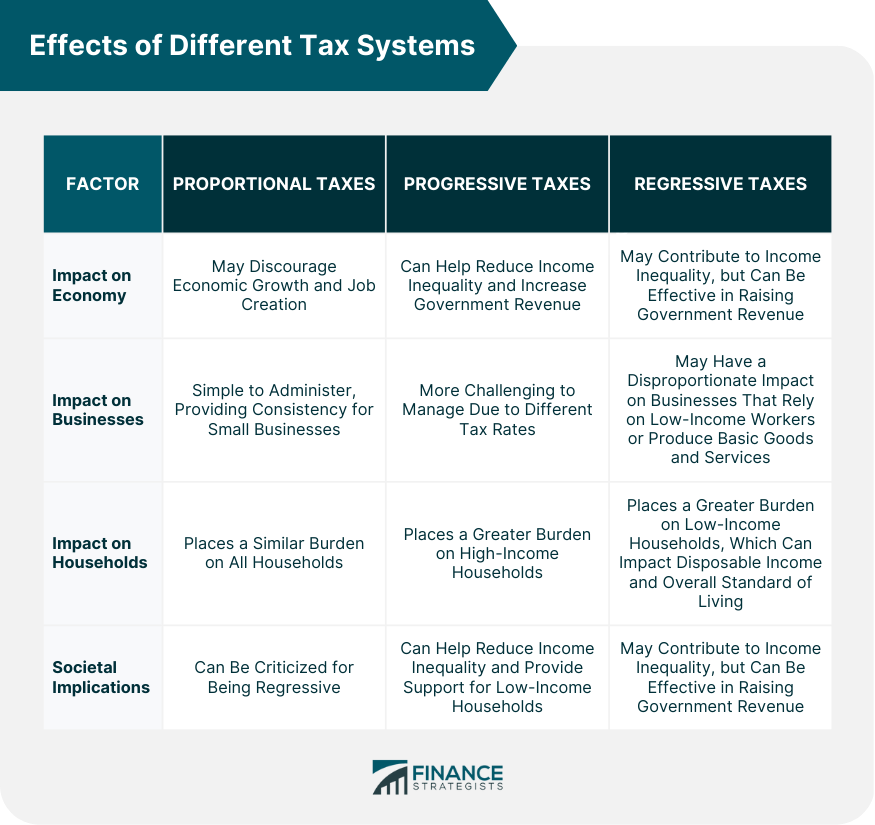
Proportional, progressive, and regressive taxes are three common types of tax systems that differ in structure, impact on different income levels, and effectiveness in achieving different policy goals. Proportional taxes are levied constantly, while progressive taxes are levied at a higher rate on higher-income earners. Regressive taxes are levied at a higher rate on lower-income earners. Understanding the differences between these tax systems is crucial for individuals, businesses, and policymakers to make informed decisions regarding taxation. The choice of the tax system can significantly impact the economy, businesses, and households, including disposable income, purchasing power, and overall standard of living. Proportional taxes are levied at a constant rate regardless of the taxpayer's income or wealth. In other words, everyone pays the same percentage of their income or wealth in taxes. For example, if the tax rate is 10%, a person earning $50,000 per year will pay $5,000 in taxes, while a person earning $100,000 will pay $10,000 in taxes. Proportional taxes are typically applied to specific goods or services, such as sales tax on goods or flat taxes on income. These taxes are straightforward to calculate and apply, making them easy to administer. However, proportional taxes can be criticized for being regressive, as they place a more considerable burden on low-income earners who have less disposable income. Progressive taxes are levied at a higher rate on higher-income earners. This means that as income increases, the percentage of income paid in taxes also increases. For example, a progressive income tax system may have tax rates of 10%, 20%, and 30% for income levels of $0-$50,000, $50,001-$100,000, and $100,001 and above, respectively. Progressive taxes aim to redistribute wealth by placing a larger burden on higher-income earners. This can help reduce income inequality and provide greater support for low-income earners. However, progressive taxes can be more complicated to administer, as different tax rates apply to different income levels. Additionally, high-income earners may be motivated to find ways to reduce their taxable income, such as through deductions or investments, which can reduce the effectiveness of the tax system. Regressive taxes are taxes that are levied at a higher rate on lower-income earners. This means that as income decreases, the percentage of income paid in taxes increases. For example, a regressive tax system may be a flat tax on essential goods and services, such as food, clothing, and housing. As these goods represent a larger percentage of a low-income earner's budget, the tax significantly impacts their finances. Regressive taxes can be criticized for increasing income inequality and placing a greater burden on low-income earners. However, these taxes can effectively raise revenue for the government without discouraging economic growth or job creation. The three types of taxes differ in their structure, impact on different income levels, and effectiveness in achieving different policy goals. Structure: Proportional taxes are straightforward to administer and apply, as everyone pays the same percentage of their income or wealth in taxes. Impact: Proportional taxes place an equal burden on all taxpayers regardless of their income level. This means that low-income earners and high-income earners pay the same percentage of their income or wealth in taxes. Effectiveness: Proportional taxes can be criticized for being regressive, as they may place a larger burden on low-income earners who have less disposable income. Progressive taxes aim to reduce income inequality by placing a larger burden on high-income earners. The choice of tax system can significantly impact the economy, businesses, and households. Taxation plays a critical role in shaping the economy. Progressive taxes can help reduce income inequality and increase government revenue, while proportional and regressive taxes may have the opposite effect. Progressive taxes can also incentivize investment and innovation by providing tax breaks for research and development. Additionally, tax systems can impact economic growth and job creation. High tax rates discourage investment and entrepreneurship, while lower taxes may incentivize these activities. The choice of tax system can also significantly impact businesses. Proportional taxes can benefit small businesses by providing a consistent tax rate that is easy to calculate and manage. Progressive taxes may be more challenging for businesses, as different tax rates apply to different income levels. Regressive taxes may have a disproportionate impact on companies that rely on low-income workers or that produce essential goods and services that are subject to regressive taxes. The impact of different tax systems on households varies depending on income level. Proportional taxes burden all households similarly, while progressive taxes burden high-income households more. Regressive taxes place a greater burden on low-income households. The choice of the tax system can impact disposable income, purchasing power, and overall standard of living. Taxation has significant societal implications, including the redistribution of wealth, the provision of public goods and services, and the promotion of social welfare. Progressive taxes can be an effective tool for reducing income inequality and providing support for low-income households. Regressive taxes may contribute to income inequality but can also effectively raise government revenue without discouraging economic growth or job creation. Proportional, progressive, and regressive taxes are three common tax systems that differ in structure, impact on different income levels, and effectiveness in achieving different policy goals. The choice of the tax system can significantly impact the economy, businesses, and households. Proportional taxes are simple to administer but can be criticized for being regressive. Regressive taxes may contribute to income inequality but can effectively raise government revenue. Understanding the differences between these tax systems is critical for taxpayers, policymakers, and business owners. By choosing an appropriate tax system, policymakers can promote economic growth, reduce income inequality, and support low-income households. Business owners can manage their tax liability more effectively, and taxpayers can make informed financial decisions. Overall, taxation is a crucial component of modern society, and the choice of the tax system has significant implications for economic growth, income inequality, and social welfare. Consider hiring a financial advisor to help navigate the complex tax system and make the most of your finances. A financial advisor can guide in several tax services such as, tax planning, investment strategies, and other financial decisions to help you achieve your long-term goals. Overview of Proportional, Progressive, and Regressive Taxes
What Are Proportional Taxes?
What Are Progressive Taxes?
What Are Regressive Taxes?
Differences Between Proportional, Progressive, and Regressive Taxes
In contrast, progressive and regressive taxes can be more complex due to different tax rates and exemptions.
In contrast, progressive taxes burden high-income earners, while regressive taxes significantly burden low-income earners. This can impact disposable income, purchasing power, and overall standard of living.
Regressive taxes may effectively raise government revenue without discouraging economic growth or job creation, but they can also contribute to income inequality.Effects of Different Tax Systems
Economy
Businesses
Households
Societal Implications
Final Thoughts
Progressive taxes aim to reduce income inequality but can be more challenging to administer.
Proportional vs Progressive vs Regressive Taxes FAQs
Proportional taxes are levied constantly, while progressive taxes are levied at a higher rate on higher-income earners. Regressive taxes are levied at a higher rate on lower-income earners.
Taxation plays a critical role in shaping the economy. Progressive taxes can help reduce income inequality and increase government revenue, while proportional and regressive taxes may have the opposite effect.
Proportional taxes are simple to administer and apply, making them easy to manage. They can also provide consistency for small businesses.
Proportional taxes burden all households similarly, while progressive taxes burden high-income households more. Regressive taxes place a more significant burden on low-income households, which can impact disposable income and the overall standard of living.
Yes, tax systems can change over time due to changes in government policies, economic conditions, and societal factors. Understanding the impact of different tax systems can help individuals and businesses prepare for potential changes in taxation.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.















