Non-discrimination testing is a set of tests that retirement plans must undergo to ensure compliance with the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) regulations. These tests are designed to verify that the plan does not disproportionately favor highly compensated employees (HCEs) over non-highly compensated employees (NHCEs), ensuring a fair distribution of retirement benefits among all participants. Non-discrimination testing is essential in retirement planning because it ensures that retirement plans comply with IRS regulations and maintain their tax-qualified status. By adhering to non-discrimination rules, employers can protect their retirement plans' tax benefits while fostering an equitable retirement system for all employees. The Actual Deferral Percentage (ADP) test is a non-discrimination test that evaluates whether employee deferrals to a defined contribution plan, such as a 401(k), are equitably distributed between HCEs and NHCEs. The test compares the average deferral percentages for each group, ensuring that HCEs do not defer a significantly higher percentage of their income than NHCEs. The ADP test helps maintain an equitable distribution of retirement plan benefits and ensures that plans remain compliant with IRS regulations. The Actual Contribution Percentage (ACP) test is another non-discrimination test that focuses on employer matching contributions and employee after-tax contributions in defined contribution plans. This test compares the average contribution percentages for HCEs and NHCEs, ensuring that the contributions are equitably distributed among all participants. The ACP test plays a vital role in maintaining compliance with non-discrimination rules and preserving the tax-qualified status of retirement plans. Coverage testing is a non-discrimination test that evaluates whether a retirement plan's eligibility requirements are nondiscriminatory, ensuring that a sufficient percentage of NHCEs are covered by the plan. This test helps to confirm that the plan does not disproportionately exclude NHCEs from participation. Periodic coverage testing is crucial for demonstrating compliance with non-discrimination rules and maintaining the tax-qualified status of retirement plans. Top-heavy testing is a non-discrimination test that determines whether a retirement plan disproportionately favors "key employees," such as owners and officers of the company. If a plan is found to be top-heavy, additional requirements and restrictions may apply to ensure that the plan remains compliant with non-discrimination rules. Annual top-heavy testing helps employers maintain compliance with non-discrimination rules and protect the tax-qualified status of their retirement plans. The Actual Deferral Percentage test is a non-discrimination test that compares the average deferral percentages of HCEs and NHCEs within a defined contribution retirement plan. This test ensures that HCEs do not defer a significantly higher percentage of their income than NHCEs, promoting an equitable distribution of plan benefits. The ADP test is essential for maintaining compliance with IRS regulations and ensuring the tax-qualified status of a retirement plan. The ADP test rules and requirements dictate the specific calculations and comparisons that must be performed during the test. The test compares the average deferral percentages of HCEs and NHCEs, with certain thresholds that must not be exceeded to maintain compliance with non-discrimination rules. Employers must be familiar with the ADP test rules and requirements to ensure that their retirement plans remain compliant with IRS regulations. If a retirement plan fails the ADP test, corrective actions must be taken to resolve the non-compliance issue. These actions may include refunding excess contributions to HCEs, making additional contributions to NHCEs, or implementing plan amendments to improve compliance with non-discrimination rules. Promptly addressing ADP test failures can help employers maintain the tax-qualified status of their retirement plans and avoid potential penalties. The Actual Contribution Percentage test is a non-discrimination test that evaluates the distribution of employer matching contributions and employee after-tax contributions in defined contribution plans. The test compares the average contribution percentages for HCEs and NHCEs, ensuring that the contributions are equitably distributed among all participants. The ACP test is vital for maintaining compliance with non-discrimination rules and protecting the tax-qualified status of retirement plans. The ACP test rules and requirements establish the specific calculations and comparisons that must be conducted during the test. The test compares the average contribution percentages of HCEs and NHCEs, with certain limits that must not be exceeded to maintain compliance with non-discrimination rules. Understanding the ACP test rules and requirements is crucial for employers to ensure their retirement plans remain compliant with IRS regulations. If a retirement plan fails the ACP test, corrective actions must be taken to address the non-compliance issue. These actions can include refunding excess contributions to HCEs, making additional contributions to NHCEs, or implementing plan amendments to enhance compliance with non-discrimination rules. Taking swift corrective action can help employers maintain the tax-qualified status of their retirement plans and avoid potential penalties. Coverage testing is a non-discrimination test that evaluates whether a retirement plan's eligibility requirements are nondiscriminatory, ensuring that a sufficient percentage of NHCEs are covered by the plan. This test helps confirm that the plan does not disproportionately exclude NHCEs from participation. Conducting coverage testing periodically is crucial for demonstrating compliance with non-discrimination rules and maintaining the tax-qualified status of retirement plans. Coverage testing rules and requirements determine the specific calculations and comparisons that must be performed during the test. The test assesses whether the plan's eligibility requirements meet the minimum coverage requirements set forth by the IRS, ensuring a fair distribution of retirement plan benefits. Employers must be aware of coverage testing rules and requirements to guarantee their retirement plans remain compliant with IRS regulations. If a retirement plan fails coverage testing, corrective actions must be taken to resolve the non-compliance issue. These actions may include amending the plan's eligibility requirements, making additional contributions to NHCEs, or implementing plan amendments to improve compliance with non-discrimination rules. Addressing coverage testing failures promptly can help employers maintain the tax-qualified status of their retirement plans and avoid potential penalties. Top-heavy testing is a non-discrimination test that determines whether a retirement plan disproportionately favors "key employees," such as owners and officers of the company. If a plan is found to be top-heavy, additional requirements and restrictions may apply to ensure that the plan remains compliant with non-discrimination rules. Conducting top-heavy testing annually helps employers maintain compliance with non-discrimination rules and protect the tax-qualified status of their retirement plans. Top-heavy testing rules and requirements specify the calculations and comparisons that must be performed during the test. The test assesses whether the plan's benefits are disproportionately concentrated among key employees, ensuring that the plan remains compliant with non-discrimination rules. Understanding top-heavy testing rules and requirements is essential for employers to ensure their retirement plans remain compliant with IRS regulations. If a retirement plan is found to be top-heavy, corrective actions must be taken to address the non-compliance issue. These actions may include making additional contributions to NHCEs, implementing plan amendments, or adjusting the plan's design to more equitably distribute retirement benefits among all participants. Taking timely corrective action can help employers maintain the tax-qualified status of their retirement plans and avoid potential penalties. Common non-discrimination testing mistakes include incorrect employee classification, using outdated data, or misinterpreting test results. These errors can lead to inaccurate test outcomes, potentially jeopardizing a retirement plan's tax-qualified status and triggering penalties. By being aware of common mistakes, employers can take proactive steps to avoid them and maintain compliance with non-discrimination rules. To avoid non-discrimination testing mistakes, employers should ensure accurate employee classification, use up-to-date data, and seek assistance from retirement plan professionals when interpreting test results. Regularly reviewing plan design, monitoring plan participation, and staying informed about regulatory updates can also help prevent testing errors. By adopting best practices and seeking professional guidance, employers can minimize the risk of non-discrimination testing mistakes and maintain the tax-qualified status of their retirement plans. Non-discrimination testing plays a critical role in retirement planning, ensuring that retirement plans comply with IRS regulations and maintain their tax-qualified status. The ADP, ACP, coverage, and top-heavy tests evaluate different aspects of retirement plans to confirm that they do not disproportionately favor certain employees over others. Compliance with non-discrimination testing is essential for maintaining the tax-qualified status of retirement plans and avoiding potential penalties. Employers must be diligent in conducting tests, interpreting results, and taking corrective action when necessary to ensure their retirement plans remain compliant with IRS regulations. By prioritizing compliance, employers can safeguard their retirement plans' tax benefits and support the financial well-being of their employees. Employers must stay informed about regulatory updates, adjust their plan designs as needed, and maintain open lines of communication with retirement plan professionals to ensure ongoing compliance with non-discrimination rules. By remaining proactive and adaptable, employers can navigate the future of non-discrimination testing and protect the tax-qualified status of their retirement plans.Definition of Non-Discrimination Testing
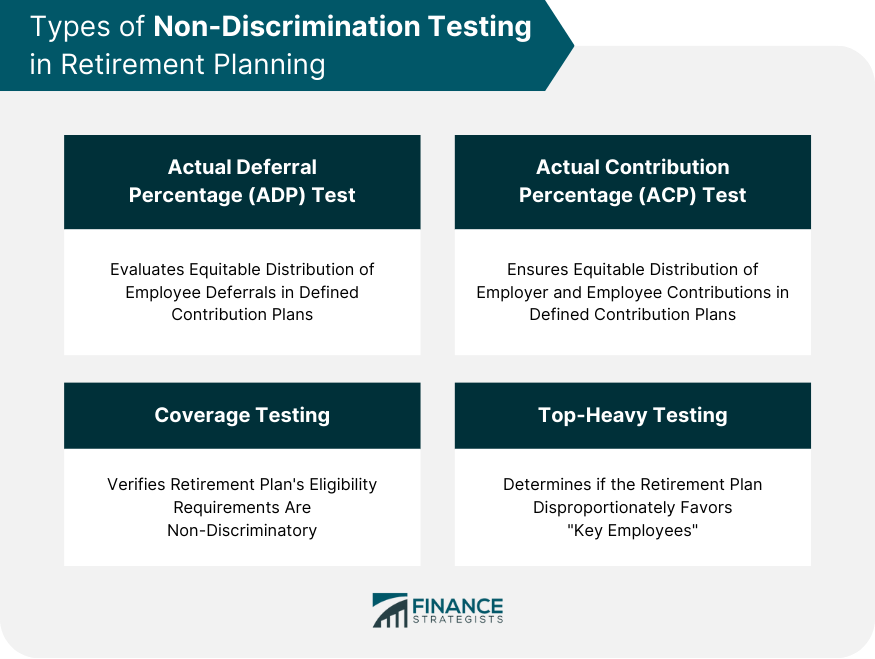
Types of Non-Discrimination Testing
Actual Deferral Percentage (ADP) Test
Actual Contribution Percentage (ACP) Test
Coverage Testing
Top-Heavy Testing
ADP Test
Explanation of ADP Test
ADP Test Rules and Requirements
ADP Test Failure and Correction Methods
ACP Test
Explanation of ACP Test
ACP Test Rules and Requirements
ACP Test Failure and Correction Methods
Coverage Testing
Explanation of Coverage Testing
Coverage Testing Rules and Requirements
Coverage Testing Failure and Correction Methods
Top-Heavy Testing
Explanation of Top-Heavy Testing
Top-Heavy Testing Rules and Requirements
Top-Heavy Testing Failure and Correction Methods
Common Non-Discrimination Testing Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Examples of Common Mistakes
Tips for Avoiding Mistakes
Bottom Line
Non-Discrimination Testing FAQs
Non-Discrimination Testing is a set of IRS regulations that ensures fairness in retirement plan benefits.
Failing a Non-Discrimination Test can result in penalties, legal liabilities, and loss of tax-exempt status for the retirement plan.
There are four types of Non-Discrimination Tests, including ADP Test, ACP Test, Coverage Testing, and Top-Heavy Testing.
Non-Discrimination Testing should be performed annually to ensure compliance with IRS regulations.
Common mistakes include improper handling of employee data, failing to include all eligible employees in testing, and not correcting failures promptly.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.















