Pension funds and provident funds are two prominent financial instruments designed to secure individuals' financial futures, yet they diverge in significant ways while sharing common objectives. These funds serve as vehicles for long-term savings, aiming to provide a stable source of income during retirement. While both operate with the goal of helping individuals accumulate wealth, they vary in terms of contributions, withdrawals, and taxation. Pension funds often involve mandatory contributions by both employees and employers, with a focus on providing regular pension payments. Provident funds, on the other hand, typically offer greater flexibility in terms of contributions and withdrawals, making them attractive for individuals seeking more control over their savings. Ultimately, the decision between these two options hinges on various factors, including personal financial goals, risk tolerance, and the regulatory landscape of one's region. The primary difference between pension funds and provident funds lies in their core objectives. Pension funds are designed to provide a stable income during retirement, aiming to replace a portion of the employee's pre-retirement earnings. They function as a financial safety net for retirees, ensuring a consistent stream of income. Provident funds, conversely, act more like savings accounts. Their main purpose is to accumulate a substantial sum that the employee receives upon retirement or under certain other conditions, offering a lump sum rather than a steady income. In terms of contribution, pension funds typically involve a combination of employee and employer contributions. The exact percentages and terms can vary significantly based on the specific plan and its rules. Provident funds, on the other hand, are also funded by both employee and employer contributions, but they often provide more flexibility in terms of contribution rates and schedules. This flexibility allows employees to adjust their savings according to their financial capacity. Investment management is another key area of divergence. Pension funds are usually managed by investment professionals who decide how the funds are allocated and invested. This professional management aims to maximize returns while mitigating risks. Provident funds, in contrast, may offer employees more control over their investment choices, allowing them to tailor their investment strategy to their individual risk tolerance and financial goals. The payout structure of these two funds also varies significantly. Pension funds typically pay out benefits in the form of annuities, providing a guaranteed income over the retiree's lifetime. Provident funds, however, generally pay out as a lump sum, giving retirees access to a larger amount of money at once, which they can use as they see fit. Taxation is an important aspect where both funds offer benefits but differ in their approach. Pension fund contributions are often tax-deductible, and the income tax on payouts is deferred until retirement. Provident funds also offer tax advantages, although the specifics can vary depending on the country's tax laws and the type of provident fund. Lastly, the level of control and accessibility differs between the two. Pension funds typically offer less control to the employees over the fund's management and investment decisions. Provident funds, in contrast, often allow more direct control over savings and investment choices, providing greater accessibility and flexibility to the employee. This difference is crucial for individuals who prefer to have a more active role in managing their retirement savings. Despite their differences, pension funds and provident funds share a common primary goal: facilitating retirement planning. Both types of funds are designed to ensure that individuals have financial support in their post-work years. Pension funds provide this through a steady income stream, while provident funds accumulate a lump sum for the retiree. In either case, these funds play a crucial role in helping individuals maintain their standard of living after they have stopped working, underscoring their importance in personal financial planning. Moreover, both pension and provident funds encourage long-term savings habits. By setting aside a portion of current income, individuals are essentially preparing for a future where their regular earnings might cease. This aspect of retirement planning is integral to both types of funds, emphasizing the foresight and discipline in financial planning for the latter stages of life. Another similarity lies in the tax benefits offered by both pension and provident funds. Contributions made towards these funds are often tax-deductible, providing immediate financial relief to contributors. Additionally, the growth of these funds is typically tax-deferred, allowing for a larger accumulation of retirement savings. These tax advantages make both pension and provident funds attractive options for tax-efficient savings and investment. Lastly, both pension and provident funds are subject to regulatory oversight, ensuring their stability and reliability for contributors. This oversight typically involves strict guidelines on how the funds are managed, invested, and disbursed. It provides a level of security to contributors, knowing that their retirement savings are being handled responsibly and in accordance with legal standards. This regulatory framework is key to maintaining the integrity and trustworthiness of both pension and provident funds, making them viable and safe options for retirement savings. When deciding between a pension fund and a provident fund, understanding your financial goals is paramount. If your aim is to secure a steady income stream post-retirement, reminiscent of a regular paycheck, pension funds might be the more suitable option. They offer a predictable and stable source of income, aligned with long-term financial security. Alternatively, if you prefer a significant lump sum to manage or invest independently upon retirement, a provident fund could be more appealing. This option allows for greater flexibility in utilizing retirement savings, suitable for those with specific post-retirement plans such as investing in a business or a major purchase. Risk tolerance is another crucial factor. Pension funds, generally managed by professionals, tend to have a more conservative investment approach, minimizing the risk to the retiree. If you prefer a low-risk approach to retirement savings, this might be ideal. Provident funds, on the other hand, often allow more personal control over investments, which can be beneficial if you have a higher risk tolerance and wish to pursue potentially higher returns. Your employment status significantly influences this choice. Some employers offer specific retirement plans, often making the decision for you. If you’re self-employed or your employer doesn’t offer a retirement plan, you may have to choose based on other factors, including the benefits each fund offers that align with your employment situation. Finally, consider the tax implications of each option. Pension and provident funds often have different tax benefits and liabilities, depending on your country’s tax laws. Understanding these implications is crucial in making a financially efficient decision, ensuring your retirement savings grow optimally while minimizing tax burdens. Understanding the differences and similarities between pension funds and provident funds is crucial for effective retirement planning. Pension funds provide a stable income during retirement and are typically characterized by a combination of employer and employee contributions, professional investment management, and annuity-style payouts. Provident funds, in contrast, offer more flexibility in contributions and control over investments, paying out as a lump sum. Both types of funds offer tax benefits and are subject to regulatory oversight, ensuring their reliability. When choosing between them, consider your financial goals, risk tolerance, employment status, and tax implications. Pension funds are ideal for those seeking a steady retirement income and lower risk, while provident funds suit those who prefer more control and flexibility with their retirement savings. Making an informed choice between these two will significantly impact your financial security in retirement.Overview of Pension Funds and Provident Funds
Differences Between Pension Funds and Provident Funds
Purpose and Objectives
Contribution Structure
Investment Management
Payout Structure
Taxation
Control and Accessibility
Similarities Between Pension Funds and Provident Funds
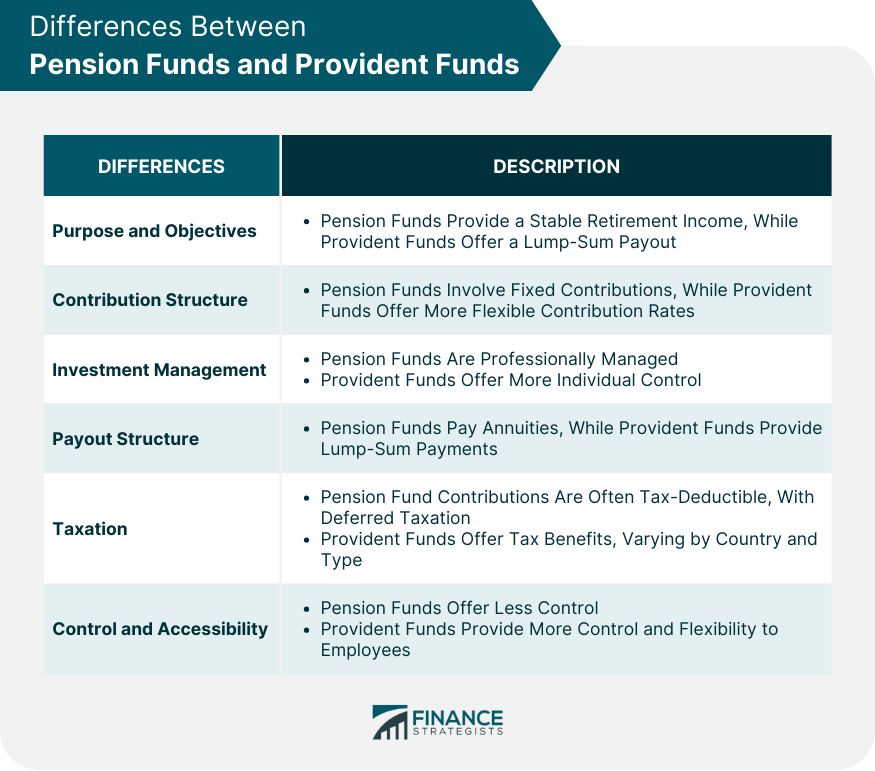
Retirement Planning
Tax Benefits
Regulatory Oversight
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between Pension Funds and Provident Funds
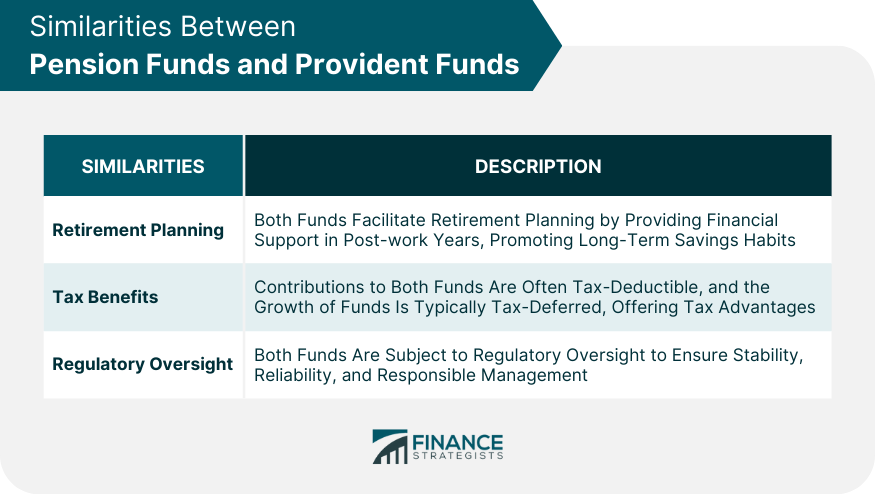
Financial Goals
Risk Tolerance
Employment Status
Tax Considerations
Bottom Line
Pension Fund vs Provident Fund FAQs
The primary difference is that pension funds provide a steady income during retirement, while provident funds offer a lump sum payout.
Yes, contributions to both types of funds are often tax-deductible, providing immediate financial relief to contributors.
Pension funds are usually managed by investment professionals who make decisions about how the funds are allocated and invested.
Factors to consider include your financial goals, risk tolerance, employment status, and tax implications.
Yes, provident funds often provide more control and flexibility over investment choices, allowing contributors to tailor their strategy to their risk tolerance and financial goals.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.















