or credit card statement transactions may indicate identity theft. The presence of unfamiliar accounts, inquiries, or charges on your credit report may be a sign of identity theft. Receiving unexpected bills or collection calls for accounts or services you did not initiate may indicate identity theft. Fraudulent correspondence or communication requesting personal information may be a sign of identity theft attempts. Being unexpectedly denied credit, despite having a good credit history may indicate potential identity theft. Receiving a notice from the IRS regarding multiple tax returns filed in your name or unreported income may be a sign of tax-related identity theft. Protecting your personal information is essential for preventing identity theft. Shred sensitive documents, use strong passwords, and safeguard your digital devices from unauthorized access. Regularly review your bank and credit card statements, check your credit reports for discrepancies, and set up account alerts to stay informed about any unusual activity. Ensure you keep your software updated and use security features, such as antivirus software and firewalls, to protect your devices. Be wary of email and phone scams, and only use secure websites for financial transactions. Do not share your Social Security number unnecessarily; be cautious when providing it to organizations or individuals. Regularly collect your mail and properly dispose of sensitive documents to prevent theft of your personal information. Implement two-factor authentication (2FA) whenever possible for online accounts to add an extra layer of security. Businesses should establish and enforce data security policies to protect customer information and reduce the risk of data breaches. Employees should be educated on the importance of cybersecurity and privacy, as well as the best practices to protect sensitive information. Businesses should adopt secure payment processing systems and technologies to minimize the risk of unauthorized access to customer payment information. Companies should have systems in place to detect and respond to potential data breaches in a timely manner. Businesses should adhere to data privacy regulations to ensure they are taking the necessary steps to protect customer information. Contact your financial institutions and credit card issuers to report unauthorized transactions or accounts. File a report with the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) and your local law enforcement agency. Close or freeze any compromised accounts, change your passwords and PINs, and continue monitoring your credit reports for any further signs of fraud. Dispute fraudulent charges and accounts with the relevant financial institutions and credit bureaus. Clear your name in any criminal records and notify government agencies of any fraudulent use of your personal information. Develop a recovery plan and maintain records of your actions and communications throughout the process. Stay vigilant and continue implementing identity theft prevention strategies to protect yourself from future incidents. In today's digital world, identity theft has become a growing concern, with criminals becoming more sophisticated in their attempts to steal personal information for financial gain or other malicious purposes. It is crucial for individuals and businesses to understand identity theft to protect themselves and minimize the potential damage caused by this crime. Prevention strategies include securing personal information, monitoring financial and personal accounts, being cautious online, protecting the social security number, being vigilant with mail and personal documents, and using two-factor authentication. If you become a victim of identity theft you may report the crime, protect your accounts, repair the damage, and develop a recovery plan. By implementing these strategies and taking immediate action if identity theft occurs, individuals and businesses can better protect themselves against this growing threat.What Is Identity Theft?
Types of Identity Theft
Financial Identity Theft
Criminal Identity Theft
Medical Identity Theft
Tax Identity Theft
Child Identity Theft
Synthetic Identity Theft
Employment Identity Theft
How Identity Theft Occurs
Phishing and Spear-Phishing
Data Breaches
Physical Theft
Skimming
Hacking and Malware
Social Engineering
Insider Threats
Common Signs of Identity Theft
Unexplained Bank Account Activity
Unfamiliar Accounts or Charges on Credit Report
Unexpected Bills or Collection Calls
Mail, Email, or Phone Call Scams
Denied Credit for No Apparent Reason
Tax-Related Discrepancies
Identity Theft Prevention Strategies for Individuals
Secure Personal Information
Monitor Financial and Personal Accounts
Be Cautious Online
Protect Your Social Security Number
Be Vigilant With Mail and Personal Documents
Use Two-Factor Authentication

How Businesses Can Help Prevent Identity Theft
Implement Strong Data Security Policies
Train Employees on Cybersecurity and Privacy Practices
Use Secure Payment Processing Systems
Monitor and Respond to Data Breaches
Comply With Data Privacy Regulations

What to Do If You Become a Victim of Identity Theft
Report the Crime
Protect Your Accounts
Repair the Damage
Recover and Move Forward
Conclusion
Identity Theft FAQs
Identity theft is a type of fraud that involves stealing someone's personal information, such as their name, date of birth, social security number, or credit card details, for the purpose of committing fraud or other crimes.
You can prevent identity theft by being cautious with your personal information, such as not sharing it with anyone you don't trust, shredding important documents before throwing them away, monitoring your financial statements regularly, and using strong passwords for your online accounts.
Suppose you become a victim of identity theft. In that case, you should immediately contact your bank or credit card company to report any unauthorized charges, contact credit reporting agencies to place a fraud alert on your credit report, and file a report with the Federal Trade Commission.
Some common signs of identity theft include unexplained charges on your credit card statement, receiving bills for accounts you didn't open, being denied credit for no apparent reason, and receiving calls from debt collectors about debts you don't owe.
You can monitor your credit for signs of identity theft by requesting a free credit report from each of the three major credit reporting agencies every year, signing up for credit monitoring services, and setting up fraud alerts or credit freezes on your credit report.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.















