Executive compensation refers to the financial remuneration and non-monetary benefits provided to top-level executives, such as CEOs, CFOs, and other senior management members, in exchange for their services to a company. Understanding executive compensation is crucial for investors, employees, and regulators as it directly impacts corporate governance, financial performance, and overall company culture. The primary purpose of executive compensation is to attract, retain, and motivate top talent to drive company performance, align executives' interests with those of shareholders, and foster long-term value creation.
I'm Taylor Kovar, a Certified Financial Planner (CFP), specializing in helping business owners with strategic financial planning. Maximize executive compensation by leveraging equity incentives for long-term value creation and aligning rewards with company performance. Opt for a balanced mix of salary, bonuses, and stock options to incentivize growth and retention. Ensure compliance with regulatory standards and consider tax implications for optimized net benefits. Stay informed and adaptive to market trends and legislative changes to maintain a competitive compensation package. Let's maximize your executive compensation strategy together! Contact me at (936) 899 - 5629 or [email protected] to discuss how we can achieve your financial objectives. WHY WE RECOMMEND: IDEAL CLIENTS: Business Owners, Executives & Medical Professionals FOCUS: Strategic Planning, Alternative Investments, Stock Options & Wealth Preservation The base salary is a fixed annual amount paid to executives for their services, typically determined by role, experience, and market competitiveness factors. Annual Bonuses - Annual bonuses are cash rewards paid to executives based on the achievement of predetermined financial or operational targets, designed to incentivize short-term performance. Profit-Sharing Plans - Profit-sharing plans distribute a portion of a company's profits to executives, linking their compensation directly to the company's financial success. Stock Options - Stock options grant executives the right to purchase company shares at a predetermined price, providing them with potential upside as the company's stock price appreciates over time. Restricted Stock - Restricted stock refers to company shares awarded to executives with certain vesting conditions, often tied to performance or tenure, promoting long-term commitment and value creation. Performance Shares - Performance shares are company shares awarded to executives based on the achievement of specific performance targets over a multi-year period, aligning executive pay with long-term success. Retirement Plans - Retirement plans, such as defined benefit pensions or 401(k) plans, help executives save for retirement and ensure financial security after their tenure with the company. Health and Insurance Benefits - Health and insurance benefits, including medical, dental, and life insurance plans, provide executives with protection and support for their well-being and that of their families. Larger companies typically offer higher executive compensation due to their increased complexity, broader scope of responsibilities, and greater exposure to risk. Executive compensation varies across industries, with sectors like technology, finance, and pharmaceuticals generally offering more competitive pay packages. Competition for top talent in the market drives companies to offer attractive compensation packages to attract and retain high-performing executives. Companies often tie executive compensation to individual performance, linking pay to the achievement of financial, operational, or strategic goals. Economic conditions, such as market fluctuations and recessions, can impact executive compensation by affecting company performance and shareholder expectations. Government regulations, such as tax policies and disclosure requirements, influence the structure and transparency of executive compensation packages. Strong corporate governance, including effective board oversight and shareholder engagement, helps ensure that executive compensation remains aligned with company performance and shareholder interests. Executive compensation has been criticized for exacerbating income inequality, with top executives earning significantly more than the average employee, raising questions about fairness and social responsibility. Critics argue that there is often a disconnect between executive pay and company performance, with executives receiving substantial compensation even when their companies underperform. Critics argue that focusing on short-term executive compensation incentives may encourage excessive risk-taking and undermine long-term value creation, potentially harming shareholders and the broader economy. Golden parachutes, or lucrative severance packages awarded to executives upon termination or change of control, have been criticized for rewarding failure and creating misaligned incentives between executives and shareholders. Tax implications of executive compensation, such as preferential tax treatment for certain types of compensation, can impact the structure and fairness of executive pay packages and create inefficiencies in the tax system. The SEC oversees the disclosure and reporting of executive compensation for publicly traded companies, ensuring transparency and compliance with relevant regulations. The IRS establishes tax rules and regulations that govern the taxation of executive compensation, influencing the design and structure of executive pay packages. The Dodd-Frank Act introduced significant reforms to executive compensation practices, including say-on-pay votes, enhanced disclosure requirements, and the clawback of incentive-based compensation in certain circumstances. Say-on-pay votes are non-binding shareholder votes on executive compensation packages, providing shareholders with a voice in the determination of executive pay. Various international bodies, such as the European Union and the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), have issued guidelines and regulations aimed at promoting responsible executive compensation practices. Companies should design executive compensation packages that align with their strategic objectives, incentivizing executives to pursue long-term growth and value creation. Compensation packages should balance short-term and long-term incentives to ensure executives remain focused on immediate and future performance. Executive compensation should be closely linked to company performance, with clear metrics and targets established to evaluate executive contributions. Companies should establish independent and accountable compensation committees that oversee the design and implementation of executive pay packages, ensuring fairness and alignment with shareholder interests. Companies should regularly review and benchmark their executive compensation practices against industry standards and peer companies to maintain competitiveness and adapt to evolving market trends. Executive compensation constantly evolves in response to market trends, regulatory changes, and emerging best practices, requiring companies to stay current and adapt their strategies accordingly. Effective executive compensation strategies are crucial for attracting, retaining, and motivating top talent, as well as aligning executive interests with those of shareholders and fostering long-term value creation. Companies should consider engaging the services of a financial advisor or compensation consultant to help design and implement effective executive compensation strategies that align with their strategic objectives, market realities, and regulatory requirements. By doing so, they can ensure that their executive pay practices remain competitive, transparent, and conducive to achieving corporate goals.What Is an Executive Compensation?
Learn From Taylor

Fee-Only Financial Advisor
Certified Financial Planner™
3x Investopedia Top 100 Advisor
Author of The 5 Money Personalities & Keynote Speaker
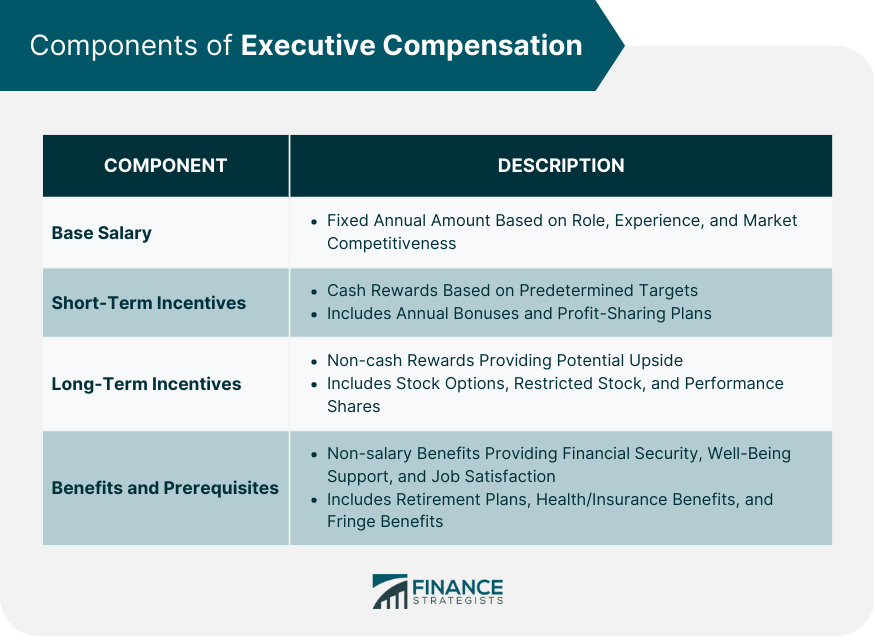
Components of Executive Compensation
Base Salary
Short-Term Incentives
Long-Term Incentives
Benefits and Prerequisites
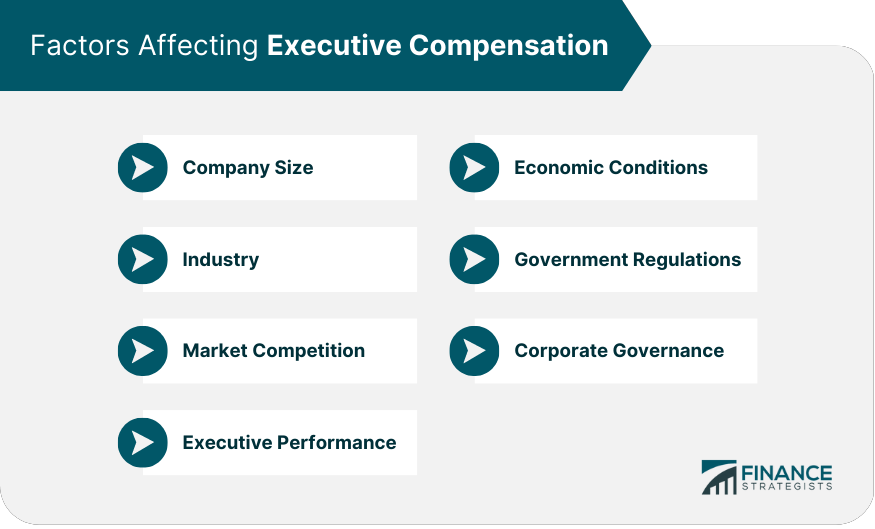
Factors Affecting Executive Compensation
Company Size
Industry
Market Competition
Executive Performance
Economic Conditions
Government Regulations
Corporate Governance
Controversies and Criticisms on Executive Compensation
Income Inequality
Pay-For-Performance Disconnect
Short-Term Focus and Risk-Taking
Golden Parachutes
Tax Implications
Regulatory Environment on Executive Compensation
Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC)
Internal Revenue Service (IRS) Regulations
Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act
Say-On-Pay Votes
International Regulations and Guidelines
Best Practices for Executive Compensation

Aligning Compensation With Company Strategy
Balancing Short-Term and Long-Term Incentives
Ensuring Pay-For-Performance Linkage
Transparent and Accountable Compensation Committees
Regular Compensation Reviews and Benchmarking
Final Thoughts
Executive Compensation FAQs
Executive compensation typically includes a combination of base salary, short-term incentives (such as annual bonuses and profit-sharing plans), long-term incentives (like stock options, restricted stock, and performance shares), and benefits and perquisites (including retirement plans, health and insurance benefits, and fringe benefits).
Company size, industry, and market competition play significant roles in determining executive compensation. Larger companies and competitive industries generally offer higher compensation due to increased complexity and broader responsibilities. Market competition for top talent also drives companies to offer attractive compensation packages to attract and retain high-performing executives.
Executive compensation has been criticized for exacerbating income inequality, creating a pay-for-performance disconnect, encouraging short-term focus and risk-taking, providing excessive golden parachutes, and causing tax inefficiencies.
Government regulations, such as those implemented by the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), Internal Revenue Service (IRS), and the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act, impact the disclosure, reporting, taxation, and overall structure of executive compensation packages. International regulations and guidelines also play a role in shaping executive compensation practices.
Best practices for executive compensation include aligning compensation with company strategy, balancing short-term and long-term incentives, ensuring pay-for-performance linkage, establishing transparent and accountable compensation committees, and conducting regular compensation reviews and benchmarking. These practices help ensure that executive pay remains competitive, transparent, and aligned with shareholder interests.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.















