Elder care, also known as senior care or geriatric care, refers to the various services and support systems designed to address the needs of older adults. These services aim to help seniors maintain their health, safety, independence, and overall quality of life as they age. As the population ages, the demand for elder care services is increasing. Providing appropriate care for the elderly is crucial to ensure they receive the support they need while respecting their autonomy and dignity. Before making decisions about elder care, it's essential to assess the specific needs of the senior. Consider factors such as health status, mobility, cognitive abilities, and daily living activities to determine the appropriate level of care and support. Understanding the costs associated with various elder care options is essential. Take into account the senior's financial resources, including savings, insurance, and government assistance programs, to determine which options are financially viable. Make sure all essential legal and healthcare documents are in place, such as wills, powers of attorney, and advance healthcare directives. These documents provide guidance on the senior's wishes and ensure their preferences are respected. The involvement of family members in elder care planning can provide valuable emotional and practical support for the senior. It's essential to communicate openly and honestly about expectations, boundaries, and each person's role in providing care. Elder care services encompass a wide range of options, including in-home care, assisted living facilities, nursing homes, and continuing care retirement communities. Each type of service offers different levels of care to address the unique needs of seniors. Personal care services provide assistance with activities of daily living, such as bathing, dressing, and grooming. These services can help seniors maintain their independence while receiving support in the comfort of their own homes. Home health care services include medical care provided by licensed professionals, such as nurses or physical therapists. These services can help seniors manage chronic health conditions or recover from illness or surgery. Companion services offer social interaction and companionship for seniors who may be isolated or lonely. These services can also provide respite for family caregivers, giving them a break from their caregiving duties. Assisted living facilities offer a combination of housing, personal care services, and healthcare assistance for seniors who need some help with daily activities but do not require the intensive care provided in nursing homes. When selecting an assisted living facility, consider factors such as location, size, cost, quality of care, and the available amenities and services. Nursing homes provide long-term care for seniors with significant health issues or disabilities that require round-the-clock medical supervision and assistance with daily activities. Skilled nursing care in nursing homes is provided by registered nurses, licensed practical nurses, and certified nursing assistants. These professionals offer services such as medication management, wound care, and therapy services. CCRCs offer a continuum of care, starting with independent living for seniors who can manage their daily activities without assistance. Independent living options typically include apartments or houses within the community. As seniors' needs change, they can transition to assisted living within the same community. This option provides additional support with daily activities and healthcare services. CCRCs also include skilled nursing facilities for seniors requiring more intensive medical care and assistance. This allows residents to receive the appropriate level of care while remaining within the same community. Many seniors and their families use personal savings to cover the costs of elder care services. It's crucial to budget and plan for these expenses in advance to ensure adequate funds are available when needed. Long-term care insurance policies can help cover the costs of various elder care services, such as in-home care, assisted living, or nursing home care. It's essential to understand the specific coverage and limitations of these policies before purchasing. Medicare is a federal health insurance program for individuals aged 65 and older. While Medicare covers some aspects of elder care, such as skilled nursing care and limited home health care, it does not cover long-term care services. Medicaid is a state and federal program that provides healthcare coverage for low-income individuals, including seniors. Medicaid may cover some long-term care services, such as nursing home care or home and community-based services, depending on the individual's eligibility and state regulations. Veterans and their spouses may be eligible for various benefits through the Department of Veterans Affairs (VA), including healthcare services, pension programs, and financial assistance for long-term care. A power of attorney is a legal document that allows a designated individual, known as the agent, to make financial or healthcare decisions on behalf of the senior when they are unable to do so themselves. Advance healthcare directives, such as living wills and healthcare proxies, specify the senior's wishes regarding medical treatment and end-of-life care in the event they are unable to communicate or make decisions. In some cases, a court may appoint a guardian or conservator to manage the personal and financial affairs of a senior who is unable to do so independently. This process can be complex and should only be considered when other options are not viable. Elder abuse can take many forms, including physical, emotional, financial, and sexual abuse. It's essential to be aware of the signs of elder abuse and report any suspected incidents to the appropriate authorities. Providing care for an aging loved one can be emotionally challenging. It's important for caregivers to prioritize self-care and seek support to manage the emotional impact of caregiving. Respite care provides temporary relief for caregivers by offering short-term care services for seniors. This allows caregivers to take a break, attend to personal matters, or simply recharge. Support groups and community resources can help caregivers connect with others facing similar challenges, share experiences, and access valuable information and resources related to elder care. Proper planning for elder care is essential to ensure seniors receive the care and support they need as they age. Evaluating the various care options, understanding the associated costs, and having the necessary legal and healthcare documents in place can help seniors and their families navigate the challenges of elder care with confidence. Each senior's needs and circumstances are unique, making it crucial to evaluate and choose the most suitable elder care options. Thorough research, consideration of the senior's preferences, and consultation with healthcare professionals can help guide the decision-making process. Ultimately, the goal of elder care is to ensure the well-being, safety, and dignity of aging loved ones. By taking a proactive approach to planning, understanding the various care options, and being aware of the legal and ethical considerations, families can help ensure their elderly family members receive the best possible care and support throughout their golden years.What Is Elder Care?
Factors to Consider in Elder Care Planning
Assessing the Needs of the Elderly
Evaluating Financial Resources
Preparing Legal and Healthcare Documents
Providing Family Support and Involvement

Types of Elder Care Services
In-Home Care
Personal Care Services
Home Health Care Services
Companion Services
Assisted Living Facilities
Services Provided
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Facility
Nursing Homes
Long-Term Care Services
Skilled Nursing Care
Continuing Care Retirement Communities (CCRCs)
Independent Living
Assisted Living
Skilled Nursing Facilities
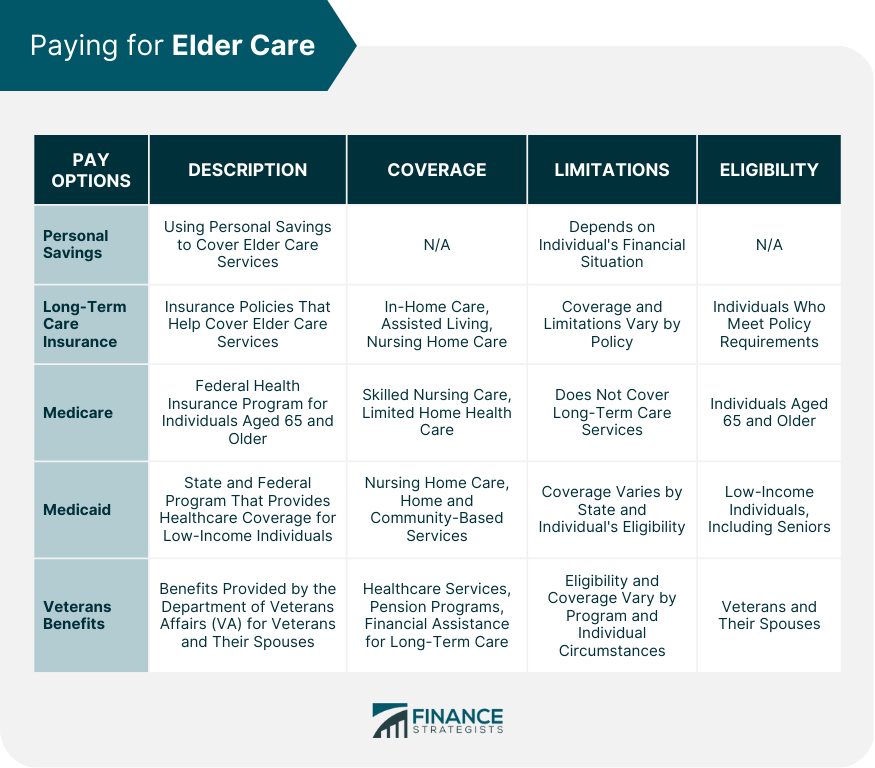
Paying for Elder Care
Private Pay Options
Personal Savings
Long-Term Care Insurance
Government Assistance Programs
Medicare
Medicaid
Veterans Benefits
Legal and Ethical Considerations in Elder Care
Power of Attorney
Advance Healthcare Directives
Guardianship and Conservatorship
Elder Abuse Prevention and Reporting
Balancing Caregiving Responsibilities
The Emotional Impact of Caregiving
Respite Care Options
Support Groups and Resources for Caregivers
Conclusion
The Importance of Planning for Elder Care
Evaluating and Choosing the Right Care Options
Ensuring the Well-Being of Aging Loved Ones
Elder Care FAQs
Elder care refers to the provision of care and support for older adults, typically those who are no longer able to fully care for themselves. This can include medical care, personal care, and assistance with daily activities.
The different types of elder care include in-home care, assisted living facilities, nursing homes, adult day care centers, and hospice care.
Families can finance elder care through a variety of options, including long-term care insurance, Medicaid, Medicare, and personal savings. It is important to work with a financial advisor to evaluate all available options and make informed decisions.
Some common challenges associated with providing elder care include managing medical conditions, coordinating care between different providers, addressing emotional and psychological needs, and balancing caregiving responsibilities with other obligations.
Families and caregivers can best support the physical and emotional well-being of older adults in their care by providing companionship and emotional support, promoting healthy lifestyle habits, coordinating medical care and treatment, and considering respite care options to prevent caregiver burnout.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.















