Graded vesting is a method of gradually granting employees ownership of their retirement or equity benefits over a specified period. This approach ensures that employees earn a higher percentage of their benefits as their tenure with the company increases. Graded vesting plays a crucial role in employee benefit plans by balancing the interests of both employees and employers. It incentivizes employees to remain with the company for a longer duration while also allowing employers to reduce turnover costs and retain valuable talent. Unlike graded vesting, cliff vesting grants employees 100% ownership of their benefits after meeting a specific requirement, such as a certain number of years with the company. Comparatively, graded vesting offers a more gradual approach, ensuring employees receive a portion of their benefits over time. Linear-graded vesting schedules evenly distribute the vesting of benefits over a predetermined period. Employees gain a consistent percentage of ownership each year until they are fully vested, providing a straightforward and easily understood progression. Accelerated graded vesting schedules allow employees to vest at an increasing rate as their tenure grows. This approach often provides a higher percentage of benefits in later years, rewarding long-term commitment and loyalty to the company. Customized graded vesting schedules enable companies to tailor vesting plans according to their unique needs and goals. These schedules can combine elements of linear and accelerated vesting or even introduce additional criteria, such as performance-based milestones. Employee Retirement Income Security Act (ERISA) sets standards for pension and benefit plans in the United States, including guidelines for vesting schedules. Graded vesting schedules must comply with ERISA's minimum requirements to ensure that employees receive fair and adequate benefits based on their years of service. The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) imposes specific rules and regulations for retirement and benefit plans, including tax implications and reporting obligations. Companies must adhere to these requirements when implementing graded vesting schedules to maintain the tax-advantaged status of their plans and avoid penalties. Companies must follow established accounting standards when reporting graded vesting schedules in their financial statements. Proper accounting and disclosure practices ensure transparency and provide investors with accurate information about a company's employee benefit obligations. Publicly traded companies are subject to Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) regulations regarding the disclosure of information related to their employee benefit plans. Companies must provide clear and comprehensive information about their graded vesting schedules to ensure compliance with SEC rules and maintain investor confidence. Graded vesting incentivizes employees to stay with a company longer, as their benefits increase with their tenure. This helps companies reduce the costs associated with employee turnover and retain valuable talent. By gradually granting benefits over time, graded vesting encourages employees to think about their long-term relationship with the company. This fosters a sense of loyalty and commitment, leading to a more stable and engaged workforce. Graded vesting ensures that employees who have dedicated more time and effort to the company receive a larger share of benefits. This approach is perceived as fair and balanced, as it acknowledges the varying levels of commitment among employees. By rewarding long-term commitment, graded vesting discourages employees from leaving the company prematurely. This helps employers save on the costs associated with hiring, training, and integrating new employees. Graded vesting plans can be more complex to administer than other vesting methods, as they require tracking each employee's progress through the vesting schedule. This increased complexity may require additional resources and administrative effort. Employees may be less satisfied with their benefits during the early years of their tenure, as they receive a smaller share of their potential benefits. This could lead to dissatisfaction and decreased motivation among newer employees. As employees accumulate more vested benefits, they may become less willing to seek new job opportunities. This reduced mobility may hinder their career development and could potentially lead to stagnation within the company. Graded vesting is commonly used in 401(k) and other retirement plans, where employees gradually earn the right to employer-contributed funds over time. This approach encourages employees to stay with the company and promotes long-term financial planning. In Employee Stock Option Plans (ESOPs), graded vesting schedules allow employees to progressively earn the right to exercise stock options. This method aligns employee interests with company performance and incentivizes long-term commitment to the organization. Graded vesting is often applied to Restricted Stock Units (RSUs), which are grants of company stock that become available to employees as they vest. This approach fosters employee retention and encourages a focus on company growth and success. Some companies use graded vesting schedules in performance-based incentive plans, tying the vesting of benefits to both time and performance metrics. This approach can further motivate employees to achieve specific goals and contribute to the company's overall success. Graded vesting gradually grants employees ownership of benefits over time, with a higher percentage earned as tenure increases. Graded vesting plays a pivotal role in balancing the interests of employees and employers. By gradually granting benefits over time, it encourages employee retention, fosters long-term commitment, and promotes company stability and growth. As the workforce continues to evolve, companies may increasingly adopt customized graded vesting schedules that consider individual performance and unique business needs. These tailored approaches can help companies remain competitive in attracting and retaining top talent. To ensure the successful implementation of a graded vesting schedule in your employee benefit plans, consider consulting with a financial advisor.What Is Graded Vesting?
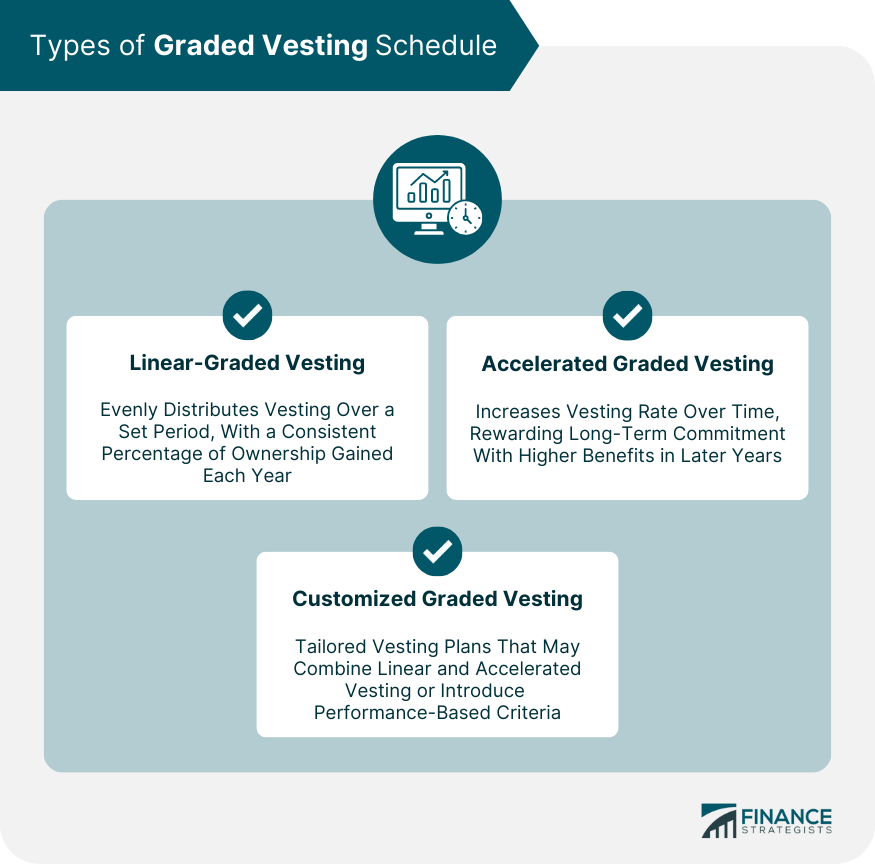
Types of Graded Vesting Schedules
Linear-Graded Vesting
Accelerated Graded Vesting
Customized Graded Vesting Schedules
Legal and Regulatory Framework for Graded Vesting
Employee Retirement Income Security Act (ERISA) Guidelines
Internal Revenue Service (IRS) Requirements
Accounting Standards and Reporting
Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) Disclosure Requirements
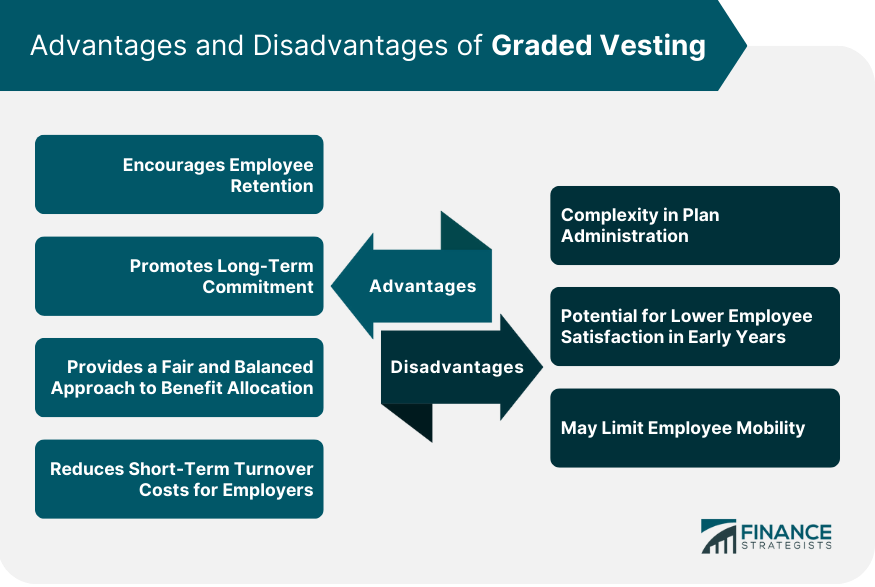
Advantages of Graded Vesting
Encourages Employee Retention
Promotes Long-Term Commitment
Provides a Fair and Balanced Approach to Benefit Allocation
Reduces Short-Term Turnover Costs for Employers
Disadvantages of Graded Vesting
Complexity in Plan Administration
Potential for Lower Employee Satisfaction in Early Years
May Limit Employee Mobility
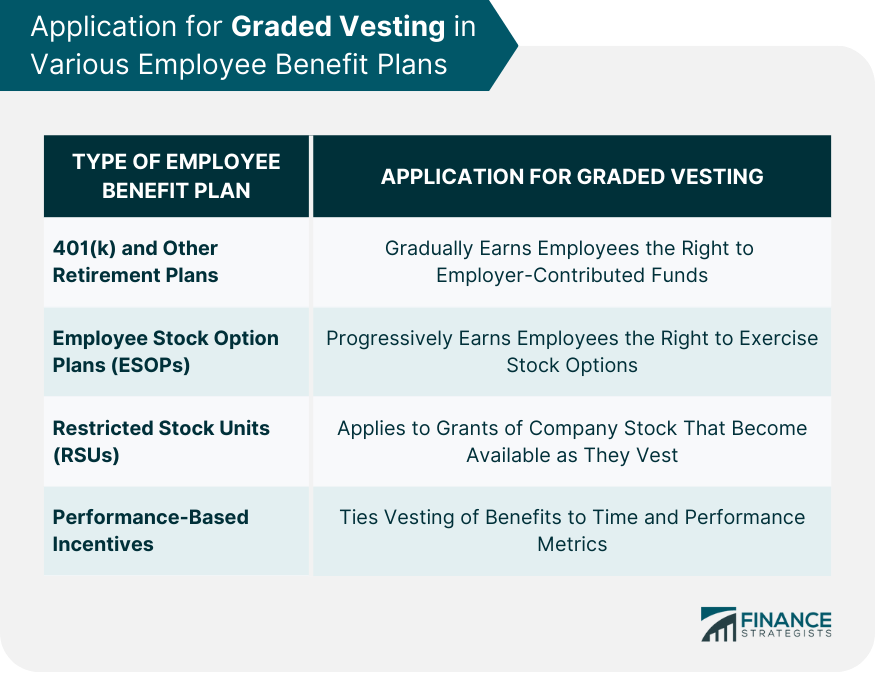
Graded Vesting in Various Employee Benefit Plans
401(k) and Other Retirement Plans
Employee Stock Option Plans (ESOPs)
Restricted Stock Units (RSUs)
Performance-Based Incentives
Final Thoughts
Graded Vesting FAQs
Graded vesting is a method of gradually granting employees ownership of their retirement or equity benefits over a specified period. This approach ensures that employees earn a higher percentage of their benefits as their tenure with the company increases, incentivizing long-term commitment and loyalty to the organization.
While both graded vesting and cliff vesting are methods of allocating employee benefits, they differ in their approach. Graded vesting gradually grants benefits over time, with employees earning an increasing share as their tenure grows. Cliff vesting, on the other hand, grants employees 100% ownership of their benefits after meeting a specific requirement, such as a certain number of years with the company.
There are three main types of graded vesting schedules: linear graded vesting, accelerated graded vesting, and customized graded vesting schedules. Linear graded vesting distributes vesting evenly over a predetermined period, while accelerated graded vesting allows employees to vest at an increasing rate as their tenure grows. Customized graded vesting schedules enable companies to tailor vesting plans according to their unique needs and goals.
Graded vesting offers several advantages, such as encouraging employee retention, promoting long-term commitment, providing a fair and balanced approach to benefit allocation, and reducing short-term turnover costs for employers. However, there are also disadvantages, including increased complexity in plan administration, the potential for lower employee satisfaction in early years, and limited employee mobility.
Graded vesting schedules must adhere to the guidelines set forth by the Employee Retirement Income Security Act (ERISA) to ensure fair and adequate benefits based on employees' years of service. Additionally, companies must comply with Internal Revenue Service (IRS) rules and regulations regarding tax implications and reporting obligations for retirement and benefit plans that include graded vesting schedules. Compliance with these legal and regulatory frameworks helps maintain the tax-advantaged status of benefit plans and avoid penalties.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.













