Blockchain technology is a decentralized digital ledger that securely records transactions across multiple computers. Introduced with Bitcoin in 2009, Blockchain's innovative appeal lies in its ability to enable peer-to-peer transactions without the need for a central authority, offering enhanced transparency, security, and traceability. Each transaction, or 'block,' is linked to the one before and after it, creating a 'chain.' This structure makes it resistant to modification, as altering one block would require changing the entire chain. These features make Blockchain a disruptive technology across sectors, particularly in finance, supply chain management, and healthcare. However, while Blockchain offers promising opportunities, it also faces limitations including high energy consumption, scalability issues, and regulatory challenges. Continuous research and development are being conducted to address these issues and unlock Blockchain's full potential. One of the most prevalent criticisms against Blockchain, especially concerning cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, is the high energy consumption. Blockchain operates on a proof-of-work mechanism that requires substantial computational power. The 'mining' process, which refers to the validation of transactions on the network, involves complex mathematical problems solved by powerful computers. This process consumes considerable energy. Unfortunately, this high energy consumption has a significant environmental impact. The carbon footprint of Bitcoin transactions is massive. For instance, one Bitcoin transaction has an energy footprint equivalent to thousands of Visa transactions. This high energy usage, besides being environmentally unsustainable, also makes Blockchain less efficient than traditional banking systems when scaled. Another major challenge that Blockchain faces is scalability. Simply put, as the size of the Blockchain increases, so does the time required to process and validate a transaction. The Bitcoin network, for example, can only process a limited number of transactions per second, which is significantly lower than the number of transactions processed by traditional payment systems like Visa. The issue of scalability doesn't just impact transaction speed and efficiency. It also affects the broader adoption of Blockchain technology. Until scalability issues are resolved, it's unlikely that Blockchain can replace conventional banking systems fully. The decentralized nature of Blockchain presents various legal and regulatory challenges. As Blockchain operates across borders, it doesn't easily fit within the traditional regulatory frameworks. For instance, issues around taxation, legality, and regulatory compliance remain significant concerns for users of Blockchain technology. These challenges further complicate the application of Blockchain within the financial sector. The high energy consumption of Blockchain impacts more than just the environment. It also affects the operational costs of using Blockchain technology. The cost of running the necessary computations for 'mining' can be prohibitively high. This can result in higher transaction costs compared to traditional banking systems, especially when scaled up. Blockchain's scalability issues further impact traditional banking and financial systems. Transaction delays can be significant on the Blockchain network, which can hinder its ability to replace conventional banking systems. Additionally, these scalability issues can lead to congestion on the network, causing transaction fees to rise, which is unfavorable for users. The limitations of Blockchain technology have a considerable effect on investment strategies and risk management in wealth management. The high energy consumption and associated costs can make Blockchain-based assets less attractive to investors. Moreover, the scalability issues might limit the potential return on investment due to transaction delays and higher costs. Wealth managers and investors need to adapt their strategies considering these limitations. For instance, it might be necessary to reassess the value and potential of Blockchain-based assets. Regulatory issues further complicate this scenario, adding an additional layer of risk that needs to be accounted for during investment planning. Compliance issues pose a significant challenge to the financial sector when it comes to adopting Blockchain technology. Different jurisdictions have different rules and regulations related to cryptocurrencies and other Blockchain-based applications, making it a complex landscape to navigate. This can affect various financial processes, including initial coin offerings (ICOs) and cryptocurrency trading. Regulatory hurdles can lead to potential legal complications and financial losses, posing a significant risk for investors and financial institutions alike. Despite the limitations, several measures are being taken to mitigate these issues. Many efforts focus on reducing the energy consumption of Blockchain. One significant development is the transition from proof-of-work (PoW) to proof-of-stake (PoS) consensus mechanisms. PoS-based Blockchains require less computational power, thus reducing energy consumption. To address scalability issues, developers are working on software upgrades and novel architectures. For instance, the concept of 'sharding', where the network is divided into smaller, more manageable parts, is being explored. Layer-2 solutions, like the Lightning Network for Bitcoin, also propose to increase the number of transactions that can be processed per second. Regulatory advancements are also in progress to address legal issues. Many countries are working on creating a legal framework to regulate Blockchain-based activities better. Global cooperation among countries can help establish standardized regulations, minimizing legal discrepancies across different jurisdictions. Despite the transformative potential of Blockchain technology, it comes with significant limitations, including high energy consumption, scalability issues, and regulatory challenges. These limitations have direct implications for its adoption in the financial sector and wealth management, impacting operational costs, transaction speed, risk management, and regulatory compliance. Nonetheless, ongoing efforts to mitigate these limitations—such as the development of more energy-efficient consensus mechanisms, software upgrades for improved scalability, and global regulatory cooperation—paint a promising future for Blockchain. The key lies in striking a balance between leveraging Blockchain's strengths and addressing its limitations for it to truly revolutionize the financial landscape. Navigating the complexities of Blockchain in financial decision-making can be a challenge. Consider seeking professional wealth management services to effectively integrate Blockchain into a financial strategy and to stay ahead in this rapidly evolving landscape.Overview of Blockchain Technology
Understanding Blockchain Limitations
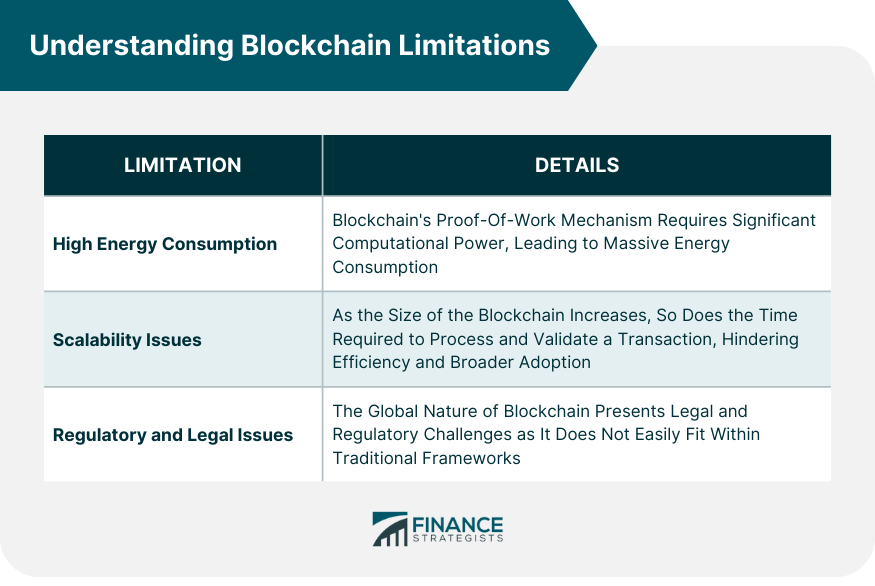
High Energy Consumption
Scalability Issues
Regulatory and Legal Issues
Blockchain Limitations in Financial Systems and Wealth Management
Impact on Traditional Banking and Financial Systems
Influence on Investment Strategies and Risk Management
Regulatory Challenges in the Financial Sector
Practical Solutions to Blockchain Limitations
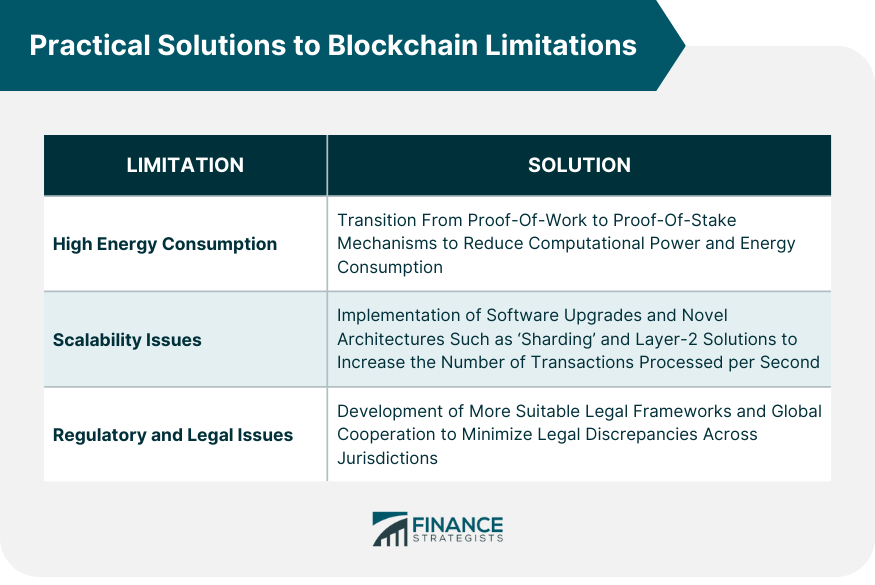
Technological Approaches to Mitigate High Energy Consumption
Software Solutions and Upgrades to Address Scalability Issues
Regulatory Advancements and Global Cooperation for Legal Issues
The Bottom Line
Blockchain Limitations FAQs
Blockchain technology faces high energy consumption, scalability issues, and regulatory and legal challenges.
The proof-of-work mechanism in Blockchain requires significant computational power, leading to massive energy consumption.
As the size of the Blockchain increases, the time required to process and validate a transaction also increases, limiting its efficiency.
Due to Blockchain's global nature, it does not fit easily within traditional legal and regulatory frameworks, presenting several challenges.
Potential solutions include transitioning to proof-of-stake mechanisms, implementing software upgrades and novel architectures for scalability, and developing suitable legal frameworks.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











